|
Rancho Punta De Los Reyes (Phelps)
Rancho Punta de los Reyes was a Mexican land grant in present day Marin County, California, given in 1836 by Governor Nicolás Gutiérrez to James Richard Berry. The grant was east of Rancho Las Baulines and south of Rancho Tomales y Baulines. History James Richard Berry (–1847), an Irishman and a colonel in the Mexican army, came to California from Mexico. In 1836, Governor Gutierriez, granted Berry the eight square league Rancho Punta de los Reyes. In 1838, Berry sold the two square league portion along the western shore of Tomales Bay (known as the "Inverness Pocket") of the Rancho Punta de los Reyes grant, to Joseph Snook (1798–1848), grantee of Rancho San Bernardo. When, in 1843, Rafael Garcia, the owner of adjacent Rancho Tomales y Baulines, moved his cattle onto Berry’s remaining land, Berry moved west, squatting on Antonio Osio’s Rancho Punta de los Reyes Sobrante. In 1844, Berry sold Rancho Punta de los Reyes to Stephen Smith of Rancho Bodega, to whom he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Patent
A land patent is a form of letters patent assigning official ownership of a particular tract of land that has gone through various legally-prescribed processes like surveying and documentation, followed by the letter's signing, sealing, and publishing in public records, made by a sovereign entity. It is the highest evidence of right, title, and interest to a defined area. It is usually granted by a central, federal, or state government to an individual, partnership, trust, or private company. The land patent is not to be confused with a land grant. Patented lands may be lands that had been granted by a sovereign authority in return for services rendered or accompanying a title or otherwise bestowed ''gratis'', or they may be lands privately purchased by a government, individual, or legal entity from their prior owners. "Patent" is both a process and a term. As a process, it is somewhat parallel to gaining a patent for intellectual property, including the steps of uniquely def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Ranchos
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ranchos Of California
These California land grants were made by Spanish (1784–1821) and Mexican (1822–1846) authorities of Las Californias and Alta California to private individuals before California became part of the United States of America.Shumway, Burgess M.,1988, ''California Ranchos: Patented Private Land Grants Listed by County'', The Borgo Press, San Bernardino, CA, Under Spain, no private land ownership was allowed, so the grants were more akin to free leases. After Mexico achieved independence, the Spanish grants became actual land ownership grants. Following the Mexican–American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. Alta California ranchos in Mexico From 1773 to 1836, the border between Alta California and Baja California was about 30 miles south of the Mexico–United States border drawn by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that ended the Mexican–American War in 1848. Under the Siete Leyes constitutional reforms of 1836, the Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco Committee Of Vigilance
The San Francisco Committee of Vigilance was a vigilante group formed in 1851. The catalyst for its formation was the criminality of the Sydney Ducks gang. It was revived in 1856 in response to rampant crime and corruption in the municipal government of San Francisco, California. The need for extralegal intervention was apparent with the explosive population growth following the discovery of gold in 1848. The small town of about 900 individuals grew to a booming city of over 20,000 very rapidly. This overwhelming growth in population made it nearly impossible for the previously established law enforcement to regulate any longer which resulted in the organization of vigilantes. These militias hanged eight people and forced several elected officials to resign. Each Committee of Vigilance formally relinquished power after three months. 1851 The 1851 Committee of Vigilance was inaugurated on June 9 with the promulgation of a written doctrine declaring its aims and hanged John Jenkins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish language, Spanish for "Francis of Assisi, Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the List of California cities by population, fourth most populous in California and List of United States cities by population, 17th most populous in the United States, with 815,201 residents as of 2021. It covers a land area of , at the end of the San Francisco Peninsula, making it the second most densely populated large U.S. city after New York City, and the County statistics of the United States, fifth most densely populated U.S. county, behind only four of the five New York City boroughs. Among the 91 U.S. cities proper with over 250,000 residents, San Francisco was ranked first by per capita income (at $160,749) and sixth by aggregate income as of 2021. Colloquial nicknames for San Francisco include ''SF'', ''San Fran'', ''The '', ''Frisco'', and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butte County, California
Butte County () is a county located in the northern part of the U.S. state of California. In the 2020 census, its population was 211,632. The county seat is Oroville. Butte County comprises the Chico, CA metropolitan statistical area. It is in the California Central Valley, north of the state capital of Sacramento. Butte County is drained by the Feather River and the Sacramento River. Butte Creek and Big Chico Creek are additional perennial streams, both tributary to the Sacramento. The county is home to California State University, Chico and Butte College. History Butte County is named for the Sutter Buttes in neighboring Sutter County; ''butte'' means "small knoll" or "small hill" in French. Butte County was incorporated as one of California's 19 original counties on February 18, 1850. The county went across the present limits of the Tehama, Plumas, Colusa, and Sutter Counties. Between November 8 and 25, 2018, a major wildfire, the Camp Fire, destroyed most of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Aguas Frias
Rancho Aguas Frias was a Mexican land grant in present-day Butte County, California given in 1844 by Governor Manuel Micheltorena to Antonio Maria Osio and his son Salvador Osio. Aguas Frias means "cold water" in Spanish. The grant, located south of present-day Chico, extended along the west bank of Butte Creek, and was bounded on the west by Rancho Llano Seco. Rancho Esquon was directly across Butte Creek. History Antonio M. Osio (1800–1878) was also the grantee of the eleven square league Rancho Punta de los Reyes Sobrante given by Governor Micheltorena in 1843. Osio's son Salvador settled on the six square league Rancho Aguas Frias. Osio sold Rancho Aguas Frias to Andrew Randall. Andrew Randall (1819–1856), a native of Rhode Island, came to California in 1849 as the newly appointed customs inspector for Monterey. Randall was an entrepreneur with training as a geologist. He founded, and was elected chairman of the California Academy of Sciences. In a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monterey County, California
Monterey County ( ), officially the County of Monterey, is a county located on the Pacific coast in the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 census, its population was 439,035. The county's largest city and county seat is Salinas. Monterey County comprises the Salinas, California, Metropolitan Statistical Area. It borders on the southern part of Monterey Bay, after which it is named. (The northern half of the bay is in Santa Cruz County.) Monterey County is a member of the regional governmental agency: the Association of Monterey Bay Area Governments. Scenic features along the coastline - including Carmel-by-the-Sea, Big Sur, State Route 1, and the 17 Mile Drive on the Monterey Peninsula - have made the county famous around the world. Back when California was under Spanish and Mexican rule, the city of Monterey was its capital. Today, the economy of the county is mostly based on tourism in its coastal regions, and on agriculture in the region of the Salinas Rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho San Lorenzo (Randall)
Rancho San Lorenzo was a Mexican land grant in present-day Monterey County, California given in 1842 by Governor Juan Alvarado to Francisco Rico. The grant extended along San Lorenzo Creek in Peach Tree Valley. History Francisco Ygnicio Rico Francisco Rico (1826–) was born Mexico and came to Monterey with his father, Vicente Rico, in 1831. Francisco Rico, was the grantee of Rancho San Lorenzo in 1842, and Rancho Del Rio Estanislao in 1843. In 1845 he was appointed by the Mexican Government second officer of the port of Monterey, under Pablo de la Guerra, and held the captaincy of a company of the Monterey cavalry. Rico was active with José María Flores on the Mexican side in the Mexican–American War. He was the leader of the escort of the captured Thomas O. Larkin. Flores dispatched Rico to retake San Diego, but he was recalled back to Los Angeles. Rico and José Antonio Carrillo revolted against Flores. Flores was placed under arrest, but quickly was restored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Cañada De La Segunda
Rancho Cañada de la Segunda was a Mexican land grant in present-day Monterey County, California given in 1839 by Governor José Castro to Lazaro Soto. The grant extended along the north bank of the Carmel River, from the Pacific coast and present day Carmel-by-the-Sea up into the Carmel Valley. History Lazaro Soto's grandfather, Ygnacio Soto, came to California with the De Anza Expedition. His father, Ysidoro Soto, was an officer in the Mexican army at Monterey. Lazaro Soto was also a soldier in the Mexican army of California. Lazaro Soto received the one square league grant in Carmel Valley in 1839. Lazaro Soto married Felicita Cantua and he and his family resided in Monterey. Lazaro Soto was the officer in charge of horses and munitions at the Battle of Natividad. Lazaro Soto sold Rancho Cañada de la Segunda to Andrew Randall. Andrew Randall (1819–1856), a native of Rhode Island, came to California in 1849 as the newly appointed customs inspector for Monterey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
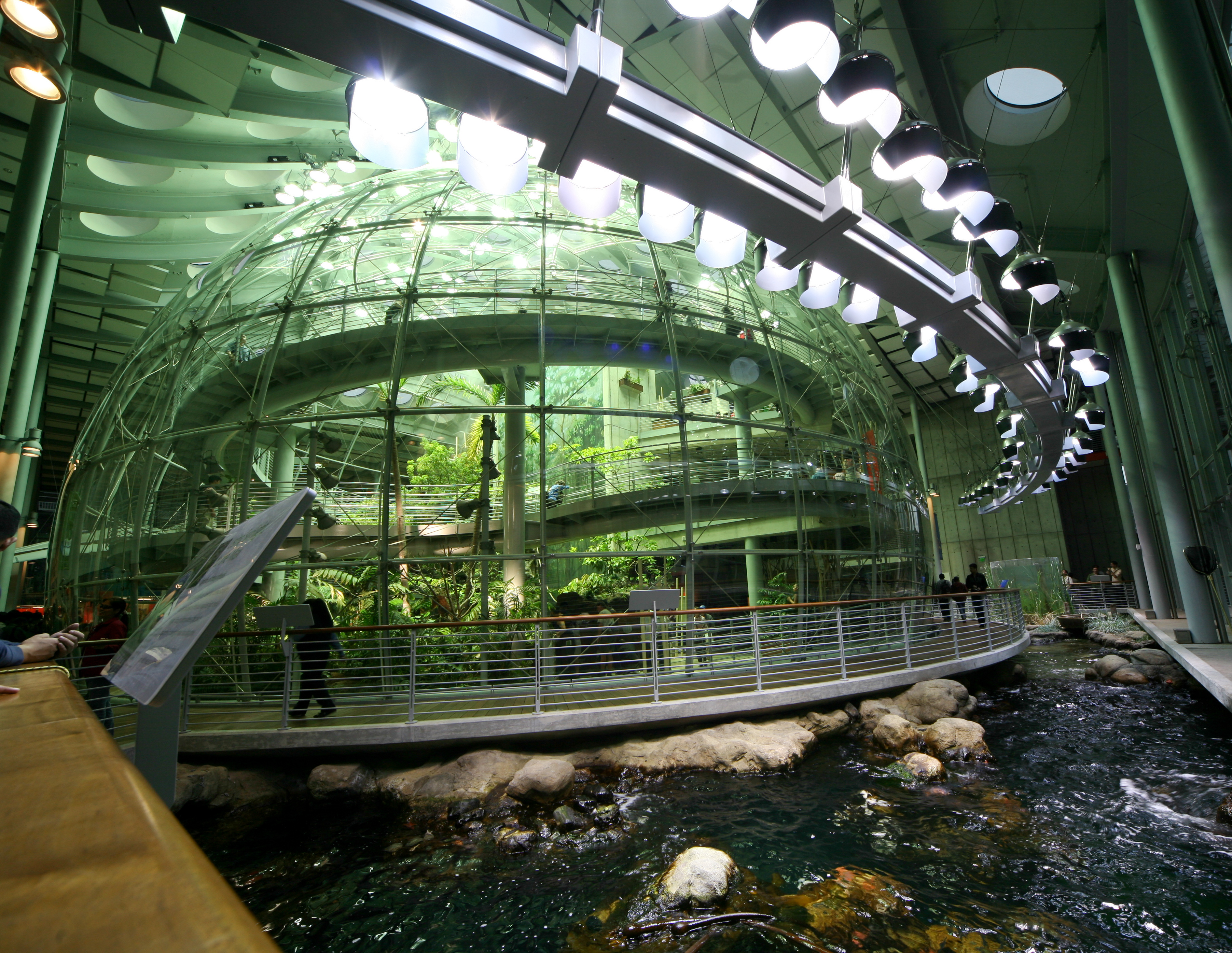
California Academy Of Sciences
The California Academy of Sciences is a research institute and natural history museum in San Francisco, California, that is among the largest museums of natural history in the world, housing over 46 million specimens. The Academy began in 1853 as a learned society and still carries out a large amount of original research. The institution is located at the Golden Gate Park in San Francisco. Completely rebuilt in 2008, the Academy's primary building in Golden Gate Park covers . In early 2020, before the COVID-19 pandemic, the California Academy of Sciences had around 500 employees and an annual revenue of about $33 million. Governance The California Academy of Sciences, California's oldest operating museum and research institution for the natural sciences, is governed by a forty-one member Board of Trustees who are nominated and chosen by the California Academy of Sciences Fellows. The Academy Fellows are, in turn, " minated by their colleagues and appointed by the Board of Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

