|
Ramagupta
Ramagupta (IAST: Rāma-gupta; r. c. late 4th century CE), according to the Sanskrit play '' Devichandraguptam'', was an emperor of the Gupta dynasty of northern India. The surviving fragments of the play, combined with other literary evidence, suggest that he agreed to surrender his wife Dhruvadevi to a Shaka enemy: However, his brother Chandragupta II killed the Shaka enemy, and later dethroned him, marrying Dhruvadevi. The official Gupta genealogy does not mention Ramagupta, and therefore, the historicity of the ''Devichandraguptam'' narrative is debated. Several other sources refer to the events mentioned in the play, but these sources do not mention Ramagupta by name, and may be based on the play itself. Three undated inscriptions, written in a variety of the Gupta script and discovered in central India, mention a king called Ramagupta: this seems to attest the existence of a Gupta emperor named Ramagupta, although it does not conclusively prove the historicity of the ''De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devichandraguptam
''Devi-Chandraguptam'' (IAST: Devīcandraguptam) or Devi-Chandragupta is an Indian Sanskrit-language political drama attributed to Vishakhadeva, who is generally identified with Vishakhadatta. The complete text of the play is now Lost literary work, lost, but its portions survive in form of quotations in the later works. The plot also survives in form of a Persian language story, which appears to be an adaptation of the play, and is included in the 11th century text ''Majmal-ut-Tawarikh''. In the play, king Ramagupta decides to surrender his queen Dhruvadevi ("Devi") to a Indo-Scythians, Shaka enemy when besieged. Ramagupta's younger brother Chandragupta II, Chandragupta enters the enemy camp disguised as the queen, and kills the enemy ruler. The rest of the story is not clear from the surviving passages, but based on other historical evidence, it appears that in the last part of the play, Chandragupta dethrones Ramagupta and marries Dhruvadevi. The historicity of the play's narrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhruvadevi
Dhruva-devi was the queen of the Gupta dynasty, Gupta king Chandragupta II (r. c. 380 – c. 415 CE), who ruled in present-day northern India. She was the mother of his successor Kumaragupta I, and was most probably same as Dhruva-svamini, who has been mentioned as a queen of Chandragupta and the mother of prince Govindagupta in a clay seal inscription as well as the Empress consort of the Gupta Empire. According to the Sanskrit play ''Devichandraguptam, Devi-Chandraguptam'', which is now partially lost, Dhruvadevi was originally a queen of Chandragupta's elder brother Ramagupta, who decided to surrender her to a Indo-Scythians, Shaka enemy after being besieged. Chandragupta entered the enemy camp disguised as the queen, and killed the enemy. A reconstruction of the play, based on other literary and epigraphic evidence, suggests that Chandragupta later killed Ramagupta, and married Dhruva-devi. The historicity of this narrative is debated among modern historians, with some scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II (r.c. 375–415), also known by his title Vikramaditya, as well as Chandragupta Vikramaditya, was an emperor of the Gupta Empire. Modern scholars generally identify him with King Chandra of the Iron pillar of Delhi, Delhi iron pillar inscription. Special:Diff/1281091362 He continued the Samudragupta#Military campaigns & territorial expansion, expansionist policy of his father Samudragupta through military conquests and marital alliances. Historical evidence attests to his remarkable victories, which include the defeat of the Sasanian Empire, Sassanids, the Gupta–Saka Wars, conquest of the Western Kshatrapas and the vassalization of the Hephthalites, Hunas. Under the reign of Chandragupta II, the Gupta Empire reached its zenith, directly controlling a vast territory which stretched from the Oxus River in the west to the Bengal region in the east, and from the foothills of the Himalayas in the north to the Narmada River in the south. Chandragupta II expanded hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Dynasty
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian subcontinent. This period has been considered as the Golden Age of India by some historians, although this characterisation has been disputed by others. The ruling dynasty of the empire was founded by Gupta. The high points of this period are the great cultural developments which took place primarily during the reigns of Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Kumaragupta I. Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as the Mahabharata and Ramayana, were canonised during this period. The Gupta period produced scholars such as Kalidasa, Aryabhata, Varahamihira and Vatsyayana, who made significant advancements in many academic fields. Science and political administration reached new heights during the Gupta era. The period, sometimes d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', ( 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India. A military genius and a patron of arts, he is regarded among the greatest rulers in Indian history. As a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta I and the Licchavi princess Kumaradevi, he inherited a kingdom and transformed it into a vast empire through his military campaigns. His reign was marked by political expansion, administrative efficiency, and cultural patronage, particularly of Sanskrit literature and Hindu rituals. Samudragupta’s legacy as a warrior, administrator, and benefactor of scholars contributed to the golden age of the Gupta Empire. The Allahabad Pillar inscription, a ''prashasti'' (eulogy) composed by his courtier Harisena, credits him with extensive military conquests. It suggests that he defeated several kings of northern India, and annexed their territories into his empire. He also marched along the south-eastern coast of In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Gupta Emperors
The Gupta Empire (c. 319–550 CE) was a Middle kingdoms of India, classical Indian Hindu empire. The dynasty was founded by Gupta (king), Sri Gupta in late 3rd century CE, but Chandragupta I is credited as real founder of empire. The empire was lasted until 550 CE. The factors for the downfall of the empire were Alchon Huns, Hunnic invasions, dynastic dissensions, taxes, internal rebellions and decentralization.Raghu Vamsa v 4.60–75 The Gupta Empire was vast and covered most of the Indian subcontinent. Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Skandagupta were some of its mightiest rulers. It brought about a golden era to the region, resulting in technological advancements and cultural improvements. Gupta emperors generally used the title Maharajadhiraja. Family tree List of rulers See also * Gupta Empire * Gupta era * Later Gupta dynasty * Middle kingdoms of India * List of monarchs of Magadha Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandraprabha
Chandraprabha () or Chandranatha is the eighth Tirthankara of of Jainism in the present age (). According to traditional accounts, he was born to King Mahasena and Queen Lakshmana Devi at Chandrapuri to the Ikshvaku dynasty. According to Jain texts, his birth-date was the twelfth day of the Posh Krishna month of the Indian calendar. He is said to have become a Siddha#Jainism, siddha, a liberated soul which has destroyed all of its Karma in Jainism, karma. Jain biography Chandraprabha was the eighth Jain ''tirthankara, Tīrthankara'' of the present age (''avasarpini''). He was born to King Mahasena and Queen Lakshmana Devi at Chandrawati Jain temple, Chandrapuri, Varanasi on 12th day month Pausa in the Ikshvaku clan. Nine months before the birth of ''Chandraprabha'', Queen ''Lakshmana Devi '' dreamt the sixteen most Auspicious dreams in Jainism, auspicious dreams. Mahasena named Tirthankar Chandraprabha because of his complexion was white as moon. According to Uttarapurana, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skandagupta
Skandagupta (Gupta script: ''Ska-nda-gu-pta'', r. –467) was a Gupta Empire, Gupta Emperor of India. His Bhitari pillar inscription of Skandagupta, Bhitari pillar inscription suggests that he restored the Gupta power by defeating his enemies, who may have been rebels or foreign invaders. He repulsed an invasion by the Indo-Hephthalites (known as Huna people, Hunas in India), probably the Kidarites. He seems to have maintained control of his inherited territory, and is generally considered the last of the great Gupta Emperors. The Gupta genealogy after him is unclear, but he was most probably succeeded by Purugupta, who appears to have been his younger half-brother. Early life Skandagupta was a son of the Gupta emperor Kumaragupta I. His mother may have been a junior queen or a concubine of Kumaragupta. This theory is based on the fact that Skandagputa's inscriptions mention the name of his father, but not of his mother. For example, Skandagupta's Bhitari pillar inscription o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Govindagupta
Govindagupta (fl. 4th-5th century) was a Gupta prince of ancient India. He was a son of Chandragupta II and Dhruvadevi, and a brother of Kumaragupta. Both Chandragupta and Kumaragupta held the Gupta thrones at different times. The Basarh clay seal of Govindagupta describes him as a ''Maharaja'' ("great king"), and the Mandsaur inscription of his son describes him as a powerful man who destroyed several kings. This has led some historians to theorize that Govindagupta also held the Gupta throne for a brief period. However, the general view among modern historians is that Govindagupta was never a sovereign ruler: he may have been a governor of the Tirabhukti province within the Gupta empire. Sources of information Basarh clay seal According to a clay seal discovered at Basarh, among the ruins of the ancient Vaishali city, Govindagupta was a son of the Gupta emperor Chandragupta II and his wife Dhruva-devi. The clay seal names queen Dhruva-svamini (presumably same as Dh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
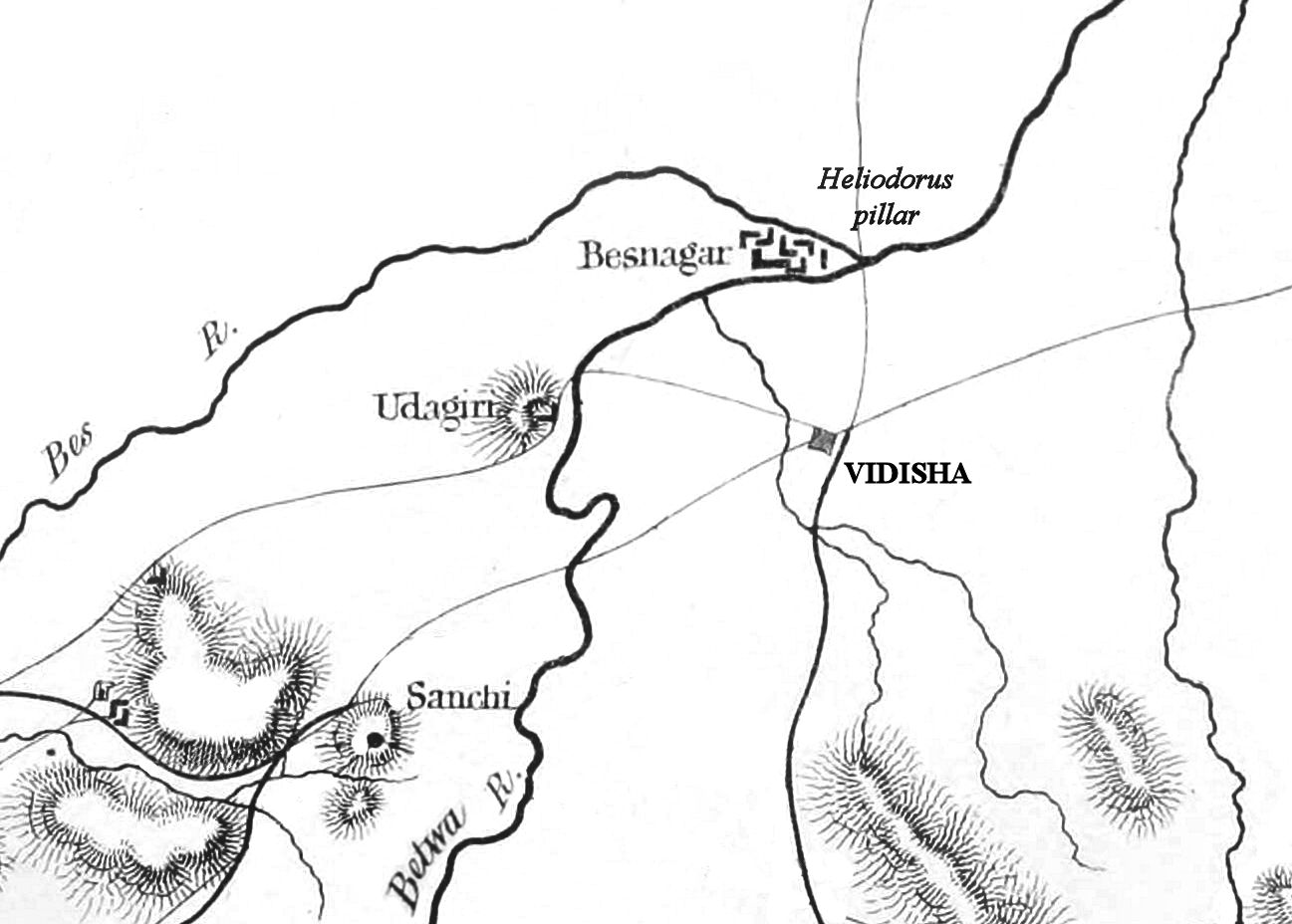
Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar and Bhaddilpur in ancient times) is a city in Indian state of Madhya Pradesh and the administrative headquarters of Vidisha district. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from the nearby river "Bais", mentioned in the Puranas. The district was created as Bhilsa District in 1904 by joining the tehsils of Vidisha (also known as Bhilsa) and Basoda (but not Basoda State) which were then part of Gwalior state. After India's independence in 1947, the former princely state of Gwalior became part of Madhya Bharat state, which was formed in 1948. Vidishā was the administrative headquarters of Bhelsa, or Bhilsa, during the Medieval period. It was renamed Vidisha in 1956. Vidisha is also amongst the 112 Aspirational District in the Aspirational District Programme launched by NITI Aayog in 2018. Towards the seventh or eighth century, Bhadravati was ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the writing and the writers. Specifically excluded from epigraphy are the historical significance of an epigraph as a document and the artistic value of a literature, literary composition. A person using the methods of epigraphy is called an ''epigrapher'' or ''epigraphist''. For example, the Behistun inscription is an official document of the Achaemenid Empire engraved on native rock at a location in Iran. Epigraphists are responsible for reconstructing, translating, and dating the trilingual inscription and finding any relevant circumstances. It is the work of historians, however, to determine and interpret the events recorded by the inscription as document. Often, epigraphy and history are competences practised by the same person. Epigraphy is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |