|
Radical Party (Italy) Politicians
Radical Party may refer to any of a number of political parties professing the progressive-liberal ideology known as Radicalism: Worldwide * Nonviolent Radical Party Transnational and Transparty (1989–present) Europe In the western Mediterranean European countries, Radicalism was one of the major political movements between 1848 and 1940. Such parties were often labelled 'Democratic', 'Radical democratic', or 'Radical liberal' parties: * In France: **Radical Left (1902–1940), parliamentary group of the Independent Radicals. **Radical-Socialist Party (France) (1901–present) **Radical Party of the Left (1971–present) **Radical Movement (2017–2021), former merger of the Radical Party and the Radical Party of the Left. * In Italy: **Italian Radical Party (1877–1925) **Radical Party (Italy) (1955–1989) **Italian Radicals (2001–present) **Radical Socialist Movement (2006-present), formed by dissidents members of the Radicals of the Left **Liberty and Equality (2010- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Party
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular country's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific political ideology, ideological or policy goals. Political parties have become a major part of the politics of almost every country, as modern party organizations developed and spread around the world over the last few centuries. It is extremely rare for a country to have Non-partisan democracy, no political parties. Some countries have Single-party state, only one political party while others have Multi-party system, several. Parties are important in the politics of autocracies as well as democracies, though usually democracies have more political parties than autocracies. Autocracies often have a single party that governs the country, and some political scientists consider competition between two or more parties to be an essential part of democracy. Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Party (Spain)
The Progressive Party ( es, Partido Progresista) was one of the two Spanish political parties that contended for power during the reign of Isabel II (reigned 1833–1868). It was to the left of the opposing Moderate Party ( es, Partido Moderado) but also characterised itself as liberal. Like the Moderate Party, it supported Isabel against the claims of the Carlists. History The party was established in 1834 as the extreme liberal opposition, during the regency of queen mother Maria Christina of the Two Sicilies; Queen Isabel was only three years old. It was the party of the ''exaltados'', ''veinteañistas'' or ''progresistas'', heirs of the '' Trienio Liberal'' ("liberal triennium") of 1820–1823, whereas the Moderate Party represented the ''doceañistas'' who traced their roots to the Spanish Constitution of 1812. The Progressives were the party of the National Militia, the jury trial, a secular state, and of national sovereignty and the broadening of the franchise un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Democratic Party Of Switzerland
french: Parti radical-démocratique it, Partito Liberale Radicale rm, Partida liberaldemocrata svizra , logo = Free Democratic Party of Switzerland logo French.png , logo_size = 200px , foundation = , dissolution = , merged = FDP.The Liberals , headquarters = Neuengasse 20 Postfach 6136CH-3001 Bern , ideology = , position = Centre-right , international = Liberal International , european = European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party , europarl = , colours = Azure , country = Switzerland The Free Democratic Party or Radical Democratic Party (german: Freisinnig-Demokratische Partei, FDP; french: Parti radical-démocratique, PRD; it, Partito liberale-radicale svizzero, PLR; rm, Partida liberaldemocrata svizra, PLD) was a liberal political party in Switzerland. Formerly one of the major parties in Switzerland, on 1 January 2009 it merged with the Libera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
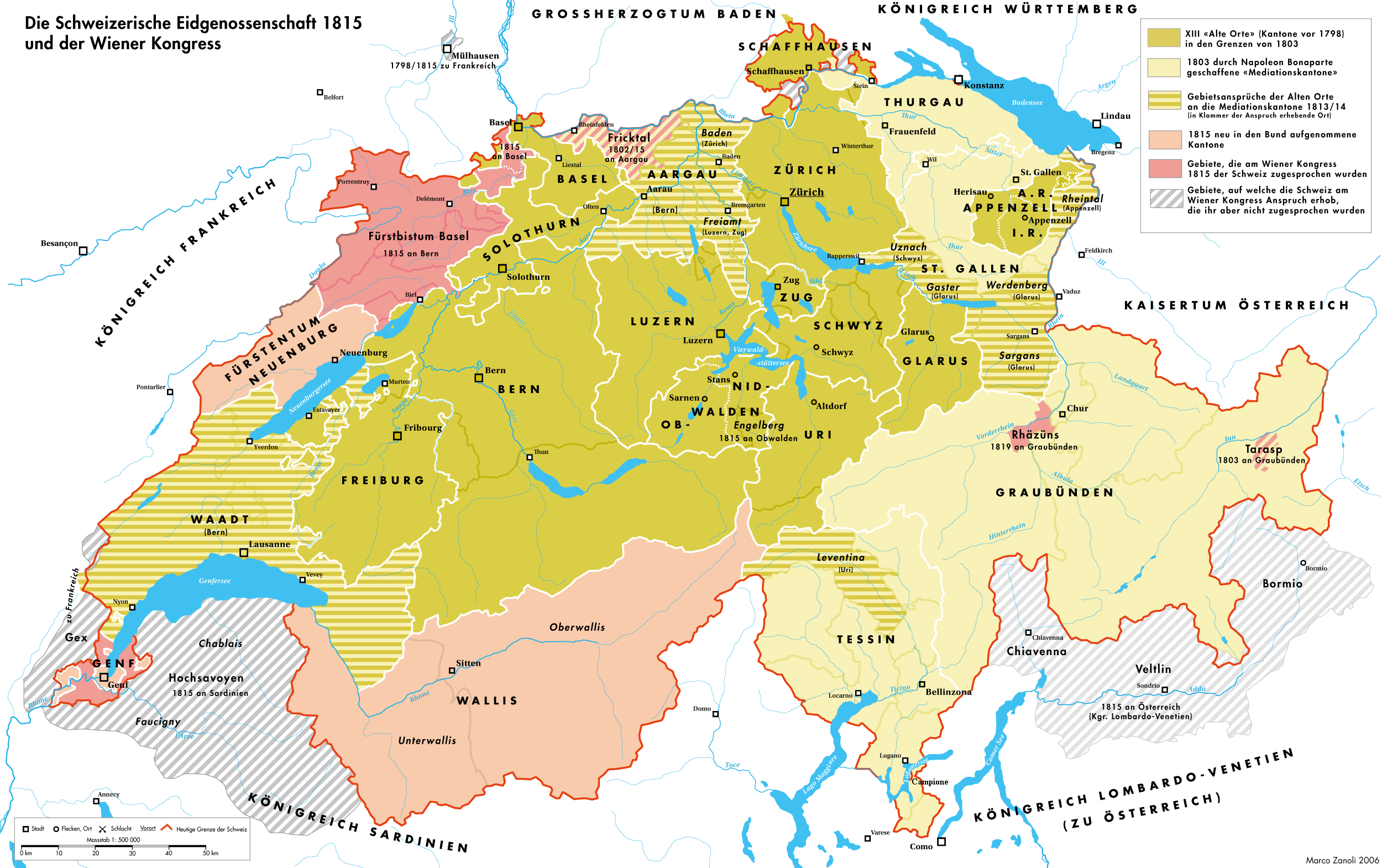
Regeneration (Switzerland)
The periods of Restoration and Regeneration in Swiss history lasted from 1814 to 1847. "Restoration" is the period of 1814 to 1830, the restoration of the ''Ancien Régime'' (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte on the centralist Helvetic Republic from 1798 and the partial reversion to the old system with the Act of Mediation of 1803. "Regeneration" is the period of 1830 to 1848, when in the wake of the July Revolution the "restored" ''Ancien Régime'' was countered by the liberal movement. In the Protestant cantons, the rural population enforced liberal cantonal constitutions, partly in armed marches on the cities. This resulted in a conservative backlash in the Catholic cantons in the 1830s, raising the conflict to the point of civil war by 1847. Restoration When Napoleon's fall appeared imminent, the Act of Mediation was suspended in late December 1813, and lengthy discussions about future constitutions were initiated in all cantons of Switzer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
; rm, citad federala, links=no). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Lucerne, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zurich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2022 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: link=no, Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: link=no, Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federal assembly-independent directorial republic , leader_title1 = Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Viktor Rossi , legislature = Federal Assembly , upper_house = Counci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rationalism
In philosophy, rationalism is the epistemological view that "regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge" or "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification".Lacey, A.R. (1996), ''A Dictionary of Philosophy'', 1st edition, Routledge and Kegan Paul, 1976. 2nd edition, 1986. 3rd edition, Routledge, London, 1996. p. 286 More formally, rationalism is defined as a methodology or a theory "in which the criterion of truth is not sensory but intellectual and deductive".Bourke, Vernon J., "Rationalism," p. 263 in Runes (1962). In an old John Locke (1690), An Essay on Human Understanding controversy, rationalism was opposed to empiricism, where the rationalists believed that reality has an intrinsically logical structure. Because of this, the rationalists argued that certain truths exist and that the intellect can directly grasp these truths. That is to say, rationalists asserted that certain rational principles exist in logic, mathematics, ethics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freethinker
Freethought (sometimes spelled free thought) is an epistemological viewpoint which holds that beliefs should not be formed on the basis of authority, tradition, revelation, or dogma, and that beliefs should instead be reached by other methods such as logic, reason, and empirical observation. According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', a freethinker is "a person who forms their own ideas and opinions rather than accepting those of other people, especially in religious teaching." In some contemporary thought in particular, free thought is strongly tied with rejection of traditional social or religious belief systems. The cognitive application of free thought is known as "freethinking", and practitioners of free thought are known as "freethinkers". Modern freethinkers consider free thought to be a natural freedom from all negative and illusive thoughts acquired from society. The term first came into use in the 17th century in order to refer to people who inquired into the bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden; the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland; and the autonomous region of Åland. The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, History of Scandinavia, history, religion and Nordic model, social structure. They have a long history of political unions and other close relations but do not form a singular entity today. The Scandinavism, Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century. With the dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden (Norwegian independence), the independence of Finland in the early 20th century and the 1944 Icelandic constitutional referendum, this movement expanded into the modern organised Nordic cooperation. Since 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Territorial Entities Where German Is An Official Language
The following is a list of the countries and territories where German is an official language (also known as the Germanosphere). It includes countries that have German as (one of) their nationwide official language(s), as well as dependent territories with German as a co-official language. German as an official language German is the official language of six countries, all of which lie in central and western Europe. These countries (with the addition of South Tyrol of Italy) also form the Council for German Orthography and are referred to as the ''German Sprachraum'' (German language area). Since 2004, Meetings of German-speaking countries have been held annually with six participants: Germany, Austria, Belgium, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, and Switzerland: Subdivisions of countries While not official at the national level, German is a co-official language in subdivisions of the countries listed below. In each of these regions, German is an official language on the administr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in Northwestern Europe forming the lower basin of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and consisting of three countries: Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg. Geographically and historically, the area also includes parts of France and Germany such as the French Flanders and the German regions of East Frisia and Cleves. During the Middle Ages, the Low Countries were divided into numerous semi-independent principalities. Historically, the regions without access to the sea linked themselves politically and economically to those with access to form various unions of ports and hinterland, stretching inland as far as parts of the German Rhineland. Because of this, nowadays not only physically low-altitude areas, but also some hilly or elevated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Union (Spain, 1934)
The Republican Union ( es, Unión Republicana) was a Spanish republican party founded in 1934 by Diego Martinez Barrio. It was formed as a result of a merger of several small republican parties, including notably Diego Martinez Barrio's Radical Democratic Party founded in May 1934 by a split from Alejandro Lerroux's Radical Party in protest at the latter's alliance with the right-wing CEDA. Integrated in the Popular Front ahead of the 1936 election, the party won 38 seats becoming the fourth largest party. It formed a governing coalition with Manuel Azaña's Republican Left. Though it participated in all republican governments during the Spanish Civil War, it played a minor role starting under Largo Caballero's government. In exile in Mexico Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Left (Spain)
The Republican Left ( es, Izquierda Republicana) was a Spanish republican party founded in 1934. History The party was founded in 1934 following the left's defeat in the 1933 election, by the merger of Manuel Azaña's Republican Action, part of Marcelino Domingo's Radical Socialist Republican Party and Santiago Casares Quiroga's Autonomous Galician Republican Organization (ORGA).De la Granja, José Luis; De Pablo, Santiago (2009). ''«La II República y la Guerra Civil». Historia del País Vasco y Navarra en el siglo XX'' (2d edition). Madrid: Biblioteca Nueva. p. 61. . Its members included José Giral, Victoria Kent and Manuel Azaña who became the party's leader. Integrated in the Popular Front ahead of the 1936 election, the party won 87 seats becoming the third largest party while Manuel Azaña obtained the office of President of the Council of Minister. Following the impeachment of Niceto Alcalá Zamora from the presidency in May 1936, Azaña was elected preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |