|
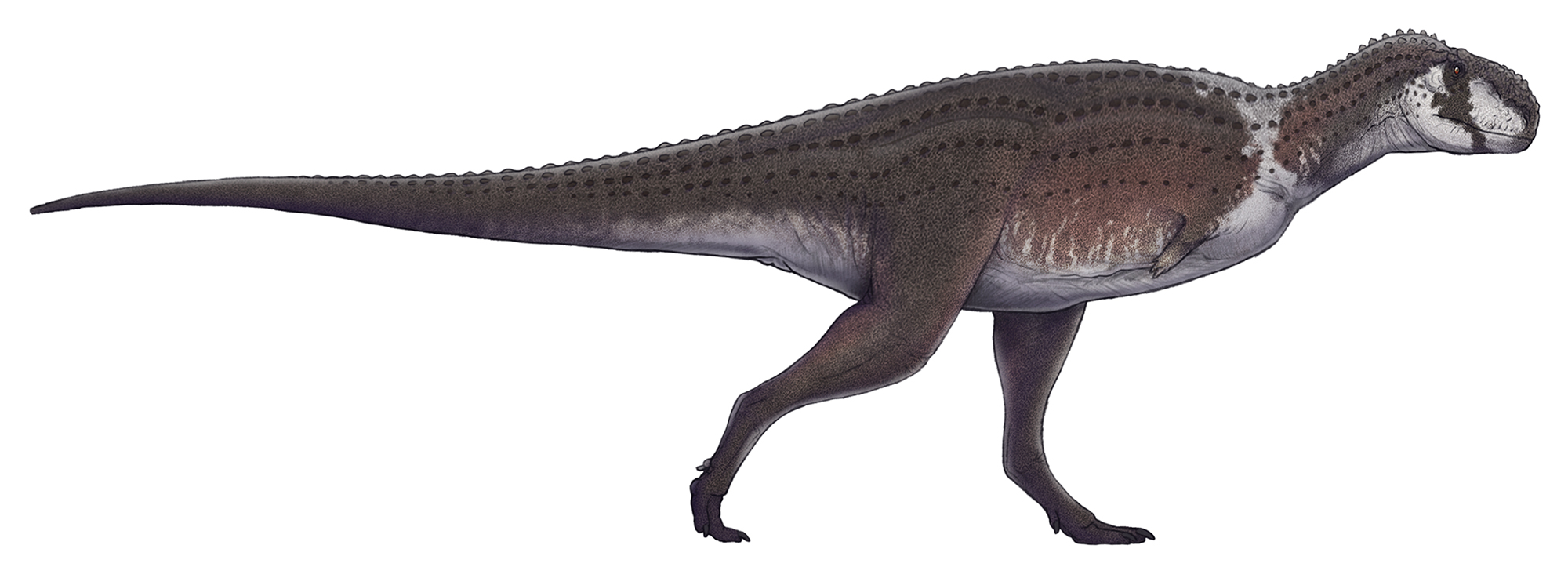
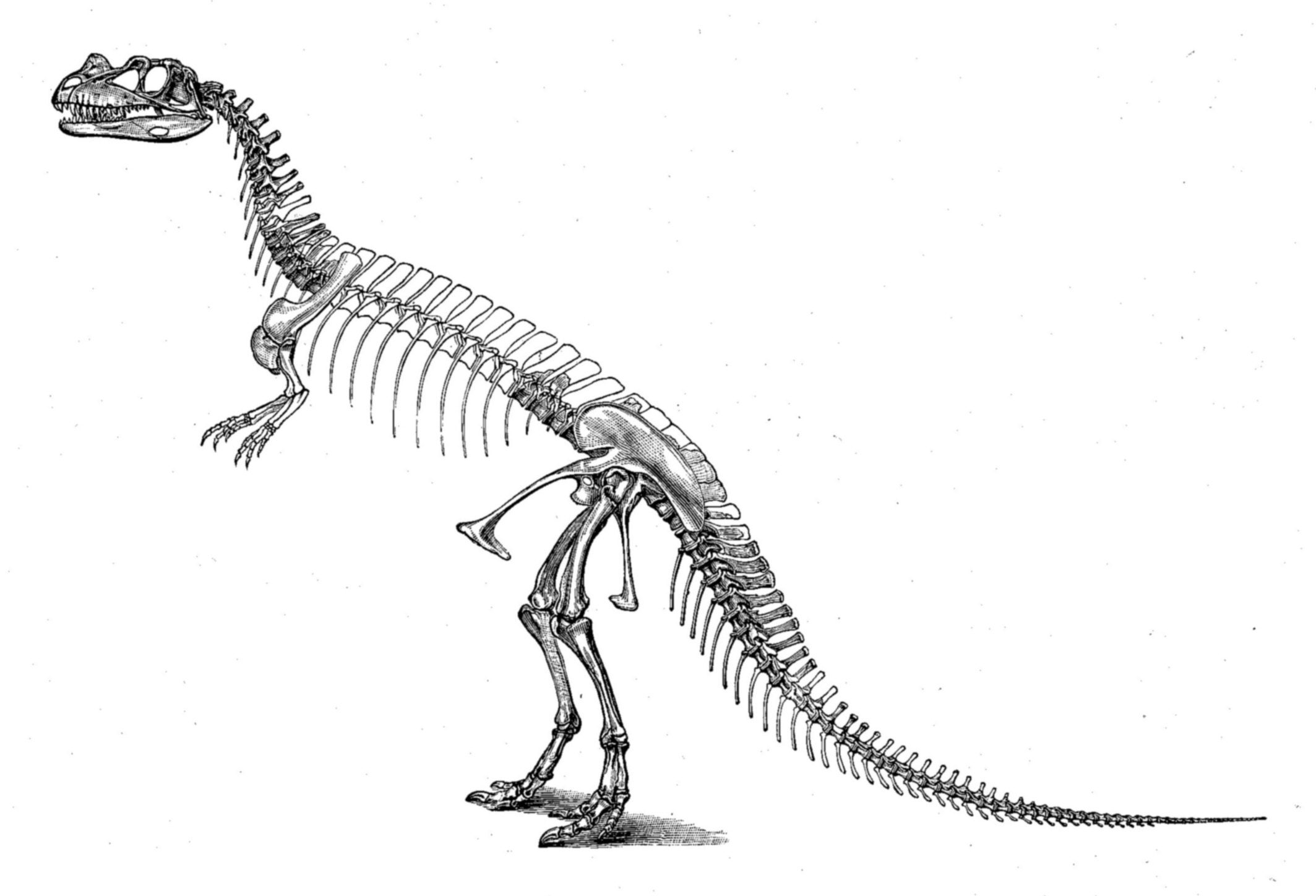
Rahiolisaurus Gujaratensis
''Rahiolisaurus'' is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur which existed in India during the Late Cretaceous period. It was described in 2010, based on fossils recovered from the Lameta Formation in the Indian state of Gujarat. These fossils include elements from at least seven different individuals and are believed to have been from the Maastrichtian stage, sometime between and million years ago, making it one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known in the fossil record. Despite representing a variety of different growth stages, all recovered fossils from the locality indicate a single species, the type species ''Rahiolisaurus gujaratensis''. Discovery and naming During two expeditions, one in 1995 and the other in 1997, numerous remains of abelisaurids were recovered from a single quarry 50 square metres in area. The collected remains included cervical, dorsal, sacral, and caudal vertebrae, portions of pectoral and pelvic girdles, and several hind limb bones. Because o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majungasaurinae
Majungasaurinae (after ''Majungasaurus'', itself named after the city of Mahajanga in Madagascar) is a subfamily of large carnivorous theropods from the Upper Cretaceous, found in Madagascar, India, and France. It is a subgroup within the theropod family Abelisauridae, a Gondwanan clade known for their thick and often horned skulls and vestigial arms. The two subfamilies of Abelisauridae are Carnotaurinae, best known from the South American ''Carnotaurus'', and Majungasaurinae, consisting of Madagascar’s ''Majungasaurus'' and its closest relatives. Their ancestors emerged in the Middle Jurassic, and the clade lasted until the Upper Cretaceous. The majungasaurines were mid-sized, bipedal predators, but relatively slow moving. Their stout legs were built for striding, not running. They had tall, deep heads with powerful jaws, but small forearms without carpals in the wrists. Because of their slow gait and small arms, they likely preyed upon the larger, slower sauropods rather th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnotaurus DB 2 White Background
''Carnotaurus'' (; ) is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period, probably sometime between 71 and 69 million years ago. The only species is ''Carnotaurus sastrei''. Known from a single well-preserved skeleton, it is one of the best-understood theropods from the Southern Hemisphere. The skeleton, found in 1984, was uncovered in the Chubut Province of Argentina from rocks of the La Colonia Formation. ''Carnotaurus'' is a derived member of the Abelisauridae, a group of large theropods that occupied the large predatorial niche in the southern landmasses of Gondwana during the late Cretaceous. Within the Abelisauridae, the genus is often considered a member of the Brachyrostra, a clade of short-snouted forms restricted to South America. ''Carnotaurus'' was a lightly built, bipedal predator, measuring in length and weighing . As a theropod, ''Carnotaurus'' was highly specialized and distinctive. It had thick horns above the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnotaurus
''Carnotaurus'' (; ) is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period, probably sometime between 71 and 69 million years ago. The only species is ''Carnotaurus sastrei''. Known from a single well-preserved skeleton, it is one of the best-understood theropods from the Southern Hemisphere. The skeleton, found in 1984, was uncovered in the Chubut Province of Argentina from rocks of the La Colonia Formation. ''Carnotaurus'' is a derived member of the Abelisauridae, a group of large theropods that occupied the large predatorial niche in the southern landmasses of Gondwana during the late Cretaceous. Within the Abelisauridae, the genus is often considered a member of the Brachyrostra, a clade of short-snouted forms restricted to South America. ''Carnotaurus'' was a lightly built, bipedal predator, measuring in length and weighing . As a theropod, ''Carnotaurus'' was highly specialized and distinctive. It had thick horns above the eyes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnotaurinae
Carnotaurinae is a subfamily of the theropod dinosaur family Abelisauridae. It includes the dinosaurs ''Aucasaurus'' (from Argentina), ''Carnotaurus'' (from Argentina). The group was first proposed by American paleontologist Paul Sereno in 1998, defined as a clade containing all abelisaurids more closely related to ''Carnotaurus'' than to ''Majungasaurus''. Classification *Subfamily Carnotaurinae **Brachyrostra ***''Ekrixinatosaurus'' (Argentina) ***''Elemgasem'' (Argentina) ***''Guemesia'' (Argentina) ***''Ilokelesia'' (Argentina) ***''Skorpiovenator'' (Argentina) ***''Thanos'' (Brazil) *** Furileusauria ****?'' Niebla'' (Argentina) ****'' Llukalkan'' (Argentina) ****'' Viavenator'' (Argentina) ****''Pycnonemosaurus'' (Brazil) ****''Quilmesaurus'' (Argentina) ****Carnotaurini *****''Carnotaurus'' (Argentina) ***** Abelisaurinae ******''Aucasaurus'' (Argentina) ******'' Abelisaurus'' (Argentina) Phylogeny In 2008, Canale ''et al.'' published a phylogenetic analysis focusing on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelisauridae
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are found on the modern continents of Africa and South America, as well as on the Indian subcontinent and the island of Madagascar. Isolated teeth were found in the Late Jurassic of Portugal, and the Late Cretaceous genera '' Tarascosaurus'' and ''Arcovenator'' have been described in France. Abelisaurids first appear in the fossil record of the early middle Jurassic period, and at least two genera (the Moroccan ''Chenanisaurus'' and the Madagascan ''Majungasaurus'') survived until the end of the Mesozoic era 66 million years ago. Like most theropods, abelisaurids were carnivorous bipeds. They were characterized by stocky hind limbs and extensive ornamentation of the skull bones, with grooves and pits. In many abelisaurids, such as ''Carnotaurus'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noasauridae
Noasauridae is an extinct family of theropod dinosaurs belonging to the group Ceratosauria. They were closely related to the short-armed abelisaurids, although most noasaurids had much more traditional body types generally similar to other theropods. Their heads, on the other hand, had unusual adaptations depending on the subfamily. 'Traditional' noasaurids, sometimes grouped in the subfamily Noasaurinae, had sharp teeth which splayed outwards from a downturned lower jaw. The most complete and well-known example of these kinds of noasaurids was ''Masiakasaurus knopfleri'' from Madagascar. Another group, Elaphrosaurinae, has also been placed within Noasauridae by some studies. Elaphrosaurines developed toothless jaws and herbivorous diets, at least as adults. The most complete and well known elaphrosaurine was ''Limusaurus inextricabilis''. At least some noasaurids had pneumatised cervical vertebrae.Arthur Souza Brum, Elaine Batista Machado, Diogenes de Almeida Campos & Alexa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratosaurus Nasicornis DB
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Greek κέρας/κέρατος, ' meaning "horn" and σαῦρος ' meaning "lizard") was a carnivorous theropod dinosaur in the Late Jurassic period ( Kimmeridgian to Tithonian). The genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh based on a nearly complete skeleton discovered in Garden Park, Colorado, in rocks belonging to the Morrison Formation. The type species is ''Ceratosaurus nasicornis''. The Garden Park specimen remains the most complete skeleton known from the genus, and only a handful of additional specimens have been described since. Two additional species, ''Ceratosaurus dentisulcatus'' and ''Ceratosaurus magnicornis'', were described in 2000 from two fragmentary skeletons from the Cleveland-Lloyd Quarry of Utah and from the vicinity of Fruita, Colorado. The Valid name (zoology), validity of these additional species has been questioned, however, and all three skeletons possibly represent different gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratosaurus
''Ceratosaurus'' (from Ancient Greek, Greek κέρας/κέρατος, ' meaning "horn" and wikt:σαῦρος, σαῦρος ' meaning "lizard") was a carnivorous Theropoda, theropod dinosaur in the Late Jurassic Period (geology), period (Kimmeridgian to Tithonian). The genus (biology), genus was first described in 1884 by American paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh based on a nearly complete skeleton discovered in Garden Park, Colorado, in rocks belonging to the Morrison Formation. The type species is ''Ceratosaurus nasicornis''. The Garden Park specimen remains the most complete skeleton known from the genus, and only a handful of additional specimens have been described since. Two additional species, ''Ceratosaurus dentisulcatus'' and ''Ceratosaurus magnicornis'', were described in 2000 from two fragmentary skeletons from the Cleveland-Lloyd Dinosaur Quarry, Cleveland-Lloyd Quarry of Utah and from the vicinity of Fruita, Colorado. The Valid name (zoology), validity of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratosauria
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with ''Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, ''Saltriovenator'', dates to the earliest part of the Jurassic, around 199 million years ago. According to the majority of the latest research, Ceratosauria includes three major clades: Ceratosauridae, Noasauridae, and Abelisauridae, found primarily (though not exclusively) in the Southern Hemisphere. Originally, Ceratosauria included the above dinosaurs plus the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic Coelophysoidea and Dilophosauridae, implying a much earlier divergence of ceratosaurs from other theropods. However, most recent studies have shown that coelophysoids and dilophosaurids do not form a natural group with other ceratosaurs, and are excluded from this group. Ceratosauria derives its names from the type species, ''Ceratosaurus nasicornis'', described by O.C. Marsh in 1884. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Hopping
Leapfrogging, also known as island hopping, was a military strategy employed by the Allies in the Pacific War against the Empire of Japan during World War II. The key idea is to bypass heavily fortified enemy islands instead of trying to capture every island in sequence en route to a final target. The reasoning is that those islands can simply be cut off from their supply chains (leading to their eventual capitulation) rather than needing to be overwhelmed by superior force, thus speeding up progress and reducing losses of troops and materiel. Background By the late 19th century, the U.S. had several interests in the western Pacific to defend; namely, access to the Chinese market, and its colonies – the Philippines and Guam – which the U.S. had gained as a result of the Spanish–American War (1898). After Japan's victories in the Sino-Japanese War (1894–95) and the Russo-Japanese War of 1904, the U.S. began to regard Japan as a potential threat to its interests in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antorbital Fenestra
An antorbital fenestra (plural: fenestrae) is an opening in the skull that is in front of the eye sockets. This skull character is largely associated with archosauriforms, first appearing during the Triassic Period. Among extant archosaurs, birds still possess antorbital fenestrae, whereas crocodylians have lost them. The loss in crocodylians is believed to be related to the structural needs of their skulls for the bite force and feeding behaviours that they employ.Preushscoft, H., Witzel, U. 2002. Biomechanical Investigations on the Skulls of Reptiles and Mammals. Senckenbergiana Lethaea 82:207–222.Rayfield, E.J., Milner, A.C., Xuan, V.B., Young, P.G. 2007. Functional Morphology of Spinosaur "Crocodile Mimic" Dinosaurs. JVP. 27(4):892–901. In some archosaur species, the opening has closed but its location is still marked by a depression, or fossa, on the surface of the skull called the antorbital fossa. The antorbital fenestra houses a paranasal sinus that is confluent with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |