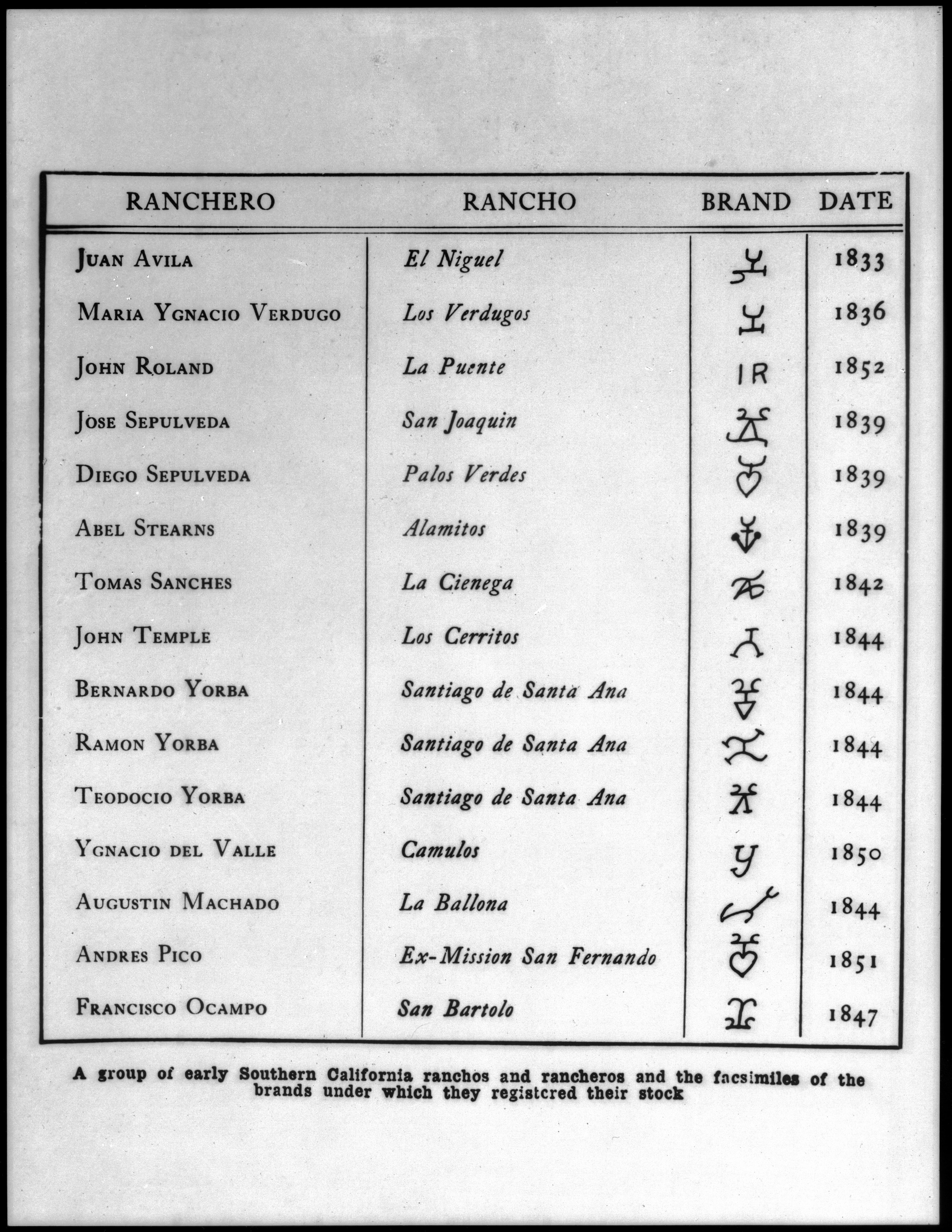
|
Rancho Azusa De Dalton
Rancho Azusa de Dalton, (originally the Rancho El Susa), was a Mexican land grant in present-day Los Angeles County, California, given in 1841 by Governor Juan Alvarado to Luis Arenas. Arenas sold his Rancho Azusa de Duarte holdings three years later to Henry Dalton (1803–1884), a wealthy merchant from Pueblo of Los Angeles. Dalton named his holding Rancho Azusa de Dalton. Henry Dalton was also called Don Enrique Dalton. Cities that have been established on the Rancho lands originally granted to Henry Dalton include Azusa, Arcadia, Monrovia, Irwindale and Baldwin Park. History Luis Arenas received the Rancho El Susa land grant from Governor (pro-tem) Manuel Jimeno in 1841. In 1844 Henry Dalton purchased El Susa from Arenas, and also Arenas one third interest in Rancho San Jose. Henry Dalton was born in England, and in 1820 sailed to Lima, Peru, and became a merchant eventually commanding a small fleet of merchant vessels. By 1841 he had become a prominent figure in Califo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of California
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rancho Santa Anita
Rancho Santa Anita was a land grant in present-day Los Angeles County, California given to naturalized Scottish immigrant Hugo Reid and his Kizh people wife. Reid built an adobe residence there in 1839, and the land grant was formally recognized by Governor Pio Pico in 1845. The land grant covered all or portions of the present day cities of Arcadia, Monrovia, Sierra Madre, Pasadena and San Marino. A small portion of the rancho has been preserved as the Los Angeles County Arboretum and Botanic Garden. History The land granted to Reid was previously owned by the Mission San Gabriel. The San Gabriel Mission was founded in 1771 as the 4th of the Spanish missions in California. The San Gabriel Mission planted acres of land, in with: wheat, barley, corn, beans, peas lentils, fruit trees and vineyards. The land also grazed about 20,000 head of cattle. After the Mexican War of Independence in 1821, the Mexican secularization act of 1833 was passed. Starting in 1834 Mexico took away much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranchos Of Los Angeles County, California
Rancho or Ranchos may refer to: Settlements and communities *Rancho, Aruba, former fishing village and neighbourhood of Oranjestad *Ranchos of California, 19th century land grants in Alta California **List of California Ranchos *Ranchos, Buenos Aires in Argentina Schools *Rancho Christian School in Temecula, California *Rancho High School in North Las Vegas, Nevada * Rancho San Joaquin Middle School in Irvine, California *Rancho Solano Preparatory School in Scottsdale, Arizona *Rancho Verde High School in Moreno Valley, California Film *Rancho, a character in the Bollywood film ''3 Idiots'' *Rancho (monkey), an Indian monkey animal actor Other *Rancho, a shock absorber brand by Tenneco Automotive * Rancho carnavalesto or Rancho, a type of dance club from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil *Rancho Los Amigos National Rehabilitation Center or Rancho *Rancho Point, a rock headland in the South Shetland Islands *Matra Rancho or Rancho, an early French leisure activity vehicle See also * * *E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Ranchos
The Spanish and Mexican governments made many concessions and land grants in Alta California (now known as California) and Baja California from 1775 to 1846. The Spanish Concessions of land were made to retired soldiers as an inducement for them to remain in the frontier. These Concessions reverted to the Spanish crown upon the death of the recipient. The Mexican government later encouraged settlement by issuing much larger land grants to both native-born and naturalized Mexican citizens. The grants were usually two or more square leagues, or in size. Unlike Spanish Concessions, Mexican land grants provided permanent, unencumbered ownership rights. Most ranchos granted by Mexico were located along the California coast around San Francisco Bay, inland along the Sacramento River, and within the San Joaquin Valley. When the government secularized the Mission churches in 1833, they required that land be set aside for each Neophyte family. But the Native Americans were quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savannah Memorial Park
Savannah Memorial Park Cemetery also known as El Monte Memorial Park and the Savannah Pioneer Cemetery is the oldest American non-sectarian cemetery in Southern California. The park is located in Rosemead, California, part of the park is in the neighboring city of El Monte. The park has been in continuous operation since its founding in 1850. Some of the burials may date back into the 1840s before Savannah Memorial Park became a Memorial Park. Savannah Memorial Park was designated a California Historical Landmark (No. 1046) on March 6, 2012. History About 1846 Henry Dalton (1803–1884) owner of Rancho San Francisquito, found two graves on his property that were protected by a cactus hedge. He set aside two acres surrounding the graves for a cemetery. Dalton was a merchant and had purchased a number of properties in Los Angeles and San Gabriel Valley during the late 1800s. He and his wife Maria nee Zamorano (1832–1914) purchased food products around the world and brought t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of California Ranchos
These California land grants were made by Spanish (1784–1821) and Mexican (1822–1846) authorities of Las Californias and Alta California to private individuals before California became part of the United States of America.Shumway, Burgess M.,1988, ''California Ranchos: Patented Private Land Grants Listed by County'', The Borgo Press, San Bernardino, CA, Under Spain, no private land ownership was allowed, so the grants were more akin to free leases. After Mexico achieved independence, the Spanish grants became actual land ownership grants. Following the Mexican–American War, the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo provided that the land grants would be honored. Alta California ranchos in Mexico From 1773 to 1836, the border between Alta California and Baja California was about 30 miles south of the Mexico–United States border drawn by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo that ended the Mexican–American War in 1848. Under the Siete Leyes constitutional reforms of 1836, the Alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Corporation
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally owned corporations. Municipal corporation as local self-government Municipal incorporation occurs when such municipalities become self-governing entities under the laws of the state or province in which they are located. Often, this event is marked by the award or declaration of a municipal charter. A city charter or town charter or municipal charter is a legal document establishing a municipality, such as a city or town. Canada In Canada, charters are granted by provincial authorities. India The Corporation of Chennai is the oldest Municipal Corporation in the world outside the United Kingdom. Ireland The title "corporation" was used in boroughs from soon after the Norman conquest until the Local Government Act 2001. Under the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dustin Bicknell
John D. Bicknell (June 25, 1838 – July 7, 1911) was an American real estate attorney and investor. He studied law in Wisconsin, later being admitted to the bar in the supreme court of that state. From 1872 to 1907 he participated in the Los Angeles real estate boom, and founded the law firm that is now known as Gibson, Dunn & Crutcher. He was also associated with the founding of Monrovia and Azusa, California, and oil developments in the Santa Maria Valley. Early life and career Bicknell was born in Jericho, Vermont, elder son of Nathaniel and Fanny (Thompson) Bicknell, and a direct descendant of Hannah Dustin. Bicknell moved to Wisconsin where he attended college. In 1860 Bicknell went to Missouri, where he taught school for two years. Troubled by his asthma he decided to move to California. In 1862 he joined a group of emigrants and was elected captain of the expedition directing them to Knights Landing, California. Bicknell stayed in California until 1863, then res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Hancock
Henry Hancock (April 11, 1822January 9, 1883) was a Harvard trained lawyer and a land surveyor working in California in the 1850s. He was the owner of Rancho La Brea, which included the La Brea Tar Pits. Early life Henry Hancock was born in Bath, New Hampshire, a son of Thomas Hancock and his wife Lucy (Smith) Hancock, and grandson of Henry Hancock and Abigail (Cotton) Hancock. He was of English ancestry, his grandfather having emigrated from Somerset in the 18th century. Hancock entered the Norwich Military Academy, then studied law at Harvard University. Graduating in 1846, he went St. Louis, Missouri, where he became a surveyor. During the Mexican–American War, he was quartermaster of the 1st Regiment Missouri Mounted Volunteers under Colonel Alexander William Doniphan. At the war's end, he returned home to New Hampshire but soon decided to go west. Life in California Hancock sailed from Chicago to San Francisco. He arrived in California in September, 1849 and opened a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Land Commission
The California Land Act of 1851 (), enacted following the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and the admission of California as a state in 1850, established a three-member Public Land Commission to determine the validity of prior Spanish and Mexican land grants. It required landowners who claimed title under the Mexican government to file their claim with a commission within two years. Contrary to the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, which guaranteed full protection of all property rights for Mexican citizens, it placed the burden on landholders to prove their title. While the commission eventually confirmed 604 of the 813 claims, almost all of the claims went to court and resulted in protracted litigation. The expense of the long court battles required many land holders to sell portions of the property or even trade it in payment for legal services. A few cases were litigated into the 1940s. Legislation California Senator William M. Gwin presented a bill that was approved by the Senate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 February 1848, in the Villa de Guadalupe Hidalgo (now a neighborhood of Mexico City) between the United States and Mexico that ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). The treaty was ratified by the United States on 10 March and by Mexico on 19 May. The ratifications were exchanged on 30 May, and the treaty was proclaimed on 4 July 1848. With the defeat of its army and the fall of its capital in September 1847, Mexico entered into negotiations with the U.S. peace envoy, Nicholas Trist, to end the war. On the Mexican side, there were factions that did not concede defeat or seek to engage in negotiations. The treaty called for the United States to pay US$15 million to Mexico and to pay off the claims of American citizens against Mex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican-American War
Mexican Americans ( es, mexicano-estadounidenses, , or ) are Americans of full or partial Mexicans, Mexican heritage. In 2019, Mexican Americans comprised 11.3% of the US population and 61.5% of all Hispanic and Latino Americans. In 2019, 71% of Mexican Americans were born in the United States, though they make up 53% of the total population of foreign-born Latino Americans and 25% of the total foreign-born population. The United States is home to the second-largest Mexicans, Mexican community in the world (24% of the entire emigration from Mexico, Mexican-origin population of the world), behind only Mexico. Most Mexican Americans reside in Southwestern United States, the Southwest (over 60% in the states of California and Texas). Many Mexican Americans living in the United States have assimilated into Culture of the United States, American culture which has made some become less connected with their culture of birth (or of their parents/ grandparents) and sometimes creates an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |