|
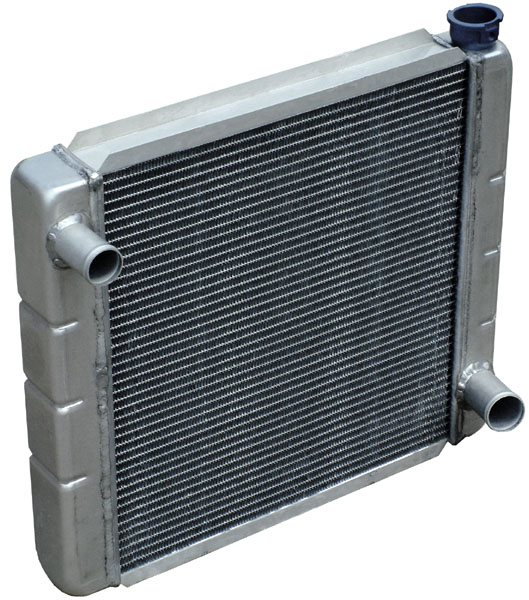
Radiators
A radiator is a heat exchanger used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics. A radiator is always a source of heat to its environment, although this may be for either the purpose of heating an environment, or for cooling the fluid or coolant supplied to it, as for automotive engine cooling and HVAC dry cooling towers. Despite the name, most radiators transfer the bulk of their heat via convection instead of thermal radiation. History The Roman hypocaust is an early example of a type of radiator for building space heating. Franz San Galli, a Prussian-born Russian businessman living in St. Petersburg, is credited with inventing the heating radiator around 1855, having received a radiator patent in 1857, but American Joseph Nason and Scot Rory Gregor developed a primitive radiator in 1841 and received a number of U.S. patents for hot wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automobile Radiator
Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in #Automobiles and motorcycles, automobiles but also in #Aircraft, piston-engined aircraft, Diesel locomotive, railway locomotives, #Automobiles and motorcycles, motorcycles, Diesel generator, stationary generating plants or any similar use of such an engine. Internal combustion engine cooling, Internal combustion engines are often cooled by circulating a liquid called ''#Engine_coolant, engine coolant'' through the engine block and cylinder head where it is heated, then through a radiator where it loses heat to the atmosphere, and then returned to the engine. Engine coolant is usually water-based, but may also be oil. It is common to employ a water pump to force the engine coolant to circulate, and also for an axial fan to force air through the radiator. Automobiles and motorcycles In automobiles and motorcycles with a liquid-cooled internal combustion engine, a radiator is connected to ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiator Op Blauw-wit-gestreepte Tegels
A radiator is a heat exchanger used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics. A radiator is always a source of heat to its environment, although this may be for either the purpose of heating an environment, or for cooling the fluid or coolant supplied to it, as for automotive engine cooling and HVAC dry cooling towers. Despite the name, most radiators transfer the bulk of their heat via convection instead of thermal radiation. History The Roman hypocaust is an early example of a type of radiator for building space heating. Franz San Galli, a Prussian-born Russian businessman living in St. Petersburg, is credited with inventing the heating radiator around 1855, having received a radiator patent in 1857, but American Joseph Nason and Scot Rory Gregor developed a primitive radiator in 1841 and received a number of U.S. patents for hot wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
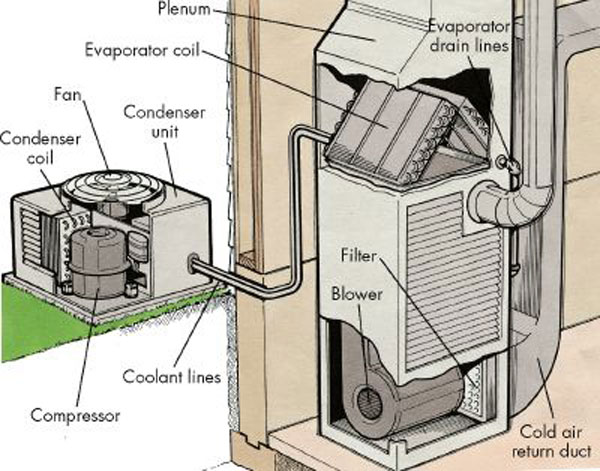
Central Heating System
A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building from one main source of heat. A central heating system has a Furnace (central heating), furnace that converts fuel or electricity to heat through processes. The heat is circulated through the building either by fans forcing heated air through Duct (flow), ducts, circulation of low-pressure steam to Radiator, radiators in each heated room, or Pump, pumps that circulate hot water through room radiators. Primary energy sources may be fuels like coal or wood, oil, kerosene, natural gas, or electricity. Compared with systems such as Fireplace, fireplaces and Wood-burning stove, wood stoves, a central heating plant offers improved uniformity of temperature control over a building, usually including automatic control of the furnace. Large homes or buildings may be divided into individually controllable zones with their own Temperature control, temperature controls. Automatic fuel (and sometimes ash) handli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, Petrochemical, petrochemical plants, Oil refinery, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant. Flow arrangement There are three primary classifications of heat exchangers accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Radiation
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted by the thermal motion of particles in matter. All matter with a temperature greater than absolute zero emits thermal radiation. The emission of energy arises from a combination of electronic, molecular, and lattice oscillations in a material. Kinetic energy is converted to electromagnetism due to charge-acceleration or dipole oscillation. At room temperature, most of the emission is in the infrared (IR) spectrum, though above around 525 °C (977 °F) enough of it becomes visible for the matter to visibly glow. This visible glow is called incandescence. Thermal radiation is one of the fundamental mechanisms of heat transfer, along with conduction and convection. The primary method by which the Sun transfers heat to the Earth is thermal radiation. This energy is partially absorbed and scattered in the atmosphere, the latter process being the reason why the sky is visibly blue. Much of the Sun's radiation tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heating, Ventilation, And Air Conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and Sick building syndrome, healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooling Tower
A cooling tower is a device that rejects waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a coolant stream, usually a water stream, to a lower temperature. Cooling towers may either use the evaporation of water to remove heat and cool the working fluid to near the Wet-bulb temperature, wet-bulb air temperature or, in the case of ''dry cooling towers'', rely solely on air to cool the working fluid to near the Dry-bulb temperature, dry-bulb air temperature using Radiator, radiators. Common applications include cooling the circulating water used in oil refineries, petrochemical and other chemical plants, thermal power stations, nuclear power stations and HVAC systems for cooling buildings. The classification is based on the type of air induction into the tower: the main types of cooling towers are Natural convection, natural draft and Forced convection, induced draft cooling towers. Cooling towers vary in size from small roof-top units to very large hyperboloid structures t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Heater
A space heater is a device used to heat a single, small- to medium-sized area. This type of heater can be contrasted with central heating, which distributes heat to multiple areas. Types Dominant mode of heat transfer All space heaters transfer heat to their environment via some combination of the three fundamental modes of heat transfer: convection, radiation, and conduction. Typically heaters are designed with either convection or radiation as the sole dominant mode. Convective heaters ''Convective space heaters'' utilize convection to transfer heat from the power source to a space. These heaters typically either rely on ''natural'' or ''forced'' convection. Natural convection is a phenomenon where temperature variations in an environment generate fluid flow. Forced convection heaters utilize a device like a fan to generate air flow and spread heat at a fast pace. Sometimes called "fan heaters," these are often cheap but lack in efficiency and versatility. Radia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiatore
''Radiatori'' are small, squat pasta shapes that are said to resemble radiators. Although it is rumored that they were created in the 1960s by an industrial designer, their invention was actually between the First and Second World War. They are often used in similar dishes as ''rotelle'' or fusilli, because their shape works well with thicker sauces. They are also used in casseroles, salads, and soups. The form is sometimes called "pagoda pasta". Design ''Radiatori'' somewhat resemble fusilli in shape, but are generally shorter and thicker with a ruffled edge, circling the pasta. They are modelled after an old industrial heating fixture, having a straight "pipe" with concentric, parallel fins. Their design creates hollows to trap sauce. See also * List of pasta There are many different varieties of pasta. They are usually sorted by size, being long (), short (), stuffed (), cooked in broth (), stretched () or in dumpling-like form (). Yet, due to the variety of shapes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiller
A chiller is a machine that removes heat from a liquid coolant via a vapor-compression refrigeration, vapor-compression, adsorption refrigeration, or absorption refrigerator, absorption refrigeration cycles. This liquid can then be circulated through a heat exchanger to cool equipment, or another process stream (such as air or process water). As a necessary by-product, refrigeration creates waste heat that must be exhausted to ambience, or for greater efficiency, recovered for heating purposes. Vapor compression chillers may use any of a number of different types of compressors. Most common today are the hermetic scroll, semi-hermetic screw, or centrifugal compressors. The condensing side of the chiller can be either air or water cooled. Even when liquid cooled, the chiller is often cooled by an induced or forced draft cooling tower. Absorption and adsorption chillers require a heat source to function. Chilled water is used to Air conditioning, cool and dehumidify air in mid- to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |