|
Ranelagh Gardens
Ranelagh Gardens (; alternative spellings include Ranelegh and Ranleigh, the latter reflecting the English pronunciation) were public pleasure gardens located in Chelsea, then just outside London, England, in the 18th century. History The Ranelagh Gardens were so called because they occupied the site of Ranelagh House, built in 1688–89 by The 1st Earl of Ranelagh, an Anglo-Irish peer who was the Treasurer of Chelsea Hospital (1685–1702), immediately adjoining the hospital; according to Bowack's ''Antiquities of Middlesex'' (1705), it was "Designed and built by himself". Its actual builder and owner was one Solomon Rieti, an Italian Jewish immigrant. Rieti's niece, Rebecca Rieti, was the grandmother of Benjamin Disraeli. Ranelagh House was demolished in 1805 (Colvin 1995, p. 561). The original Ranelagh ( ga, Raghnallach) was one of the Earl's Irish estates: a similar pleasure garden was opened near Dublin city, and this gives its name to the present-day suburb of R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotunda At Ranleigh T Bowles 1754
Rotunda or The Rotunda may refer to: * Rotunda (architecture), any building with a circular ground plan, often covered by a dome Places Czech Republic * Znojmo Rotunda, in Znojmo, Czech Republic Greece * Arch of Galerius and Rotunda, Rotunda of St. George, built in Thessaloniki in 306 AD Ireland * Rotunda Hospital, Dublin, Ireland Malta * Rotunda of Mosta, in Mosta, Malta Moldova * Rotunda, Edineț, a commune in Edineţ District, Moldova Romania * Rotunda, Olt, a commune in Olt County * Rotunda, a village in Corbeni Commune, Argeș County * Rotunda, a village in Buza Commune, Cluj County * Rotunda, a village in Doljești Commune, Neamț County * Rotunda, a village administered by Liteni town, Suceava County * Rotunda, a tributary of the Bistrița in Suceava County * Rotunda (Lăpuș), a tributary of the Lăpuș in Maramureș County United Kingdom * Rotunda, Birmingham, a cylindrical highrise building in Birmingham * Rotunda, Woolwich, a John Nash building in Woolwich, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rococo
Rococo (, also ), less commonly Roccoco or Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and theatrical style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, and ''trompe-l'œil'' frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque movement. The Rococo style began in France in the 1730s as a reaction against the more formal and geometric Louis XIV style. It was known as the "style Rocaille", or "Rocaille style". It soon spread to other parts of Europe, particularly northern Italy, Austria, southern Germany, Central Europe and Russia. It also came to influence the other arts, particularly sculpture, furniture, silverware, glassware, painting, music, and theatre. Although originally a secular style primarily used for interiors of private residences, the Rococo had a spiritual aspect to it which led to its widespread use in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelsea Bridge Road
Chelsea Bridge Road is the modern eastern boundary of Chelsea, in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea, London, England. To the northeast is the district of Pimlico in the City of Westminster. The road runs between Chelsea Bridge on the Chelsea Embankment, with the River Thames to the southeast and a junction with Royal Hospital Road, Lower Sloane Street and Pimlico Road to the northwest. The closest tube station is Sloane Square to the north along Lower Sloane Street. The road is part of the A3216 route. Immediately to the southwest are Ranelagh Gardens. Beyond that are the grounds of the Royal Hospital Chelsea. Also close by is the National Army Museum The National Army Museum is the British Army's central museum. It is located in the Chelsea district of central London, adjacent to the Royal Hospital Chelsea, the home of the "Chelsea Pensioners". The museum is a non-departmental public body. ..., next to the Royal Hospital Chelsea on Royal Hospital Road. The Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cremorne Gardens, London
Cremorne Gardens were popular pleasure gardens by the side of the River Thames in Chelsea, London. They lay between Chelsea Harbour and the end of the King's Road and flourished between 1845 and 1877; today only a vestige survives, on the river at the southern end of Cheyne Walk. Within the Chelsea area, Cremorne is a ward of the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea. The 2011 census assessed the population of the ward at 7,974. History Originally the property of the Earl of Huntingdon (c. 1750), father of Steele's Aspasia, who built a mansion here, the property passed through various hands into those of The 1st Viscount Cremorne (1725–1813), an Irish peer from County Monaghan, who greatly beautified it. The name Cremorne is the name of a barony, an old administrative unit, in County Monaghan in Ireland. It is an Anglicisation of what in modern Irish is ''Críoch Mhúrn''. This roughly translates as the 'Bounds of Mourne', from the territorial domain of an anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelsea Flower Show
The RHS Chelsea Flower Show, formally known as the ''Great Spring Show'',Phil Clayton, ''The Great Temple Show'' in ''The Garden'' 2008, p.452, The Royal Horticultural Society is a garden show held for five days in May by the Royal Horticultural Society (RHS) in the grounds of the Royal Hospital Chelsea in Chelsea, London. Held at Chelsea since 1912, the show is attended by members of the British Royal Family. Highlights to the Chelsea Flower Show include the avant-garde show gardens designed by leading names with Floral Marquee at the centrepiece. The Show also features smaller gardens such as the Artisan and Urban Gardens. History Great Spring Show The first Royal Horticultural Society Great Spring Show was held in 1862, at the RHS garden in Kensington. Before this date the RHS had held flower shows from 1833 in their garden in Chiswick, which themselves had been preceded by fetes. The Kensington Garden was chosen as a site because the flower shows in Chiswick were experiencin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleasure Ground
In English gardening history, the pleasure ground or pleasure garden was the parts of a large garden designed for the use of the owners, as opposed to the kitchen garden and the wider park. It normally included flower gardens, typically directly outside the house, and areas of lawn, used for playing games (bowling grounds were very common, later croquet lawns), and perhaps "groves" or a Wilderness (garden history), wilderness for walking around. Smaller gardens were often or usually entirely arranged as pleasure grounds, as are modern public parks. The concept survived a number of major shifts in the style of English gardens, from the Renaissance, through Baroque formal gardens, to the English landscape garden style. The pleasure grounds of English country house gardens have typically been remade a number of times, and awareness has recently returned that even the designs of the famous 18th-century landscapists such as Capability Brown originally included large areas of pleas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), gaining independence from the British Crown and establishing the United States of America as the first nation-state founded on Enlightenment principles of liberal democracy. American colonists objected to being taxed by the Parliament of Great Britain, a body in which they had no direct representation. Before the 1760s, Britain's American colonies had enjoyed a high level of autonomy in their internal affairs, which were locally governed by colonial legislatures. During the 1760s, however, the British Parliament passed a number of acts that were intended to bring the American colonies under more direct rule from the British metropole and increasingly intertwine the economies of the colonies with those of Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
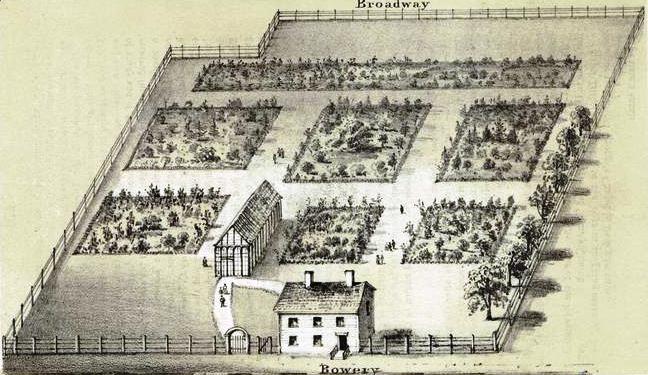
New York Vauxhall Gardens
The Vauxhall Gardens (in New York City), was a pleasure garden and theater. It was named for the Vauxhall Gardens of London.Ogasapian, John (2004). ''American History through Music: Music of the Colonial and Revolutionary Era''. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. . Though the venue passed through a long list of owners, and suffered buyouts, closings, relocations, and re-openings, it lasted until the mid-19th century.Caldwell, Mark (2005). ''New York Night: The Mystique and Its History''. New York City: Scribner. . History Vauxhall Gardens, Greenwich Street In the mid-1760s, out-of-town taverns, such as John Clapp's in the Bowery, had become popular in Colonial New York, taking advantage of the " Sunset Strip-like" jurisdiction, two miles from the post office,. At a site called "Bowling Green" since 1722, Samuel Fraunces opened a pleasure garden, first called the '' Vaux-Hall Gardens'', in New York, in 1767 and it received a chief competitor in the much larger Ranelagh Garde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelsea Hospital Ranelagh
Chelsea or Chelsey may refer to: Places Australia * Chelsea, Victoria Canada * Chelsea, Nova Scotia * Chelsea, Quebec United Kingdom * Chelsea, London, an area of London, bounded to the south by the River Thames ** Chelsea (UK Parliament constituency), a former parliamentary constituency at Westminster until the 1997 redistribution ** Chelsea (London County Council constituency), 1949–1965 ** King's Road Chelsea railway station, a proposed railway station ** Chelsea Bridge, a bridge across the Thames ** Metropolitan Borough of Chelsea, a former borough in London United States * Chelsea, Alabama * Chelsea (Delaware City, Delaware), a historic house * Chelsea, Georgia * Chelsea, Indiana * Chelsea, Iowa, in Tama County * Chelsea, Maine * Chelsea, Massachusetts ** Bellingham Square station, which includes a commuter rail stop called Chelsea ** Chelsea station (MBTA), a bus rapid transit station in Chelsea * Chelsea, Michigan * Chelsey Brook, a stream in Minnesota * Chelsea, Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, ''The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, is known for the quality and irony of its prose, its use of primary sources, and its polemical criticism of organised religion. Early life: 1737–1752 Edward Gibbon was born in 1737, the son of Edward and Judith Gibbon at Lime Grove, in the town of Putney, Surrey. He had six siblings, five brothers and one sister, all of whom died in infancy. His grandfather, also named Edward, had lost his assets as a result of the South Sea bubble stock-market collapse in 1720 but eventually regained much of his wealth. Gibbon's father was thus able to inherit a substantial estate. One of his grandmothers, Catherine Acton, descended from Sir Walter Acton, 2nd Baronet. As a youth, Gibbon's health was under constant threat. He described himself as "a puny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Saints Church, Evesham
All Saints Church is an active Anglican church in the centre of the town of Evesham, Worcestershire, England. All Saints and its neighbour St Lawrence's Church were built by the Benedictine monks of Evesham Abbey in the 12th century to serve the people of Evesham. All Saints is now the town's parish church, as St Lawrence's was declared redundant in the 1970s. It has been designated as a Grade I listed building by Historic England. History Intriguingly, the two parish churches share the same churchyard. After the Dissolution All Saints adopted a strongly Puritan method of preaching and worship (in common with many other English churches). This style lasted until, roughly, the major Victorian restoration (1872-6) by Frederick Preedy, when All Saints moved to a high church (Anglo-Catholic) tradition of worship. Through the 1970s it became increasingly clear that the upkeep of two medieval churches, with all the attendant challenges and problems, was to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaletto
Giovanni Antonio Canal (18 October 1697 – 19 April 1768), commonly known as Canaletto (), was an Italian painter from the Republic of Venice, considered an important member of the 18th-century Venetian school. Painter of city views or ''vedute'', of Venice, Rome, and London, he also painted imaginary views (referred to as capricci), although the demarcation in his works between the real and the imaginary is never quite clearcut.Alice Binion and Lin Barton. "Canaletto." Grove Art Online. Oxford Art Online. Oxford University Press. Web. 6 Jan. 2017 He was further an important printmaker using the etching technique. In the period from 1746 to 1756 he worked in England where he painted many views of London and other sites including Warwick Castle and Alnwick Castle. He was highly successful in England, thanks to the British merchant and connoisseur Joseph "Consul" Smith, whose large collection of Canaletto's works was sold to King George III in 1762. Early career He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)
