|
Rail Transport In Hungary
Rail transport in Hungary is mainly owned by the national rail company MÁV, with a significant portion of the network owned and operated by GySEV. The railway network consists of 7,893 km, its gauge is and 3,060 km are electrified. Hungary is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC country code for Hungary is 55. Statistics * Railway lines total: ** Standard gauge: ** Broad gauge: of ** Narrow gauge: Note: The standard and broad gauge railways are operated by the State Railways and also the following narrow gauge railways: Nyíregyháza–Balsai Tisza part/ Dombrád; Balatonfenyves–Somogyszentpál; Kecskemét–Kiskunmajsa/Kiskőrös and the Children's Railway in Budapest. All the other narrow gauge railways are run by State Forest companies or local non-profit organisations. See also Narrow gauge railways in Hungary. Financial performance and corporate statistics * Revenue = 372,549 million Ft (2014) * Net income = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian State Railways
Hungarian State Railways ( hu, Magyar Államvasutak, MÁV) is the Hungarian national railway company, with divisions "MÁV START Zrt." (passenger transport), "MÁV-Gépészet Zrt." (maintenance), "MÁV-Trakció Zrt." and "MÁV Cargo Zrt" (freight transport). The head office is in Budapest. History 1846–1918 Construction of Hungary's first railway line began in the second half of 1844. The first steam locomotive railway line was opened on 15 July 1846 between Pest and Vác. This date is regarded as the birth date of the Hungarian railways. The Romantic poet Sándor Petőfi rode on the first train and wrote a poem predicting that rails would connect Hungary like blood vessels in the human body. After the failed revolution, the existing lines were nationalized by the Austrian State and new lines were built. As a result of the Austro-Sardinian War in the late 1850s, all these lines were sold to Austrian private companies. During this time the company of Ábrahám ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiskunmajsa
Kiskunmajsa is a town in Bács-Kiskun county, Hungary. Twin towns – sister cities Kiskunmajsa is twinned Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to: * In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so; * Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning * Twinning inst ... with: * Bačka Topola, Serbia * Bad Schönborn, Germany * Baiyin, China * Gheorgheni, Romania * Lommatzsch, Germany * Lubliniec, Poland * Ukmergė, Lithuania Gallery File:Kiskunmajsa2.jpg File:Kiskunmajsa3.jpg File:Gyógyfürdő- és Élményfürdő, Kiskunmajsa4.jpg References External links * in Hungarian {{DEFAULTSORT:Kiskunmajsa Populated places in Bács-Kiskun County Towns in Hungary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
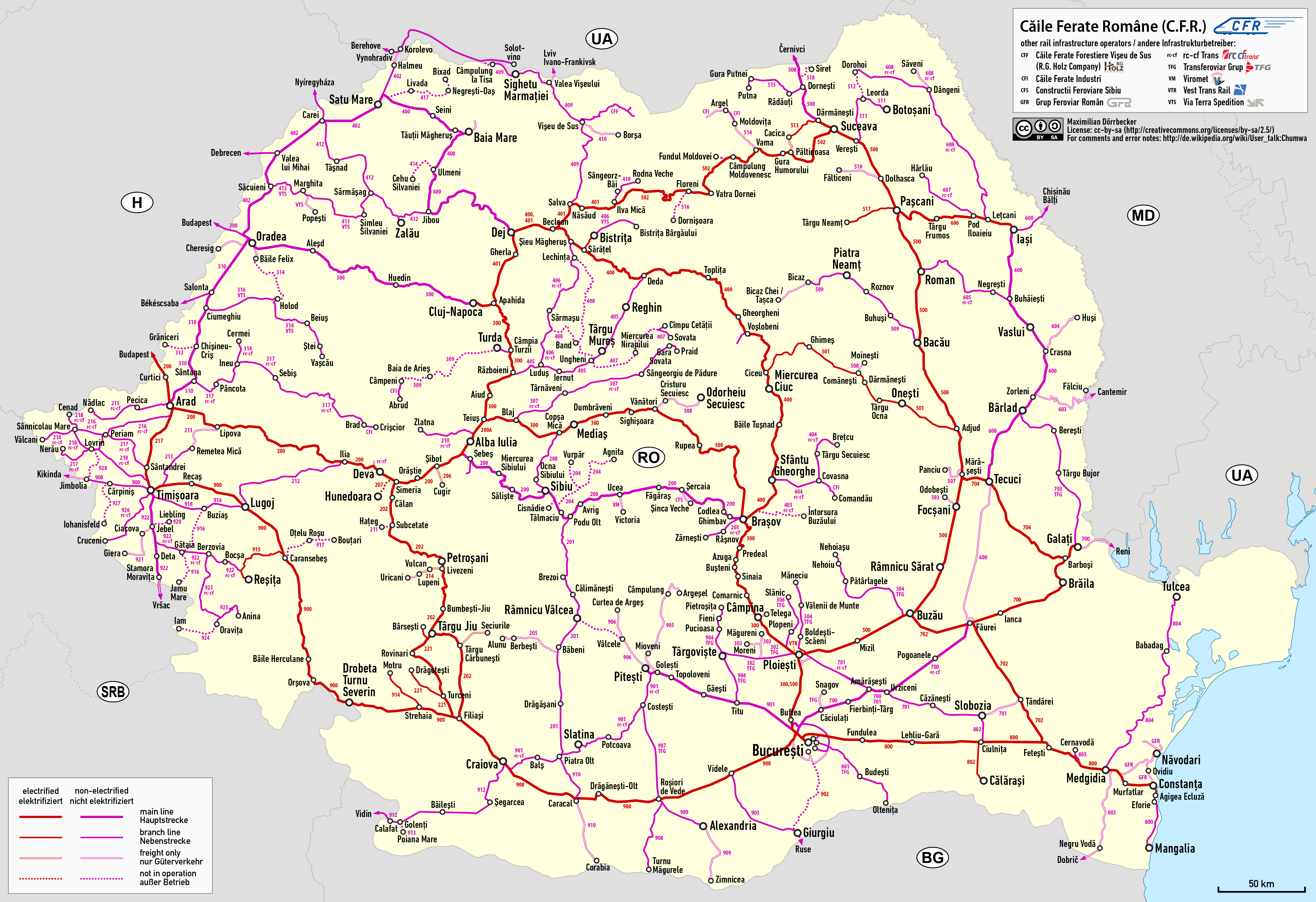
Rail Transport In Romania
The first railway in the Kingdom of Romania opened in 1869 and linked Bucharest and Giurgiu. The first railway on electric current in the current Romanian territory opened in 1854, between Oravița and Baziaș in Banat, right next to the border with Serbia; however, that region was under the administration of the Austrian Empire at the time, and became part of Romania after World War I. Since then, the Romanian railway network has been significantly expanded, and is now the fourth largest in Europe by total track length, comprising . Of these, some are electrified. The route length is . Romania's railway system is inadequately-connected and one of the least durable railway systems globally.NewsroomFeatured - "Railway reform": Destroy half of the national railroad network and fire 10,000 people Romania Business Review, retrieved on 9 June 2019Archived at the wayback machine "Romania’s Government issued a memorandum regarding 'methods of increasing efficiency in the country’ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Serbia
Serbian Railways ( sr, Железнице Србије/''Železnice Srbije'', abbr. ŽS or ЖС) is a Serbian engineering and technical consulting company based in Belgrade, Serbia. In 2015, the Government of Serbia established three new companies which took over Serbian Railways' former jurisdictions: Srbija Voz (passenger transport), Srbija Kargo (cargo transport) and Serbian Railways Infrastructure (infrastructure management). Since then, Serbian Railways continued with modified business activity: engineering and technical consulting, consulting activities in the field of information technology and other information technology services, buying and selling real estate, rental and management activities, accounting, bookkeeping and auditing activities, tax advisory services, technical testing and analysis, rental and leasing of other machinery, equipment of non-material goods, activities of the museums, galleries and collections. Serbia is a member of the International Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Railway Electrification Systems
This is a list of the power supply systems that are, or have been, used for tramway and railway electrification systems. Note that the voltages are nominal and vary depending on load and distance from the substation. Many modern trams and trains use on-board solid-state electronics to convert these supplies to run three-phase AC induction motors. Tram electrification systems are listed here. Key to the tables below * Volts: voltage or volt * Current: ** DC = direct current ** # Hz = frequency in hertz (alternating current (AC)) *** AC supplies are usually single-phase (1Ø) except where marked three-phase (3Ø). * Conductors: ** overhead line or ** conductor rail, usually a third rail to one side of the running rails. Conductor rail can be: *** top contact: oldest, least safe, most affected by ice, snow, rain and leaves. Protection boards are being installed on most top contact systems, which increases safety and reduces these affections. *** side contact: newer, safer, less af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Croatia
Croatian Railways ( hr, Hrvatske željeznice; abbreviated as HŽ) is the national railway company of Croatia. Croatia is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Croatia is 78. The Croatian rail network carried 20.270 million passengers in 2018. Railway network , the Croatian railway system consists of 2,617 km of rails (of which 275 km is double track). 970 km of track (37.1% of the network) is electrified. There are several major railway routes in the country: * (via Ljubljana, Slovenia) from Dobova via Zagreb, Slavonski Brod and Vinkovci to Tovarnik (and onwards to Belgrade, Serbia), with a connection in Strizivojna–Vrpolje towards Osijek * from Zagreb to Koprivnica * from Zagreb to Oštarije and Rijeka * from Oštarije to Split * from Zagreb to Sisak * from Zagreb to Varaždin There are other routes to Slovenia, Hungary, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Serbia, as well as regular overnight trains to Austria (name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Slovenia
Slovenian Railways ( sl, Slovenske železnice, ''SŽ'') is the state railway company of Slovenia, created in 1991. Slovenia is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Slovenia is 79. History What is now Slovenia received its first railway connection in the 1840s, when the Austrian Empire built a railway connection – Südliche Staatsbahn or Austrian Southern Railway – between its capital, Vienna, and its major commercial port, Trieste. Thus, Maribor was connected by railway to Graz in 1844. The stretch was extended via Pragersko to Celje in 1846, and further via Zidani Most to Ljubljana in 1849. A double-track line was continued via Postojna, Pivka, and Divača, finally reaching Trieste in 1857. Before World War I, numerous other railways were built. In 1860, Pragersko was connected to Ormož and further to Čakovec, Croatia, thus connecting the Austrian and the Hungarian parts of the empire. In 1862, a single-track railway (expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 KV AC Railway Electrification
Railway electrification systems using at are used on transport railways in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Sweden, and Norway. The high voltage enables high power transmission with the lower frequency reducing the losses of the traction motors that were available at the beginning of the 20th century. Railway electrification in late 20th century tends to use AC systems which has become the preferred standard for new railway electrifications but extensions of the existing networks are not completely unlikely. In particular, the Gotthard Base Tunnel (opened on 1 June 2016) still uses 15 kV, 16.7 Hz electrification. Due to high conversion costs, it is unlikely that existing systems will be converted to despite the fact that this would reduce the weight of the on-board step-down transformers to one third that of the present devices. History The first electrified railways used series-wound DC motors, first at 600 V and then 1,500 V. Areas with 3 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Austria
Rail transport in Austria is mainly owned by the national rail company ÖBB. The railway network consists of 6,123 km, its gauge is and 3,523 km are electrified. Austria is a member of the International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Austria is 81. History The history of Austrian rail transport starts with the Reisszug, a private, horse-drawn funicular serving Hohensalzburg Fortress. Built at the end of the 15th century and first documented in 1515, it is the oldest known funicular in the world, and possibly the oldest existing railway line. In the 19th century, after a building of several horse tramways, it opened in 1837 the '' Nordbahn'' line Vienna- Břeclav. The Imperial Royal Austrian State Railways, a company serving Austrian side of Austria-Hungary, was created in 1884 and in 1923, some years after the dissolution of the empire, it was founded the national company "ÖBB". In 1998 the market was liberalised and had one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Ownership
State ownership, also called government ownership and public ownership, is the ownership of an industry, asset, or enterprise by the state or a public body representing a community, as opposed to an individual or private party. Public ownership specifically refers to industries selling goods and services to consumers and differs from public goods and government services financed out of a government's general budget. Public ownership can take place at the national, regional, local, or municipal levels of government; or can refer to non-governmental public ownership vested in autonomous public enterprises. Public ownership is one of the three major forms of property ownership, differentiated from private, collective/cooperative, and common ownership. In market-based economies, state-owned assets are often managed and operated as joint-stock corporations with a government owning all or a controlling stake of the company's shares. This form is often referred to as a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Income
In business and accounting Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial and non financial information about economic entities such as businesses and corporations. Accounting, which has been called the "language ..., net income (also total comprehensive income, net earnings, net profit, bottom line, sales profit, or credit sales) is an entity's income minus cost of goods sold, expenses, depreciation and Amortization (accounting), amortization, interest, and taxes for an accounting period. It is computed as the residual of all revenues and gains less all expenses and losses for the period,Stickney, et al. (2009) Financial Accounting: An Introduction to Concepts, Methods, and Uses. Cengage Learning and has also been defined as the net increase in Equity (finance), shareholders' equity that results from a company's operations.Needles, et al. (2010) Financial Accounting. Cengage Learning. It is different from gross in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Forint
The forint ( sign Ft; code HUF) is the currency of Hungary. It was formerly divided into 100 fillér, but fillér coins are no longer in circulation. The introduction of the forint on 1 August 1946 was a crucial step in the post-World War II stabilisation of the Hungarian economy, and the currency remained relatively stable until the 1980s. Transition to a market economy in the early 1990s adversely affected the value of the forint; inflation peaked at 35% in 1991. Between 2001 and 2022, inflation was in single digits, and the forint has been declared fully convertible. In May 2022, inflation reached 10.7% amid the war in Ukraine and economic uncertainty. As a member of the European Union, the long-term aim of the Hungarian government may be to replace the forint with the euro, although under the current government there is no target date for adopting the euro. History The forint's name comes from the city of Florence, where gold coins called '' fiorino d'oro'' were minte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |