|
Ramah (other)
Ramah may refer to: In ancient Israel * Ramathaim-Zophim, the birthplace of Samuel * Ramoth-Gilead, a Levite city of refuge * Ramah in Benjamin, mentioned in the Book of Jeremiah and also in the Gospel of Matthew * Baalath-Beer, also known as Ramoth of the South, in the tribe of Simeon * a city of Asher, which seems to be difficult to identify. Some have believed it to be the same as Rameh, southeast of Tyre * a city in Naphtali's territory. It may be the same as Khirbet Zeitun er-Rameh east of today's Rameh village Others *Camp Ramah, a number of Jewish summer camps affiliated with the Conservative Movement of Judaism *Ramah, the Hebrew acronym of Rabbi Meir Abulafia *Ramah Navajo Indian Reservation, New Mexico * Ramah, New Mexico, a town in the U.S. state of New Mexico *Ramah, Colorado, a town in the U.S. state of Colorado * Ramah, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada *Ramah, an alternate name used in the Book of Mormon for the hill Cumorah See also * Rama (other) * Ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramathaim-Zophim
Ramathaim-Zophim ( he, רמתיים־צופים), also called Ramah () and Ramatha in the Douay–Rheims Bible translation (Ramathaimsophim in the Vulgate), is a city from the Hebrew Bible, the home town and resting place of prophet Samuel. The name of the town means "the heights of the views." Identification Ramah, the home of Elkanah, Samuel's father (), the birthplace of Samuel and the seat of his authority (), the town is frequently mentioned in the history of that prophet and of David (). Here Samuel died and was buried (). The historian Josephus distinguishes between Ramathaim, "a city of the tribe of Ephraim," and Ramah, the burial place of Samuel the prophet. Ramathaim-Zophim has been tentatively identified with one of two sites. One of them is the modern Palestinian village of Nabi Samwil, the other the former village, now town, of er-Ram. Er-Ram as Ramah Ramah, according to Eusebius' '' Onomasticon'', was located 6 milestones north of Jerusalem (Ailia), opposite Beth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
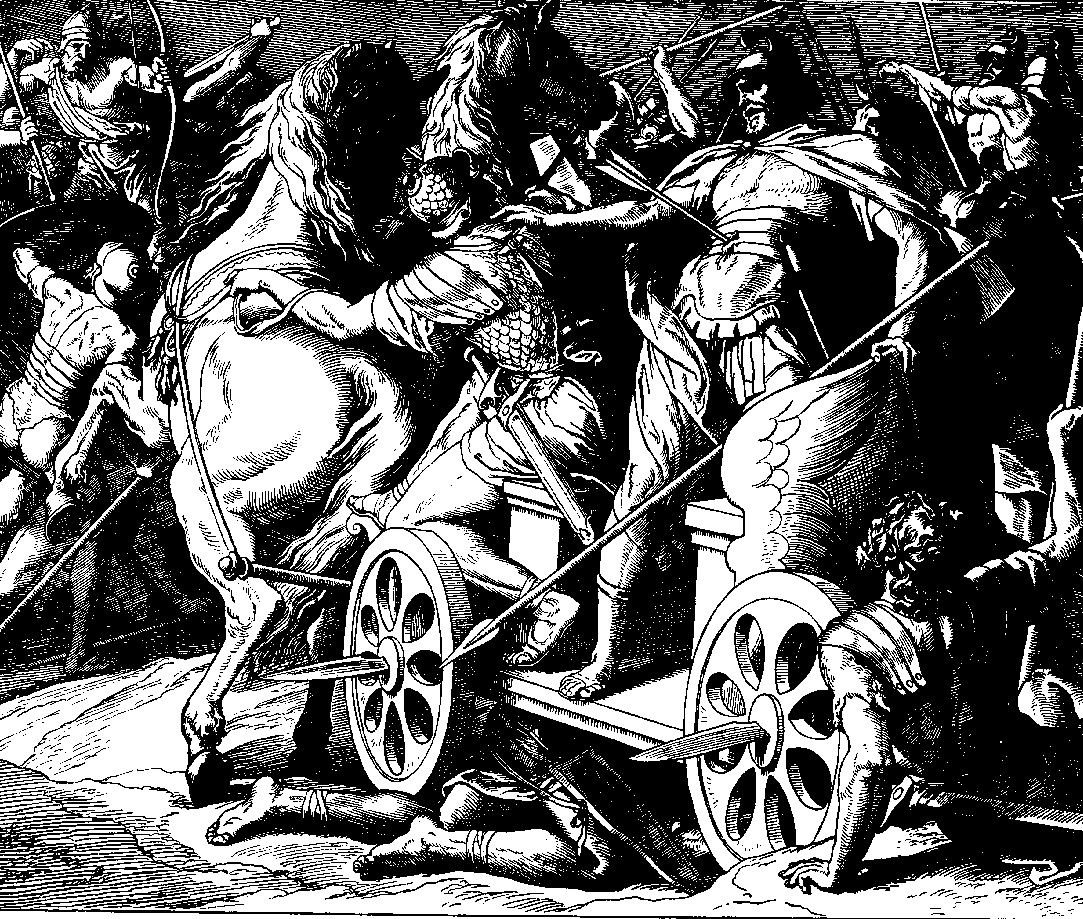
Ramoth-Gilead
Ramoth-Gilead ( he, רָמֹת גִּלְעָד, meaning "Heights of Gilead"), was a Levitical city and city of refuge east of the Jordan River in the Hebrew Bible, also called "Ramoth in Gilead" (; ; ) or "Ramoth Galaad" in the Douay–Rheims Bible. It was located in the tribal territorial allotment of the tribe of Gad. Biblical events According to (), Ramothgilead was the base of Ben-Geber, one of King Solomon's regional governors. He was responsible for ("to him belonged") the towns of Jair the son of Manasseh, in Gilead and the region of Argob in Bashan: sixty large cities with walls and bronze gate-bars. It appears to have been lost to Syria (Aram-Damascus) during the battles between the northern kingdom of Israel and Syria, as Ahab, King of Israel, proposed to go to battle to win it back. After consulting prophets about the prospects of success, Ahab went to fight for Ramoth in Gilead, aided by Jehoshaphat, King of Judah. During the battle, Ahab was wounded by an arrow. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramah In Benjamin
Ramah (from Hebrew: "height") was, according to the Hebrew Bible, a city in ancient Israel in the land allocated to the tribe of Benjamin. It was located near Gibeon and Mizpah to the West, Gibeah to the South, and Geba to the East. It has been identified with modern Er-Ram, about north of Jerusalem. Biblical accounts The city is first mentioned in , near Gibeah of Benjamin. In the Book of Judges, a Levite came traveling to Gibeah, with Ramah just ahead (). Ramathaim-zophim is the town that was home to Samuel's mother Hannah and his father Elkanah, from which they journeyed to the sanctuary at Shiloh, where Hannah prayed to God to end her barrenness and give her a child (). Ramah is mentioned in in reference to a meeting place during Samuel's rule. Ramah was later fortified by Baasha, king of the northern kingdom, in order to control access to Jerusalem (; ). Asa, king of the southern kingdom of Judah, employed Ben-Hadad I, the Syrian king, successfully to attack Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baalath-Beer
A town named Baalath-Beer is mentioned in the Masoretic Text of Joshua 19:8, which places near the end of a list of towns belonging to the Tribe of Simeon (19:1-9). Where the Masoretic Text reads "Baalath-beer Ramath-negeb", one version of the Septuagint The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond ... reads "Baalath as you come to Ramath-negeb." It is unclear which is the earlier reading. For Ramath-negeb, various biblical translations render the Hebrew ''rmt ngb'' as "Ramah of the South", "Ramah in the Negev", "Ramah of the Negev", and so on. Modern archaeologists have not agreed on whether the site of Baalath-Beer can be identified. The existing evidence is ambiguous as to whether or not Baalath-beer is the same town as Ramath-negeb, and Baalath-beer may be the same as the locati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asher
Asher ( he, אָשֵׁר ''’Āšēr''), in the Book of Genesis The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning") ..., was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Zilpah (Jacob's eighth son) and the founder of the Israelites, Israelite Tribe of Asher. Name The text of the Torah states that the name of ''Asher'' means "happy" or "blessing", implying a derivation from the Hebrew language, Hebrew term ''osher'' in two variations—''beoshri'' (meaning ''in my good fortune''), and ''ishsheruni'', which some textual criticism, textual scholars who embrace the JEDP hypothesis attribute to different sources—one to the Yahwist and the other to the Elohist. The Bible states that at his birth Leah exclaimed, "Happy am I! for the daughters will call me happy: so she called his name Asher", mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphtali
According to the Book of Genesis, Naphtali (; ) was the last of the two sons of Jacob and Bilhah (Jacob's sixth son). He was the founder of the Israelite Tribe of Naphtali. Some biblical commentators have suggested that the name ''Naphtali'' may refer to the struggle between Rachel and Leah for the favours of Jacob. Bilhah was the handmaid of Rachel, who was infertile at the time, and had persuaded Jacob to have a child with Bilhah as a proxy for having one with herself. Biblical references According to the Targum Pseudo-Jonathan, Naphtali was a swift runner, though this appears to have been inferred from the Blessing of Jacob, which equates Naphtali to a hind. However, Biblical scholars believe this to actually be a description of the tribe of Naphtali. Naphtali is listed in Deuteronomy 34.2 when God takes Moses up to the mountain of Nebo and shows him the extent of the land which he had promised to Abraham, Isaac and Jacob. See article on Tribe of Simeon for a map of the twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camp Ramah
Camp Ramah ( he, מחנה רמה, Machaneh Ramah) is a network of Jewish summer camps affiliated with the Conservative Movement. The camps operate in the United States, Canada, and Israel. All Ramah camps serve kosher food and are '' Shabbat''-observant. History During the 1940s, the Jewish Theological Seminary established Camp Ramah as a tool for furthering Jewish education. The founders, including Rabbi Ralph Simon of Chicago, envisioned an informal camp setting where Jewish youth would reconnect with the synagogue and Jewish tradition, and a new cadre of American-born Jewish leadership could be cultivated. The founders of Ramah camps were inspired by Camp Massad and Camp Cejwin. The first camp opened in Conover, Wisconsin in 1947. The program was drawn up by Moshe Davis and Sylvia Ettenberg of the JTS Teachers' Institute. In October 2007, Ettenberg was awarded ''Pras Ramah'' (the Ramah Prize) as part of Ramah's 60th anniversary celebrations. Many of the early staff wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meir Abulafia
:''Meir Abulafia is commonly known as "the Ramah" (Hebrew: רמ"ה). He should not be confused with Moses Isserles, known as "the Rema" or "the Rama" (Hebrew: רמ"א).'' Meir ben Todros HaLevi Abulafia ( ; c. 1170 – 1244), also known as the Ramah ( he, הרמ"ה) (an acronym of his Hebrew name), was a major Sephardic Talmudist and Halachic authority in medieval Spain. Biography He was the scion of a wealthy and scholarly family, the son of Todros ben Judah, to whom the physician Judah ben Isaac dedicated his poem, ''The Conflict of Wisdom and Wealth,'' published in 1214. In his 30s, he was already one of the three appointed rabbis on the Toledo Beth Din (one of the other two was Joseph ibn Migash's son, Meir). As the Spanish kings gave the Jews more self-rule, Rabbi Abulafia played a substantial role in establishing ritual regulations for Spanish Jewry. He was also the head of an important yeshiva in Toledo. He was so highly esteemed in Toledo that on his father's death in 122 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramah Navajo Indian Reservation
The Ramah Navajo Indian Reservation ( nv, Tł'ohchiní}) is a non-contiguous section of the Navajo Nation lying in parts of west-central Cibola and southern McKinley counties in New Mexico, United States, just east and southeast of the Zuni Indian Reservation. It has a land area of 230.675 sq mi (597.445 km²), over 95 percent of which is designated as off-reservation trust land. According to the 2000 census, the resident population is 2,167 persons. The Ramah Reservation's land area is less than one percent of the Navajo Nation's total area. Although part of the Navajo Nation, the Ramah Navajo Indian Reservation has had an independent history from that of the other Navajo lands. The Ramah Navajo have been recorded in this area of New Mexico since 1540, when they came to the aid of the Zuni in their defense against the Spanish conquistador Francisco Vásquez de Coronado. In the years from 1868 through the 1960s, the Ramah Navajo acted independently of the Navajo Nation. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramah, New Mexico
Ramah ( nv, – place of wild onions) is a census-designated place (CDP) in McKinley County, New Mexico. The population was 407 at the time of 2000 census and 370 at the 2010 United States Census. Geography Ramah is located at (35.135013, -108.487798). Its altitude is 6,926 feet (2,111 m). According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , all land. Surrounding countryside Established in 1876, Ramah was one of fifty locations in the New Mexico Territory settled, under the direction of Brigham Young, by Mormon pioneers and is one of only three that remain today. Ramah was originally settled for the purpose of missionary work to be carried out within the Zuni and Navajo communities. Many of the original stone houses are still standing and are a testament to the hard work and skill of Ramah's early founders. One such building has been restored and preserved as a museum to display the heritage of the valley's past. Ramah Lake was built by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramah, Colorado
The town of Ramah is a Colorado municipalities#Statutory town, Statutory Town in El Paso County, Colorado, El Paso County, Colorado, United States. The population was 123 as of the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census. According to tradition, the name is derived from India. History The area was first settled in a place called Old Zounds, which was 27 miles southeast of Kiowa. The post office, called O.Z. because the applicant just used the initials, existed until at least 1881. The post office was moved from Old Zounds to nearby Ramah in 1889. Ramah began as a small railroading town along the Rock Island Railroad in the late 1800s. It was incorporated on July 18, 1927. During its peak, it was home to several hundred residents. Eventually, by the mid-1900s, the railroad was shut down, and Ramah suffered, since the railroad connected it to Colorado Springs, forty miles to the southwest. Despite its decline, Ramah continues to exist, with ranching as the mainstay of its economy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramah, Newfoundland And Labrador
Ramah was a small mission run by the Moravian Church in northern Labrador from 1871 until 1908. It was located on Ramah Bay. Ramah Chert Ramah Bay is the site of an uncommon semi-translucent light-grey stone with dark banding called "Ramah chert". The Ramah chert outcrops in a narrow geological bed stretching from Saglek Fiord to Nachvak. At Ramah Bay the highest quality stone, for flaking chipped stone tools (mostly bifaces and projectile points), is most readily accessible. Discovered by pioneering Native American groups, which archaeologists identify as the Maritime Archaic Culture, around 7000 years ago, the stone was highly valued for its functional as well as spiritual qualities. Ramah chert was the preferred raw material for the Maritime Archaic Indians (ca. 7000 to 3500 years ago) and for succeeding populations of Dorset paleoeskimos (ca. 2200 to 800 years ago) and by the immediate ancestors of the Innu (from about 2000 years ago to contact with the Europeans in the 18t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |