|
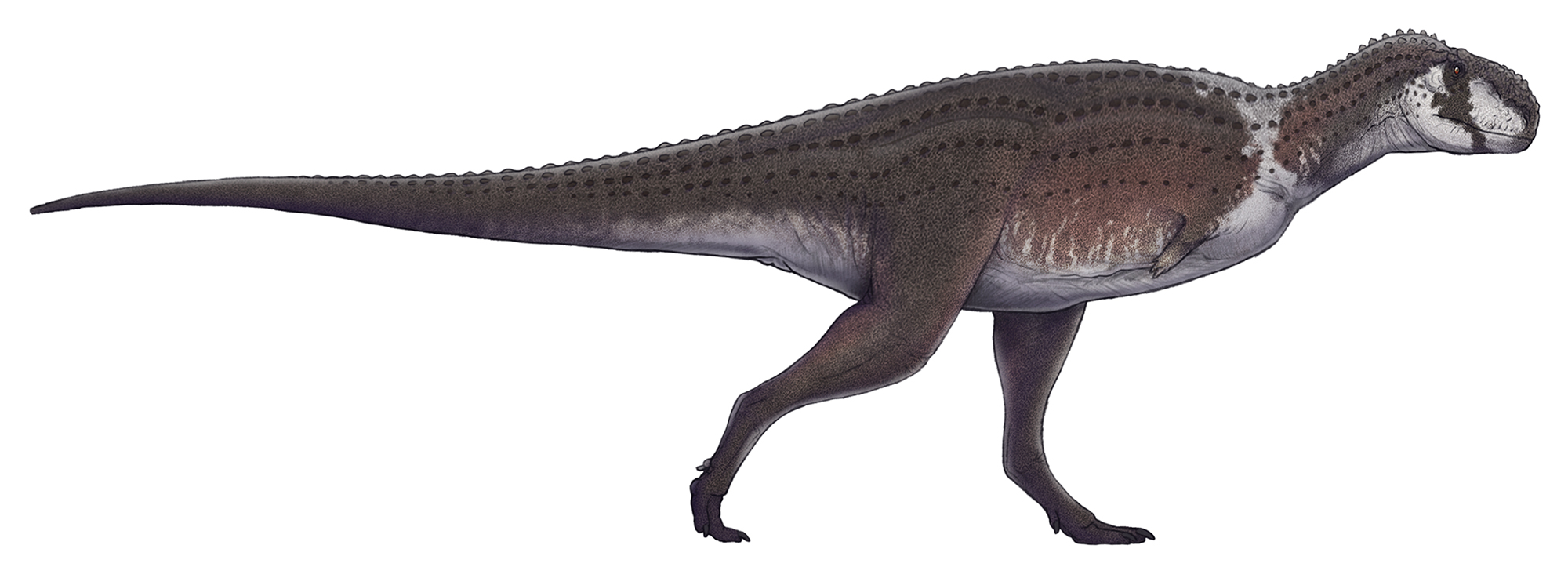
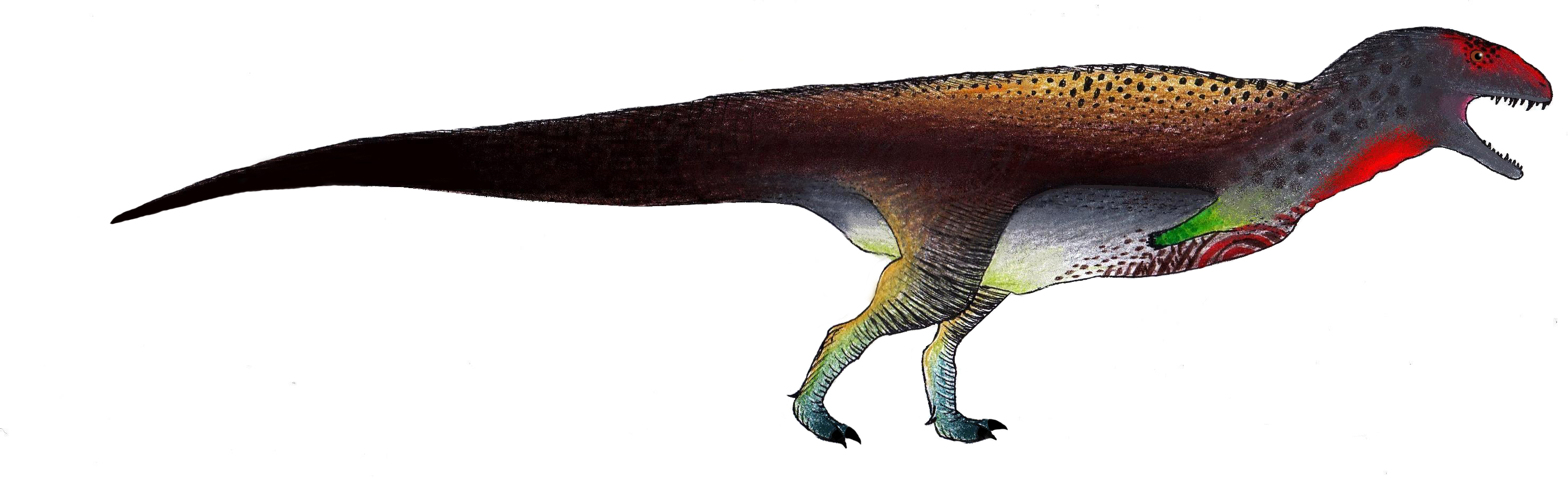
Rahiolisaurus
''Rahiolisaurus'' is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur which existed in India during the Late Cretaceous period. It was described in 2010, based on fossils recovered from the Lameta Formation in the Indian state of Gujarat. These fossils include elements from at least seven different individuals and are believed to have been from the Maastrichtian stage, sometime between and million years ago, making it one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known in the fossil record. Despite representing a variety of different growth stages, all recovered fossils from the locality indicate a single species, the type species ''Rahiolisaurus gujaratensis''. Discovery and naming During two expeditions, one in 1995 and the other in 1997, numerous remains of abelisaurids were recovered from a single quarry 50 square metres in area. The collected remains included cervical, dorsal, sacral, and caudal vertebrae, portions of pectoral and pelvic girdles, and several hind limb bones. Because o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rahiolisaurus Size
''Rahiolisaurus'' is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur which existed in India during the Late Cretaceous period. It was described in 2010, based on fossils recovered from the Lameta Formation in the Indian state of Gujarat. These fossils include elements from at least seven different individuals and are believed to have been from the Maastrichtian stage, sometime between and million years ago, making it one of the last non-avian dinosaurs known in the fossil record. Despite representing a variety of different growth stages, all recovered fossils from the locality indicate a single species, the type species ''Rahiolisaurus gujaratensis''. Discovery and naming During two expeditions, one in 1995 and the other in 1997, numerous remains of abelisaurids were recovered from a single quarry 50 square metres in area. The collected remains included cervical, dorsal, sacral, and caudal vertebrae, portions of pectoral and pelvic girdles, and several hind limb bones. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majungasaurinae
Majungasaurinae (after ''Majungasaurus'', itself named after the city of Mahajanga in Madagascar) is a subfamily of large carnivorous theropods from the Upper Cretaceous, found in Madagascar, India, and France. It is a subgroup within the theropod family Abelisauridae, a Gondwanan clade known for their thick and often horned skulls and vestigial arms. The two subfamilies of Abelisauridae are Carnotaurinae, best known from the South American ''Carnotaurus'', and Majungasaurinae, consisting of Madagascar’s ''Majungasaurus'' and its closest relatives. Their ancestors emerged in the Middle Jurassic, and the clade lasted until the Upper Cretaceous. The majungasaurines were mid-sized, bipedal predators, but relatively slow moving. Their stout legs were built for striding, not running. They had tall, deep heads with powerful jaws, but small forearms without carpals in the wrists. Because of their slow gait and small arms, they likely preyed upon the larger, slower sauropods rather t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abelisaurid
Abelisauridae (meaning "Abel's lizards") is a family (or clade) of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaurs. Abelisaurids thrived during the Cretaceous period, on the ancient southern supercontinent of Gondwana, and today their fossil remains are found on the modern continents of Africa and South America, as well as on the Indian subcontinent and the island of Madagascar. Isolated teeth were found in the Late Jurassic of Portugal, and the Late Cretaceous genera '' Tarascosaurus'' and ''Arcovenator'' have been described in France. Abelisaurids first appear in the fossil record of the early middle Jurassic period, and at least two genera (the Moroccan '' Chenanisaurus'' and the Madagascan ''Majungasaurus'') survived until the end of the Mesozoic era 66 million years ago. Like most theropods, abelisaurids were carnivorous bipeds. They were characterized by stocky hind limbs and extensive ornamentation of the skull bones, with grooves and pits. In many abelisaurids, such as ''Carnotaurus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajasaurus
''Rajasaurus'' (meaning "princely lizard") is a genus of carnivorous abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of India, containing one species: ''Rajasaurus narmadensis''. The bones were excavated from the Lameta Formation in the Gujarat state of Western India, probably inhabiting what is now the Narmada River Valley. It was formally described by palaeontologist Jeffrey A. Wilson and colleagues in 2003 based on a partial skeleton comprising the braincase, spine, hip bone, legs, and tail–a first for an Indian theropod. The dinosaur likely measured , and had a single horn on the forehead which was probably used for display and head-butting. Like other abelisaurids, ''Rajasaurus'' was probably an ambush predator. India at this time was an island, due to the break-up of the supercontinent Gondwana, though it is possible animals still were able to migrate to and from nearby continents. The creation of the subfamily Majungasaurinae, and its inclusion of abelisau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnotaurinae
Carnotaurinae is a subfamily of the theropod dinosaur family Abelisauridae. It includes the dinosaurs ''Aucasaurus'' (from Argentina), ''Carnotaurus'' (from Argentina). The group was first proposed by American paleontologist Paul Sereno in 1998, defined as a clade containing all abelisaurids more closely related to ''Carnotaurus'' than to ''Majungasaurus''. Classification *Subfamily Carnotaurinae **Brachyrostra ***'' Ekrixinatosaurus'' (Argentina) ***'' Elemgasem'' (Argentina) ***'' Guemesia'' (Argentina) ***'' Ilokelesia'' (Argentina) ***'' Skorpiovenator'' (Argentina) ***''Thanos'' (Brazil) ***Furileusauria ****?'' Niebla'' (Argentina) ****'' Llukalkan'' (Argentina) ****'' Viavenator'' (Argentina) ****'' Pycnonemosaurus'' (Brazil) ****'' Quilmesaurus'' (Argentina) ****Carnotaurini *****''Carnotaurus'' (Argentina) ***** Abelisaurinae ******''Aucasaurus'' (Argentina) ******'' Abelisaurus'' (Argentina) Phylogeny In 2008, Canale ''et al.'' published a phylogenetic analysis focu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lameta Formation
The Lameta Formation, also known as the Infratrappean Beds, is a sedimentary geological formation found in Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Maharashtra, India, associated with the Deccan Traps. It is of Maastrichtian age (Late Cretaceous), and is notable for its dinosaur fossils. Many dubious names have been created for isolated bones, but several genera of dinosaurs from these rocks are well-supported, including the titanosaur sauropod ''Isisaurus'' and the abelisaurs '' Indosaurus'', '' Indosuchus'', '' Laevisuchus'', and ''Rajasaurus''.Weishampel et al., 2004, pp.517-606 As well as mammals, snakes and other fossils. Lithology The formation is underlain by the Lower Cretaceous sedimentary "Upper Gondwana Sequence" also known as the Jabalpur Formation, and is overlain by the Deccan Traps basalt. The Lameta Formation is only exposed at the surface as small isolated outcrops associated with the Satpura Fault. The lithology of the formation, depending on the outcrop, consists of al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcovenator
''Arcovenator'' ("Arc hunter") is an extinct genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaurs hailing from the Late Cretaceous of France. The type and only described species is ''Arcovenator escotae''. Description Though shallower, the nearly complete braincase of ''Arcovenator'' is otherwise similar in size to those of '' Majungasaurus'' and ''Carnotaurus''; it was thus initially estimated as being about long, but it was estimated in 2016 as being in length. The same year Molina-Pérez and Larramendi estimated to be 7.2 m (23.6 ft) in length and 950 kg (2,094 lbs). The skull roof exhibits as a unique diagnostic character a midline foramen, possibly housing the pineal gland, situated on the posterior surface of a slight dome formed by frontal bones as moderately thick as in ''Aucasaurus'', thus less so than for '' Rajasaurus'', though more than those of '' Rugops''. Less characteristically, above the orbit is a low fossa with a small fenestra bordered by the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majungasaurus
''Majungasaurus'' (; ) is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in Madagascar from 70 to 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous Period, making it one of the last known non-avian dinosaurs that went extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The genus contains a single species, ''Majungasaurus crenatissimus''. This dinosaur is also called ''Majungatholus'', a name which is considered a junior synonym of ''Majungasaurus''. Like other abelisaurids, ''Majungasaurus'' was a bipedal predator with a short snout. Although the forelimbs are not completely known, they were very short, while the hind limbs were longer and very stocky. It can be distinguished from other abelisaurids by its wider skull, the very rough texture and thickened bone on the top of its snout, and the single rounded horn on the roof of its skull, which was originally mistaken for the dome of a pachycephalosaur. It also had more teeth in both upper and lower jaws than mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratosauria
Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with '' Ceratosaurus'' than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, '' Saltriovenator'', dates to the earliest part of the Jurassic, around 199 million years ago. According to the majority of the latest research, Ceratosauria includes three major clades: Ceratosauridae, Noasauridae, and Abelisauridae, found primarily (though not exclusively) in the Southern Hemisphere. Originally, Ceratosauria included the above dinosaurs plus the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic Coelophysoidea and Dilophosauridae, implying a much earlier divergence of ceratosaurs from other theropods. However, most recent studies have shown that coelophysoids and dilophosaurids do not form a natural group with other ceratosaurs, and are excluded from this group. Ceratosauria derives its names from the type species, '' Ceratosaurus nasicornis'', described by O.C. Marsh in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antorbital Fenestra
An antorbital fenestra (plural: fenestrae) is an opening in the skull that is in front of the eye sockets. This skull character is largely associated with archosauriforms, first appearing during the Triassic Period. Among extant archosaurs, birds still possess antorbital fenestrae, whereas crocodylians have lost them. The loss in crocodylians is believed to be related to the structural needs of their skulls for the bite force and feeding behaviours that they employ.Preushscoft, H., Witzel, U. 2002. Biomechanical Investigations on the Skulls of Reptiles and Mammals. Senckenbergiana Lethaea 82:207–222.Rayfield, E.J., Milner, A.C., Xuan, V.B., Young, P.G. 2007. Functional Morphology of Spinosaur "Crocodile Mimic" Dinosaurs. JVP. 27(4):892–901. In some archosaur species, the opening has closed but its location is still marked by a depression, or fossa, on the surface of the skull called the antorbital fossa. The antorbital fenestra houses a paranasal sinus that is confluent with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
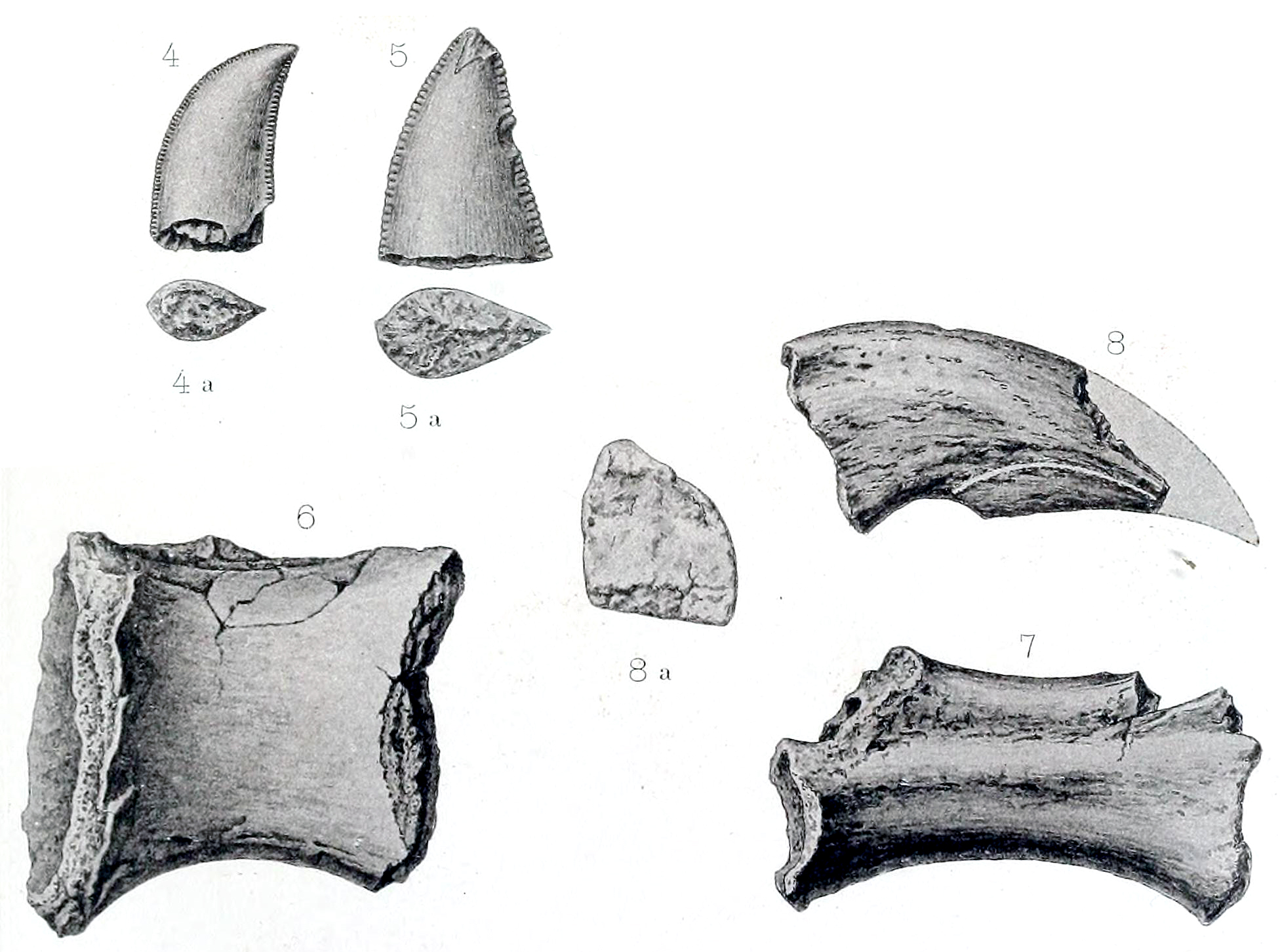
Indosaurus
''Indosaurus'' () is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now India, about 69 to 66 million years ago during the Maastrichtian The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interv ... division of the Late Cretaceous. The species I. matleyi weighed roughly 700 kg (1540 lb). History The type species, ''Indosaurus matleyi'', was named by Friedrich von Huene, Huene and Matley in 1933 making Indosaurus the first Majungasaurinae, Majungasaurine to be discovered.F. von Huene and C. A. Matley, 1933, "The Cretaceous Saurischia and Ornithischia of the Central Provinces of India", ''Palaeontologica Indica (New Series), Memoirs of the Geological Survey of India'' 21(1): 1-74 The generic name refers to India and the specific name (zoology), specific name honours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |