|
Ramsey–Cass–Koopmans Model
The Ramsey–Cass–Koopmans model (also known as the Ramsey growth model or the neoclassical growth model) is a foundational model in neoclassical economics that describes the dynamics of economic growth over time. It builds upon the pioneering work of Frank P. Ramsey (1928), with later extensions by David Cass and Tjalling Koopmans in the 1960s. The model extends the Solow–Swan model by Exogenous and endogenous variables, endogenizing the Saving, savings rate through explicit microfoundations of Consumption (economics), consumption behavior: rather than assuming a constant saving rate, the model derives it from the intertemporal optimization of a representative agent who chooses Consumption (economics), consumption to maximize utility over an infinite horizon. This approach leads to a richer dynamic structure in the transition to the long-run Steady state (macroeconomics), steady state, and yields a Pareto efficiency, Pareto efficient outcome.This efficiency result depends not o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassical Economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption, and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good or service is determined through a hypothetical maximization of utility by income-constrained individuals and of profits by firms facing production costs and employing available information and factors of production. This approach has often been justified by appealing to rational choice theory. Neoclassical economics is the dominant approach to microeconomics and, together with Keynesian economics, formed the neoclassical synthesis which dominated mainstream economics as "neo-Keynesian economics" from the 1950s onward. Classification The term was originally introduced by Thorstein Veblen in his 1900 article "Preconceptions of Economic Science", in which he related marginalists in the tradition of Alfred Marshall ''et al.'' to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Diamond
Peter Arthur Diamond (born , 1940) is an American economist known for his analysis of U.S. Social Security policy and his work as an advisor to the Advisory Council on Social Security in the late 1980s and 1990s. He was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 2010, along with Dale T. Mortensen and Christopher A. Pissarides. He is an Institute Professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. On June 6, 2011, he withdrew his nomination to serve on the Federal Reserve's board of governors, citing intractable Republican opposition for 14 months. Early life and education Diamond was born to a Jewish family in New York City. His grandparents immigrated to the U.S. at the turn of the 20th century. His mother's parents and six older siblings came from Poland. His father's parents met in New York, she came from Russia and he came from Romania. His parents, both born in 1908, grew up in New York City and never lived outside the metropolitan area. Both finis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
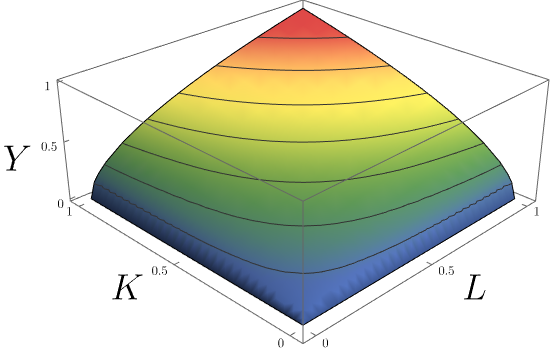
Cobb–Douglas Production Function
In economics and econometrics, the Cobb–Douglas production function is a particular functional form of the production function, widely used to represent the technological relationship between the amounts of two or more inputs (particularly physical capital and labor) and the amount of output that can be produced by those inputs. The Cobb–Douglas form was developed and tested against statistical evidence by Charles Cobb and Paul Douglas between 1927 and 1947; according to Douglas, the functional form itself was developed earlier by Philip Wicksteed. Formulation In its most standard form for production of a single good with two factors, the function is given by: : Y(L,K)=AL^\beta K^\alpha where: * ''Y'' = total production (the real value of all goods produced in a year or 365.25 days) * ''L'' = labour input (person-hours worked in a year or 365.25 days) * ''K'' = capital input (a measure of all machinery, equipment, and buildings; the value of capital input divided by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggregate Production Function
Aggregate or aggregates may refer to: Computing and mathematics * Aggregate (data warehouse), a part of the dimensional model that is used to speed up query time by summarizing tables * Aggregate analysis, a technique used in amortized analysis in computer science, especially in analysis of algorithms * Aggregate class, a type of class supported by C++ * Aggregate data, in statistics, data combined from several measurements * Aggregate function, aggregation function, in database management is a function wherein the values of multiple rows are grouped together to form a single summary value * Aggregate Level Simulation Protocol (ALSP), a protocol and supporting software that enables simulations to interoperate with one another * Aggregate root, a concept in the Domain-driven Design software development process * Aggregate Server Access Protocol, used by the Reliable server pooling (RSerPool) framework * Aggregate throughput, total throughput measured over all links and in all d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broader viewpoint, an investment can be defined as "to tailor the pattern of expenditure and receipt of resources to optimise the desirable patterns of these flows". When expenditures and receipts are defined in terms of money, then the net monetary receipt in a time period is termed cash flow, while money received in a series of several time periods is termed cash flow stream. In finance, the purpose of investing is to generate a Return (finance), return on the invested asset. The return may consist of a capital gain (profit) or loss, realised if the investment is sold, unrealised capital appreciation (or depreciation) if yet unsold. It may also consist of periodic income such as dividends, interest, or rental income. The return may also inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton's Notation
In differential calculus, there is no single standard notation for differentiation. Instead, several notations for the derivative of a function or a dependent variable have been proposed by various mathematicians, including Leibniz, Newton, Lagrange, and Arbogast. The usefulness of each notation depends on the context in which it is used, and it is sometimes advantageous to use more than one notation in a given context. For more specialized settings—such as partial derivatives in multivariable calculus, tensor analysis, or vector calculus—other notations, such as subscript notation or the ∇ operator are common. The most common notations for differentiation (and its opposite operation, antidifferentiation or indefinite integration) are listed below. Leibniz's notation The original notation employed by Gottfried Leibniz is used throughout mathematics. It is particularly common when the equation is regarded as a functional relationship between dependent and independe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Accumulation
Capital accumulation is the dynamic that motivates the pursuit of profit, involving the investment of money or any financial asset with the goal of increasing the initial monetary value of said asset as a financial return whether in the form of profit, rent, interest, royalties or capital gains. The goal of accumulation of capital is to create new fixed capital and working capital, broaden and modernize the existing ones, grow the material basis of social-cultural activities, as well as constituting the necessary resource for reserve and insurance. The process of capital accumulation forms the basis of capitalism, and is one of the defining characteristics of a capitalist economic system.''Capital'', Encyclopedia on Marxists.org: http://marxists.org/glossary/terms/c/a.htm#capital Definition In economics and accounting, capital accumulation is often equated with investment of profit income or savings, especially in real capital goods. The concentration and centralisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Intensity
Capital intensity is the amount of fixed or real capital present in relation to other factors of production, especially labor. At the level of either a production process or the aggregate economy, it may be estimated by the capital to labor ratio, such as from the points along a capital/labor isoquant. The inverse of capital intensity is labor intensity. Capital intensity is sometimes associated with industrialism, while labor intensity is sometimes associated with agrarianism. Growth The use of tools and machinery makes labor more effective, so rising capital intensity (or " capital deepening") pushes up the productivity of labor. Capital intensive societies tend to have a higher standard of living over the long run. Calculations made by Robert Solow claimed that economic growth was mainly driven by technological progress (productivity growth) rather than inputs of capital and labor. However recent economic research has invalidated that theory, since Solow did not properly consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Per Capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person". Social statistics The term is used in a wide variety of social science, social sciences and statistical research contexts, including government statistics, economic indicators, and built environment studies. It is commonly used in the academic discipline, field of statistics in place of saying "per person" (although ''per caput'' is the Latin for "per head"). It is also used in will and testament, wills to indicate that each of the named beneficiary, beneficiaries should receive, by devise or bequest and devise, bequest, equal shares of the estate. This is in contrast to a ''per stirpes'' division, in which each branch (Latin: ''stirps'', : ''stirpes'') of the inheritance, inheriting family inherits an equal share of the estate (law), estate. This is often used with the '2-0 rule', a statistical principle that determines which group is larger ''per capit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Business Cycle Theory
Real business-cycle theory (RBC theory) is a class of new classical macroeconomics models in which business-cycle fluctuations are accounted for by real, in contrast to nominal, shocks. RBC theory sees business cycle fluctuations as the efficient response to exogenous changes in the real economic environment. That is, the level of national output necessarily maximizes ''expected'' utility. In RBC models, business cycles are described as "real" because they reflect optimal adjustments by economic agents rather than failures of markets to clear. As a result, RBC theory suggests that governments should concentrate on long-term structural change rather than intervention through discretionary fiscal or monetary policy. These ideas are strongly associated with freshwater economics within the neoclassical economics tradition, particularly the Chicago School of Economics. Business cycles If we were to take snapshots of an economy at different points in time, no two photos woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shock (economics)
In economics, a shock is an unexpected or unpredictable event that affects an economy, either positively or negatively. Technically, it is an unpredictable change in exogenous factors—that is, factors unexplained by an economic model—which may influence endogenous economic variables. The response of economic variables, such as GDP and employment, at the time of the shock and at subsequent times, is measured by an impulse response function. Types of shocks A technology shock is the kind resulting from a technological development that affects productivity. If the shock is due to constrained supply, it is termed a supply shock and usually results in price increases for a particular product. Supply shocks can be produced when accidents or disasters occur. The 2008 Western Australian gas crisis resulting from a pipeline explosion at Varanus Island is one example. A demand shock is a sudden change of the pattern of private expenditure, especially of consumption spendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Agents
In economic theory and econometrics, the term heterogeneity refers to differences across the units being studied. For example, a macroeconomic model in which consumers are assumed to differ from one another is said to have heterogeneous agents. Unobserved heterogeneity in econometrics In econometrics, statistical inferences may be erroneous if, in addition to the observed variables under study, there exist other relevant variables that are unobserved, but correlated with the observed variables; dependent and independent variables .M. Arellano (2003), Panel Data Econometrics', Chapter 2, 'Unobserved heterogeneity', pp. 7-31. Oxford University Press. Methods for obtaining valid statistical inferences in the presence of unobserved heterogeneity include the instrumental variables method; multilevel models, including fixed effects and random effects models; and the Heckman correction for selection bias. Economic models with heterogeneous agents {{Further, Agent-based computational ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |