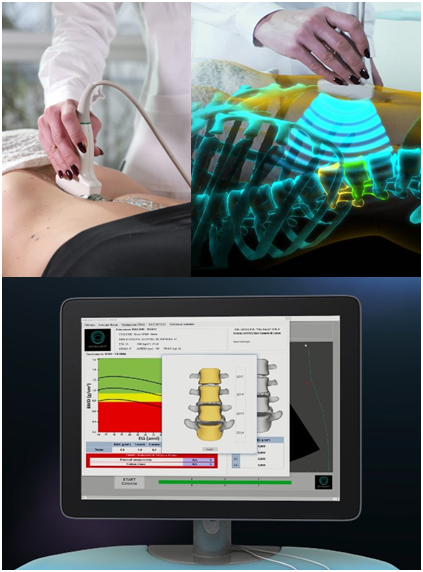
|
Radiofrequency Echographic Multi Spectrometry
Radiofrequency Echographic Multi Spectrometry (REMS) is a non-ionizing technology for osteoporosis diagnosis and for fracture risk assessment. REMS processes the raw, unfiltered ultrasound signals acquired during an echographic scan of the axial sites, femur and spine. The analysis is performed in the frequency domain. Bone mineral density ( BMD) is estimated by comparing the results against reference models. The accuracy has been tested by comparing it against to DXA technology. Working principles Traditionally, ultrasound B-Mode imaging has been designed for allowing a visual evaluation of human organs and their features by clinicians; however, this implies that the huge quantity of information carried by ultrasound signals is processed and significantly reduced for visualization purposes. REMS technology instead analyses the raw, unfiltered ultrasound signals by comparing their spectral representation with the spectral models stored in a proprietary database which ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
REMS Technology Spine Scan
Rems or REMS may refer to: * Radiofrequency Echographic Multi Spectrometry * Rams (card game), a card game also known as Rems * Rapid eye movement sleep, a sleep phase * Rems (river), a river in Germany * Research, Evaluation, Measurement, and Statistics, a concentration in Educational Psychology at Texas Tech University *No. 204 Reserve Equipment Maintenance Satellite at RCAF Station Assiniboia * Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies, risk management plans to ensure safe use of dangerous pharmaceuticals * Romanian Electron Microscopy Society, a member society of the European Microscopy Society and consequently the International Federation of Societies for Microscopy. * Rover Environmental Monitoring Station, meteorological sensors on the Mars rover Curiosity * Ryan Rems, a Filipino comedian and television personality * Rems Umeasiegbu, a Nigerian professor, scholar, novelist, poet and folklorist * Tadej Rems, a Slovenian football player See also * Rem (other) *''Kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Materials'' 12, 476-478 (2013). causing it to harden. Calcifications may be classified on whether there is mineral balance or not, and the location of the calcification. Calcification may also refer to the processes of normal mineral deposition in biological systems, such as the formation of stromatolites or mollusc shells (see Biomineralization). Signs and symptoms Calcification can manifest itself in many ways in the body depending on the location. In the pulpal structure of a tooth, calcification often presents asymptomatically, and is diagnosed as an incidental finding during radiographic interpretation. Individual teeth with calcified pulp will typically respond negatively to vitality testing; teeth with calcified pulp often lack sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Mass Index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres. The BMI may be determined using a table or chart which displays BMI as a function of mass and height using contour lines or colours for different BMI categories, and which may use other units of measurement (converted to metric units for the calculation). The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as ''underweight'', ''normal weight'', ''overweight'', or ''obese'' based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult BMI classifications are underweight (under 18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 to 24.9), overweight (25 to 29.9), and obese (30 or more). When used to predict an individual's health, rather than as a statistical measurement for groups, the BMI has limitations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often define menopause as having occurred when a woman has not had any menstrual bleeding for a year. It may also be defined by a decrease in hormone production by the ovaries. In those who have had surgery to remove their uterus but still have functioning ovaries, menopause is not considered to have yet occurred. Following the removal of the uterus, symptoms typically occur earlier. In the years before menopause, a woman's periods typically become irregular, which means that periods may be longer or shorter in duration or be lighter or heavier in the amount of flow. During this time, women often experience hot flashes; these typically last from 30 seconds to ten minutes and may be associated with shivering, sweating, and reddening of the skin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves and blood. This may result in a low red blood cell count, inflammation around the lungs, and inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the joint capsule. It also affects the underlying bone and cartilage. The diagnosis is made mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An '' embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term ''fetus'' is used until birth. Signs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fragility Score REMS Technology
{{disambig ...
Fragility may refer to: * A property of a solid, related to brittleness * Fragility (glass physics), a concept to characterize viscous slow down during glass formation * Fragility of financial systems, an idea developed by scholar Nassim Nicholas Taleb * Fragility Tour, a 1999 concert tour by rock band Nine Inch Nails * ''Fragility'' (film), a 2016 Swedish documentary film * Fragility (cultural studies) * White fragility See also * Fragile States Index The Fragile States Index (FSI; formerly the Failed States Index) is an annual report published by the United States think tank the Fund for Peace and the American magazine ''Foreign Policy'' from 2005 to 2018, then by The New Humanitarian since 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repeatability
Repeatability or test–retest reliability is the closeness of the agreement between the results of successive measurements of the same measure, when carried out under the same conditions of measurement. In other words, the measurements are taken by a single person or instrument on the same item, under the same conditions, and in a short period of time. A less-than-perfect test–retest reliability causes test–retest variability. Such variability can be caused by, for example, intra-individual variability and inter-observer variability. A measurement may be said to be ''repeatable'' when this variation is smaller than a pre-determined acceptance criterion. Test–retest variability is practically used, for example, in medical monitoring of conditions. In these situations, there is often a predetermined "critical difference", and for differences in monitored values that are smaller than this critical difference, the possibility of variability as a sole cause of the difference ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision (statistics)
In statistics, the precision matrix or concentration matrix is the matrix inverse of the covariance matrix or dispersion matrix, P = \Sigma^. For univariate distributions, the precision matrix degenerates into a scalar precision, defined as the reciprocal of the variance, p = \frac. Other summary statistics of statistical dispersion also called ''precision'' (or ''imprecision'') include the reciprocal of the standard deviation, p = \frac; the standard deviation itself and the relative standard deviation; as well as the standard error and the confidence interval (or its half-width, the margin of error). Usage One particular use of the precision matrix is in the context of Bayesian analysis of the multivariate normal distribution: for example, Bernardo & Smith prefer to parameterise the multivariate normal distribution in terms of the precision matrix, rather than the covariance matrix, because of certain simplifications that then arise. For instance, if both the prior and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity And Specificity
''Sensitivity'' and ''specificity'' mathematically describe the accuracy of a test which reports the presence or absence of a condition. Individuals for which the condition is satisfied are considered "positive" and those for which it is not are considered "negative". *Sensitivity (true positive rate) refers to the probability of a positive test, conditioned on truly being positive. *Specificity (true negative rate) refers to the probability of a negative test, conditioned on truly being negative. If the true condition can not be known, a " gold standard test" is assumed to be correct. In a diagnostic test, sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives. For all testing, both diagnostic and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensitivities will mean lower specificities and vice versa. If the goal is to return the ratio at w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohen's Kappa
Cohen's kappa coefficient (''κ'', lowercase Greek kappa) is a statistic that is used to measure inter-rater reliability (and also intra-rater reliability) for qualitative (categorical) items. It is generally thought to be a more robust measure than simple percent agreement calculation, as ''κ'' takes into account the possibility of the agreement occurring by chance. There is controversy surrounding Cohen's kappa due to the difficulty in interpreting indices of agreement. Some researchers have suggested that it is conceptually simpler to evaluate disagreement between items. History The first mention of a kappa-like statistic is attributed to Galton in 1892. The seminal paper introducing kappa as a new technique was published by Jacob Cohen in the journal ''Educational and Psychological Measurement'' in 1960. Definition Cohen's kappa measures the agreement between two raters who each classify ''N'' items into ''C'' mutually exclusive categories. The definition of \kappa is :\k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Correlation Coefficient
In statistics, the Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC, pronounced ) ― also known as Pearson's ''r'', the Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (PPMCC), the bivariate correlation, or colloquially simply as the correlation coefficient ― is a measure of linear correlation between two sets of data. It is the ratio between the covariance of two variables and the product of their standard deviations; thus, it is essentially a normalized measurement of the covariance, such that the result always has a value between −1 and 1. As with covariance itself, the measure can only reflect a linear correlation of variables, and ignores many other types of relationships or correlations. As a simple example, one would expect the age and height of a sample of teenagers from a high school to have a Pearson correlation coefficient significantly greater than 0, but less than 1 (as 1 would represent an unrealistically perfect correlation). Naming and history It was developed by Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |