|
Raffael Schuster-Woldan
Raffael Hans Ulrich Schuster-Woldan (7 January 1870, Striegau - 13 December 1951, Garmisch-Partenkirchen) was a German painter and art professor; associated with the Munich Secession. Life and work He was the youngest of three children born to , a Court Councilor, and his wife Clara née Seifart. In 1887, he left the local gymnasium without graduating, and followed his older brother, to Munich, where they took lessons at the private art school operated by Frank Kirchbach. In 1889, he accompanied Kirchbach on visits to Frankfurt and Paris. As an addition to his studies, he visited the workshops of other artists. He was also influenced by the Rembrandt etchings he saw at the Münchner Kupferstichkabinett. During this time, he adopted the pseudonym "Woldan", from his father, who had used it to publish a volume of poetry.Richard Braungart: ''Der letzte Malerfürst'', Der Kunsthandel 1952, After completing his studies, he settled in Dinkelsbühl, but soon moved to Rothenburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raffael Schuster-Woldan
Raffael Hans Ulrich Schuster-Woldan (7 January 1870, Striegau - 13 December 1951, Garmisch-Partenkirchen) was a German painter and art professor; associated with the Munich Secession. Life and work He was the youngest of three children born to , a Court Councilor, and his wife Clara née Seifart. In 1887, he left the local gymnasium without graduating, and followed his older brother, to Munich, where they took lessons at the private art school operated by Frank Kirchbach. In 1889, he accompanied Kirchbach on visits to Frankfurt and Paris. As an addition to his studies, he visited the workshops of other artists. He was also influenced by the Rembrandt etchings he saw at the Münchner Kupferstichkabinett. During this time, he adopted the pseudonym "Woldan", from his father, who had used it to publish a volume of poetry.Richard Braungart: ''Der letzte Malerfürst'', Der Kunsthandel 1952, After completing his studies, he settled in Dinkelsbühl, but soon moved to Rothenburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
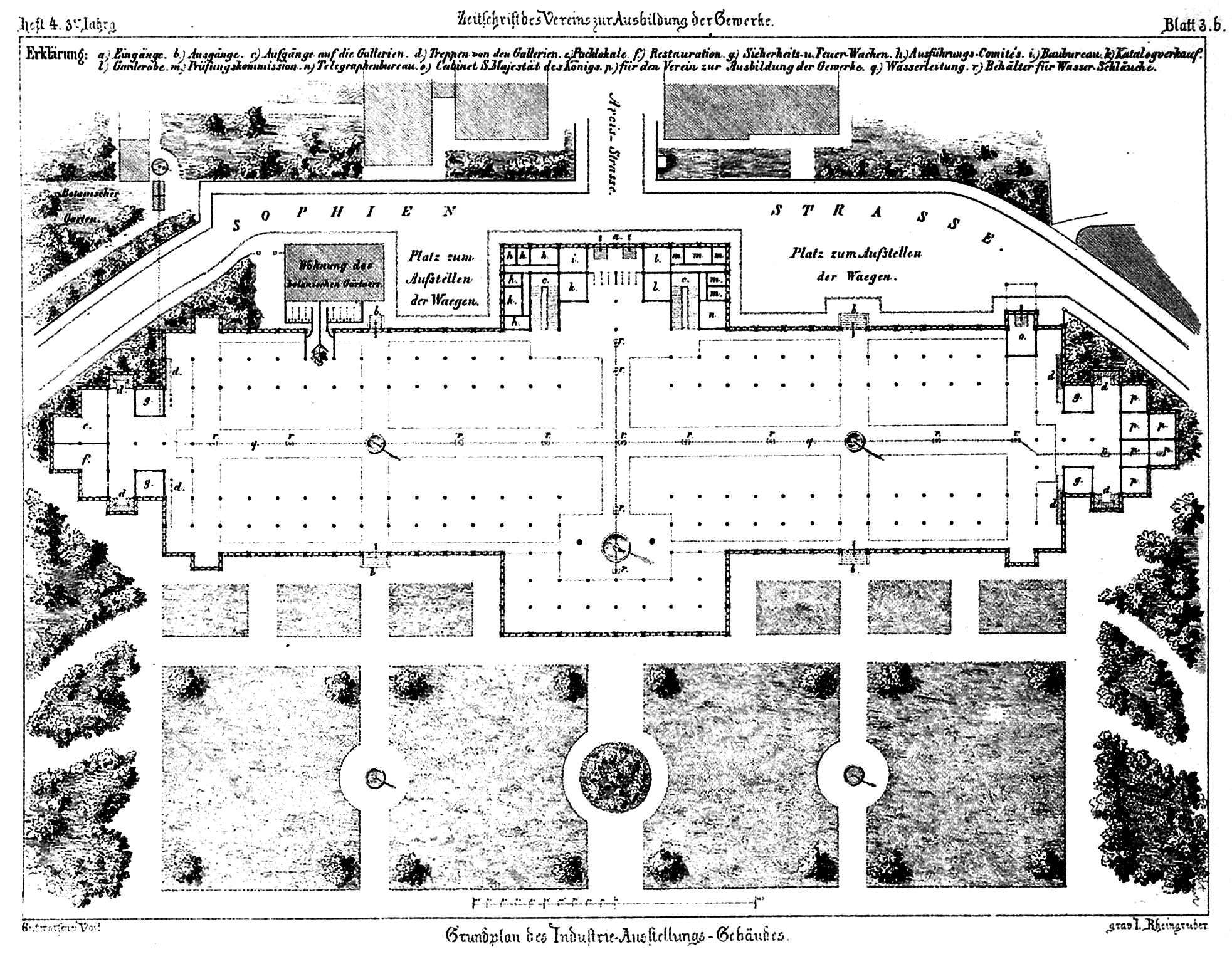
Glaspalast (Munich)
The ''Glaspalast'' (Glass Palace) was a glass and iron exhibition building located in the Old botanical garden - Munich in Munich modeled after The Crystal Palace in London. The Glaspalast opened for the first General German Industrial Exhibition on July 15, 1854. Planning Following other examples around Europe, the ''Glaspalast'' was ordered by Maximilian II, King of Bavaria, in order to hold the ''Erste Allgemeine Deutsche Industrieausstellung'' (First General German Industrial Exhibition) on July 15, 1854. Originally it was planned to erect the building on Maximilianplatz. However, the relevant Commission decision preferred an area near the railway station. Designed by architect August von Voit and built by MAN AG, the building was built in 1854 to the north of the Old Botanical Garden close to the Stachus. Construction Following the completion of 1853 Schrannenhalle and the planned and conservatory of Munich Residence, a glass with cast iron design was used, using exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and then taking the title of in 1934. During his dictatorship, he initiated World War II in Europe by invading Poland on 1 September 1939. He was closely involved in military operations throughout the war and was central to the perpetration of the Holocaust: the genocide of about six million Jews and millions of other victims. Hitler was born in Braunau am Inn in Austria-Hungary and was raised near Linz. He lived in Vienna later in the first decade of the 1900s and moved to Germany in 1913. He was decorated during his service in the German Army in World War I. In 1919, he joined the German Workers' Party (DAP), the precursor of the Nazi Party, and was appointed leader of the Nazi Party in 1921. In 1923, he attempted to seize governmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Große Deutsche Kunstausstellung
The Große Deutsche Kunstausstellung (Great German Art Exhibition) was held a total of eight times from 1937 to 1944 in the purpose-built Haus der Deutschen Kunst in Munich. It was representative of art under National Socialism. History The ''Great German Art Exhibition'', which spanned the first floor, the upper floor and the two-story "Hall of Honour" in the centre of the building, was promoted as the most important cultural event in National Socialist Germany. The show was conceived as a sales exhibition; artists could be represented with several works (usually up to ten works), and sometimes non-saleable works, such as loans, were also exhibited. During each exhibition, a "special show" gave a selected artist the opportunity to present himself more comprehensively. While the organizational and technical part of the exhibition preparation was the responsibility of the "Haus der Deutschen Kunst (Neuer Glaspalast)" as an institution under public law, the overall artistic dir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goethe-Medaille Für Kunst Und Wissenschaft
The Goethe-Medaille für Kunst und Wissenschaft (Goethe Medal for Art and Science) is a German award. It was authorized by Reichspräsident Paul von Hindenburg to commemorate the centenary of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's death on March 22, 1932. It consists of a silver, non-wearable medal (62mm, after about 1938 69.5mm in diameter). This medal should not be confused with the Goldene Goethe-Medaille (Goethe Medal in Gold) of the Weimar Goethe Society (61 awards from 1910 to 2017), the "Goethepreis der Stadt Frankfurt" (Goethe Prize of the City of Frankfurt) which since 1927 has been awarded first annually, then triennially (45 awards from 1927 to 2017 – no medal), the "Goethe-Plakette der Stadt Frankfurt" (Goethe Plaque of the City of Frankfurt) 158 awards from 1947–2017, or the "Goethe-Medaille" (Goethe Medal) of the Goethe-Institut, which from 1955 to 2017 has been awarded to 345 personalities from 57 countries. With more than 600 recipients, the "Goethe-Medaille für Kunst und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Passau
The University of Passau (''Universität Passau'' in German) is a public research university located in Passau, Lower Bavaria, Germany. Founded in 1973, it is the youngest university in Bavaria and consequently has the most modern campus in the state. Nevertheless, its roots as the Institute for Catholic Studies dates back to the early 17th century. Today it is home to four faculties and 39 different undergraduate and postgraduate degree programmes. History The university was established on 1 January 1973 by a resolution of the Bayerischer Landtag (Bavarian State Parliament). However its history goes back to 1622 when an Institute for Catholic Studies was incorporated into the Gymnasium founded by Fürst Leopold in 1612. In 1773, the school was renamed ''fürstbischöfliche Akademie'', highlighting its relationship to the bishop. Nevertheless, in 1803 it was downgraded to a ''kurfürstliches Lyzeum'', which meant a loss of status. After a period of abandonment, it was re-estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmy Göring
Emma Johanna Henny "Emmy" Göring (; 24 March 1893 – 8 June 1973) was a German actress and the second wife of ''Luftwaffe'' Commander-in-Chief Hermann Göring. She served as Adolf Hitler's hostess at many state functions and thereby staked a claim to the title of " First Lady of the Third Reich". Early life She was born Emma Sonnemann in Hamburg, Germany on 24 March 1893 to a wealthy salesman. After schooling, she became an actress at the National Theatre in Weimar. On 13 January 1916, Sonnemann married actor Karl Köstlin in Trieste, Austria-Hungary. Thereafter, she was known as Emmy Köstlin. In her autobiography, Göring said that she and Köstlin soon realized that they were more suited as friends and soon separated. They eventually divorced in 1926. Marriage to Hermann Göring On 10 April 1935, she married the prominent Nazi and ''Luftwaffe'' chief Hermann Göring, becoming Emmy Göring. It was also Göring's second marriage; his first wife, Carin, had died in October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosima Wagner
Francesca Gaetana Cosima Wagner ( née Liszt; 24 December 1837 – 1 April 1930) was the daughter of the Hungarian composer and pianist Franz Liszt and Franco-German romantic author Marie d'Agoult. She became the second wife of the German composer Richard Wagner, and with him founded the Bayreuth Festival as a showcase for his stage works; after his death she devoted the rest of her life to the promotion of his music and philosophy. Commentators have recognised Cosima as the principal inspiration for Wagner's later works, particularly ''Parsifal''. In 1857, after a childhood largely spent under the care of her grandmother and with governesses, Cosima married the conductor Hans von Bülow. Although the marriage produced two children, it was largely a loveless union, and in 1863 Cosima began a relationship with Wagner, who was 24 years her senior. They married in 1870; after Wagner's death in 1883 she directed the Bayreuth Festival for more than 20 years, increasing its reper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winifred Wagner
Winifred Marjorie Wagner ( Williams; 23 June 1897 – 5 March 1980) was the English-born wife of Siegfried Wagner, the son of Richard Wagner, and ran the Bayreuth Festival after her husband's death in 1930 until the end of World War II in 1945. She was a friend and supporter of Adolf Hitler, himself a Wagner enthusiast, and she and Hitler maintained a regular correspondence. Biography Early life and marriage to Siegfried Wagner Wagner was born Winifred Marjorie Williams in Hastings, England, to John Williams, a journalist and critic, and his wife, née Emily Florence Karop. She lost both her parents before the age of two and initially was raised in a number of homes. Eight years later, she was adopted by a distant German relative of her mother, Henrietta Karop, and her husband Karl Klindworth, a musician and a friend of Richard Wagner. The Bayreuth Festival was seen as a family business, with the leadership to be passed from Richard Wagner to his son Siegfried Wagner, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Nazi Germany. During Hitler's rise to power in 1930s Europe, it was frequently referred to as Hitlerism (german: Hitlerfaschismus). The later related term " neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideas which formed after the Second World War. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. It incorporates a dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, scientific racism, and the use of eugenics into its creed. Its extreme nationalism originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist '' Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationalism since the late 19th century, and it was strongly influenced by the paramilitary groups that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |