|
Raman Frequency
Raman spectroscopy () (named after Indian physicist C. V. Raman) is a spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible, near infrared, or near ultraviolet range is used, although X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar yet complementary information. Typically, a sample is illuminated with a laser beam. Electrom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Energy Levels , or Hadad, a storm and rain god
{{Disambiguation, geo ...
Raman may refer to: People *Raman (name) *C. V. Raman (1888–1970), Indian Nobel Prize-winning physicist Places * Raman, Punjab (India) * Raman, Rawalpindi, Pakistan * Raman District, Yala Province, Thailand ** Raman Railway Station * Raman oil field, in Batman, Turkey Other uses * Raman (crater), a lunar impact crater * ''Raman'' (film), a 2008 Indian Malayalam film * Raman Scattering, a physical effect named after C. V. Raman * Raman Spectroscopy, an analytical technique based on Raman Scattering See also * * Rahman (other) * Rama (other) * Ramen (other) * Rehman (other) * Ramman Hadad ( uga, ), Haddad, Adad ( Akkadian: 𒀭𒅎 '' DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur ( Sumerian) was the storm and rain god in the Canaanite and ancient Mesopotamian religions. He was attested in Ebla as "Hadda" in c. 2500 BCE. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering ( ), named after the 19th-century British physicist Lord Rayleigh (John William Strutt), is the predominantly elastic scattering of light or other electromagnetic radiation by particles much smaller than the wavelength of the radiation. For light frequencies well below the resonance frequency of the scattering particle (normal dispersion regime), the amount of scattering is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength. Rayleigh scattering results from the electric polarizability of the particles. The oscillating electric field of a light wave acts on the charges within a particle, causing them to move at the same frequency. The particle, therefore, becomes a small radiating dipole whose radiation we see as scattered light. The particles may be individual atoms or molecules; it can occur when light travels through transparent solids and liquids, but is most prominently seen in gases. Rayleigh scattering of sunlight in Earth's atmosphere causes d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the photoelectric effect, Eins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called ''diffuse reflections'' and unscattered reflections are called ''specular'' (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering (going back at least as far as Isaac Newton in the 17th century). As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" (not then recognized as electromagnetic in nature) in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering resear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie wavele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
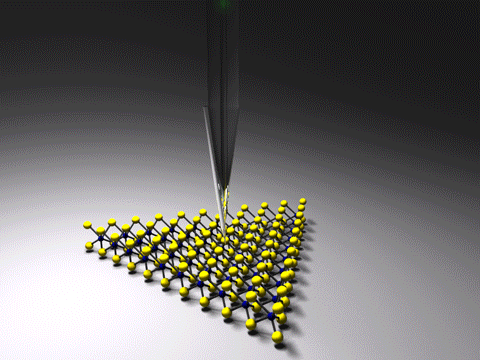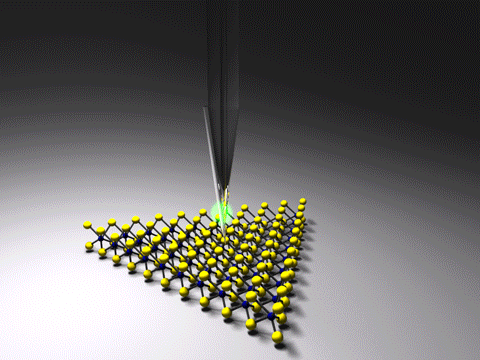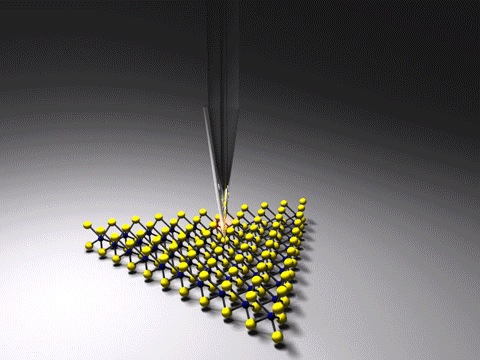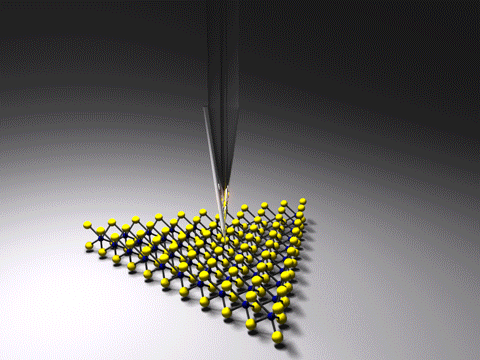
Tip-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) is a variant of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) that combines scanning probe microscopy with Raman spectroscopy. High spatial resolution chemical imaging is possible ''via'' TERS, with routine demonstrations of nanometer spatial resolution under ambient laboratory conditions, or better at ultralow temperatures and high pressure. The maximum resolution achievable using an optical microscope, including Raman microscopes, is limited by the Abbe limit, which is approximately half the wavelength of the incident light. Furthermore, with SERS spectroscopy the signal obtained is the sum of a relatively large number of molecules. TERS overcomes these limitations as the Raman spectrum obtained originates primarily from the molecules within a few tens of nanometers of the tip. History The earliest reports of tip enhanced Raman spectroscopy typically used a Raman microscope coupled with an atomic force microscope. Tip-enhanced Raman spectrosco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance Raman Spectroscopy
Resonance Raman spectroscopy (RR spectroscopy) is a Raman spectroscopy technique in which the incident photon energy is close in energy to an electronic transition of a compound or material under examination. The frequency coincidence (or ''resonance'') can lead to greatly enhanced intensity of the Raman scattering, which facilitates the study of chemical compounds present at low concentrations. Raman scattering is usually extremely weak, since only about 1 in 10 million photons that hit a sample are scattered with a loss ( Stokes) or gain (anti-Stokes) in energy from changes in vibrational energy of the molecules in the sample; the rest of the photons are scattered with no change in energy. Resonance enhancement of Raman scattering requires the incident wavelength (usually from a laser) to be close to that of an electronic transition of the molecules. In larger molecules the change in electron density can be largely confined to one part of the molecule, a chromophore, and in these c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy or surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) is a surface-sensitive technique that enhances Raman scattering by molecules adsorbed on rough metal surfaces or by nanostructures such as plasmonic-magnetic silica nanotubes. The enhancement factor can be as much as 1010 to 1011, which means the technique may detect single molecules. History SERS from pyridine adsorbed on electrochemically roughened silver was first observed by Martin Fleischmann, Patrick J. Hendra and A. James McQuillan at the Department of Chemistry at the University of Southampton, UK in 1973. This initial publication has been cited over 6000 times. The 40th Anniversary of the first observation of the SERS effect has been marked by the Royal Society of Chemistry by the award of a National Chemical Landmark plaque to the University of Southampton. In 1977, two groups independently noted that the concentration of scattering species could not account for the enhanced signal and each p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Transform Spectroscopy
Fourier-transform spectroscopy is a measurement technique whereby spectra are collected based on measurements of the coherence of a radiative source, using time-domain or space-domain measurements of the radiation, electromagnetic or not. It can be applied to a variety of types of ''spectroscopy'' including optical spectroscopy, infrared spectroscopy ( FTIR, FT-NIRS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI), mass spectrometry and electron spin resonance spectroscopy. There are several methods for measuring the temporal coherence of the light (see: field-autocorrelation), including the continuous-wave and the pulsed Fourier-transform spectrometer or Fourier-transform spectrograph. The term "Fourier-transform spectroscopy" reflects the fact that in all these techniques, a Fourier transform is required to turn the raw data into the actual spectrum, and in many of the cases in optics involving interferometers, is based on the Wiener– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and professional digital cameras, act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochromator
A monochromator is an optical device that transmits a mechanically selectable narrow band of wavelengths of light or other radiation chosen from a wider range of wavelengths available at the input. The name is from the Greek roots ''mono-'', "single", and ''chroma'', "colour", and the Latin suffix ''-ator'', denoting an agent. Uses A device that can produce monochromatic light has many uses in science and in optics because many optical characteristics of a material are dependent on wavelength. Although there are a number of useful ways to select a narrow band of wavelengths (which, in the visible range, is perceived as a pure color), there are not as many other ways to easily select any wavelength band from a wide range. See below for a discussion of some of the uses of monochromators. In hard X-ray and neutron optics, crystal monochromators are used to define wave conditions on the instruments. Techniques A monochromator can use either the phenomenon of optical dispersion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomultiplier
A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal. Kinds of photomultiplier include: * Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for short) are members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, which are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. ** Magnetic photomultiplier, developed by the Soviets in the 1930s. ** Electrostatic photomultiplier, a kind of photomultiplier tube demonstrated by Jan Rajchman of RCA Laboratories in Princeton, NJ in the late 1930s which became the standard for all future commercial photomultipliers. The first mass-produced photomultiplier, the Type 931, was of this design and is still commercially produced today. * Silicon photomultiplier, a solid-state device converting incident photons into an electric signal. Silicon photomultiplie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)