|
Ramoplanin
Ramoplanin (INN) is a glycolipodepsipeptide antibiotic drug derived from strain ATCC 33076 of ''Actinoplanes''. It is effective against Gram-positive bacteria. Mechanism It exerts its bacteriocidal effect by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis, acting by inhibiting the transglycosylation step of peptidoglycan synthesis. Ramoplanin specifically binds to and sequesters lipid intermediates I and II, preventing intracellular glycosyltransferase (MurG) and other steps of the peptidoglycan assembly system. Uses Its development has been fast-tracked by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as a treatment for multiple antibiotic-resistant '' Clostridium difficile'' infection of the gastrointestinal tract, Unlike vancomycin, it is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, although it is unstable in the bloodstream, so can be taken only orally against ''Clostridium difficile'' infections of the gastrointestinal tract. Ramoplanin is "particularly useful" in cases ''E. faecalis'' no ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinoplanes
''Actinoplanes'' is a genus in the family Micromonosporaceae. They have aerial mycelia and spherical, motile spores. ''Actinoplanes'' species produce the pharmaceutically important compounds valienamine (a precursor to the antidiabetic drug acarbose and to the antibiotic validamycin), teicoplanin, and ramoplanin Ramoplanin (INN) is a glycolipodepsipeptide antibiotic drug derived from strain ATCC 33076 of ''Actinoplanes''. It is effective against Gram-positive bacteria. Mechanism It exerts its bacteriocidal effect by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesi .... Species ''Actinoplanes'' comprises the following species: * '' A. abujensis'' Sazak et al. 2012 * "'' A. arizonaensis''" Karwowski et al. 1988 * '' A. atraurantiacus'' Zhang et al. 2012 * '' A. auranticolor'' (Couch 1963) Stackebrandt and Kroppenstedt 1988 * "'' A. aureus''" Song et al. 2021 * '' A. bogorensis'' corrig. Nurkanto et al. 2016 * '' A. brasiliensis'' Thiemann et al. 1969 (Approved Lists 1980) * '' A. camp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall. Gram-positive bacteria take up the crystal violet stain used in the test, and then appear to be purple-coloured when seen through an optical microscope. This is because the thick peptidoglycan layer in the bacterial cell wall retains the stain after it is washed away from the rest of the sample, in the decolorization stage of the test. Conversely, gram-negative bacteria cannot retain the violet stain after the decolorization step; alcohol used in this stage degrades the outer membrane of gram-negative cells, making the cell wall more porous and incapable of retaining the crystal violet stain. Their peptidoglycan layer is much thinner and sandwiched between an inner cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane, causing them to take up the counterstain (saf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria). A major function is to act as pressure vessels, preventing over-expansion of the cell when water enters. The composition of cell walls varies between taxonomic group and species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. Often, other polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae possess cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides such as carrageenan and agar that are absent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like peptidoglycan layer outside the plasma membrane, the rigid cell wall (murein sacculus) characteristic of most bacteria (domain ''Bacteria''). The sugar component consists of alternating residues of β-(1,4) linked ''N''-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and ''N''-acetylmuramic acid (NAM). Attached to the ''N''-acetylmuramic acid is a oligopeptide chain made of three to five amino acids. The peptide chain can be cross-linked to the peptide chain of another strand forming the 3D mesh-like layer. Peptidoglycan serves a structural role in the bacterial cell wall, giving structural strength, as well as counteracting the osmotic pressure of the cytoplasm. This repetitive linking results in a dense peptidoglycan layer which is critical for maintaining cell form and withstanding high osmotic pressures, and it is regularly replaced by peptidoglycan production. Pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
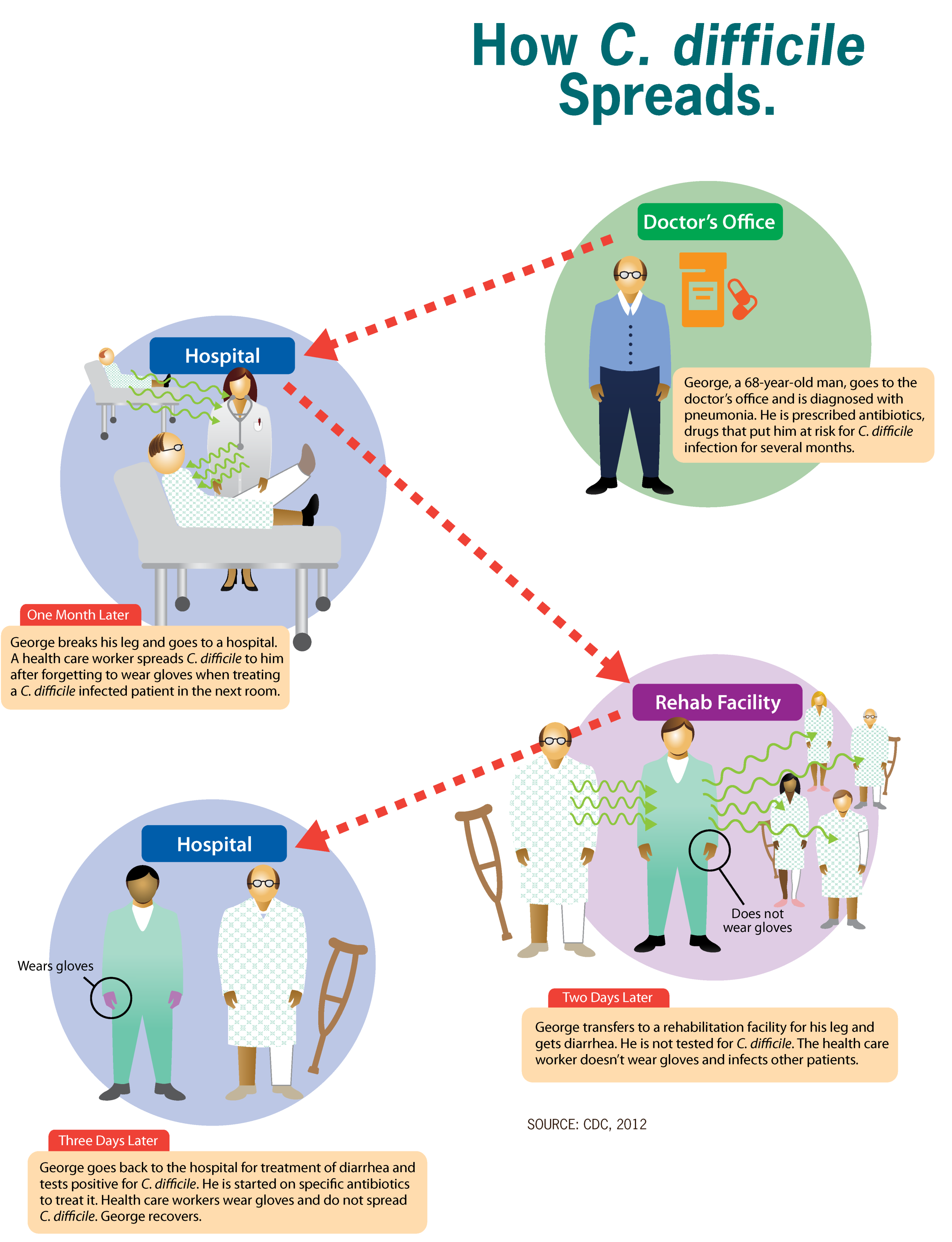
Clostridium Difficile Colitis
''Clostridioides difficile'' infection (CDI or C-diff), also known as ''Clostridium difficile'' infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium ''Clostridioides difficile''. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, fever, nausea, and abdominal pain. It makes up about 20% of cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Antibiotics can contribute to detrimental changes in gut microbiota; specifically, they decrease short-chain fatty acid absorption which results in osmotic, or watery, diarrhea. Complications may include pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon, perforation of the colon, and sepsis. ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection is spread by bacterial spores found within feces. Surfaces may become contaminated with the spores with further spread occurring via the hands of healthcare workers. Risk factors for infection include antibiotic or proton pump inhibitor use, hospitalization, other health problems, and older age. Diagnosis is by stool culture or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal Tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digestion, digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Nephrozoa, Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores (ostium (sponges), ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vancomycin
Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections. It is recommended intravenously as a treatment for complicated skin infections, bloodstream infections, endocarditis, bone and joint infections, and meningitis caused by methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Blood levels may be measured to determine the correct dose. Vancomycin is also taken by mouth as a treatment for severe ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis. When taken by mouth it is poorly absorbed. Common side effects include pain in the area of injection and allergic reactions. Occasionally, hearing loss, low blood pressure, or bone marrow suppression occur. Safety in pregnancy is not clear, but no evidence of harm has been found, and it is likely safe for use when breastfeeding. It is a type of glycopeptide antibiotic and works by blocking the construction of a cell wall. Vancomycin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958. It is on the World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be made by bacteria inside Inside may refer to: * Insider, a member of any group of people of limited number and generally restricted access Film * ''Inside'' (1996 film), an American television film directed by Arthur Penn and starring Eric Stoltz * ''Inside'' (2002 f ... these organisms. While there exist a wide range of peptides that are not synthesized by ribosomes, the term ''nonribosomal peptide'' typically refers to a very specific set of these as discussed in this article. Nonribosomal peptides are synthesized by nonribosomal peptide synthetases, which, unlike the ribosomes, are independent of messenger RNA. Each nonribosomal peptide synthetase can synthesize only one type of peptide. Nonribosomal peptides often have cyclic compound, cyclic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula ( CH3)2NC(O)H. Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such as SN2 reactions. Structure and properties As for most amides, the spectroscopic evidence indicates partial double bond charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetra-n-butylammonium Fluoride
Tetra-''n''-butylammonium fluoride, commonly abbreviated to TBAF and ''n''-Bu4NF, is a quaternary ammonium salt with the chemical formula (CH3CH2CH2CH2)4N+F−. It is commercially available as the white solid trihydrate and as a solution in tetrahydrofuran. TBAF is used as a source of fluoride ion in organic solvents. Preparation and properties TBAF can be prepared by passing hydrofluoric acid through an ion-exchange resin, followed by tetrabutylammonium bromide. Upon evaporation of the water, TBAF can be collected as an oil in quantitative yield. Preparing anhydrous samples is of interest as the basicity of fluoride increases by more than 20 p''K'' units on passing from aqueous to aprotic solvent. However, heating samples of the hydrated material to 77 °C under vacuum causes decomposition to the hydrogen difluoride salt. Similarly, samples dried at 40 °C under high vacuum still contain 10-30 mol% of water and some 10% of difluoride. Instead, anhydrous TBAF ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |