|
Rachitic
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone metabolism causes inadequate bone mineralization. Osteomalacia in children is known as rickets, and because of this, use of the term "osteomalacia" is often restricted to the milder, adult form of the disease. Signs and symptoms can include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragility of the bones. In addition to low systemic levels of circulating mineral ions (for example, caused by vitamin D deficiency or renal phosphate wasting) that result in decreased bone and tooth mineralization, accumulation of mineralization-inhibiting proteins and peptides (such as osteopontin and ASARM peptides), and small inhibitory molecules (such as pyrophosphate), can occur in the extracellular matrix of bones and teeth, contributing locally to cause m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications may include bone deformities, bone pseudofractures and fractures, muscle spasms, or an abnormally curved spine. The most common cause of rickets is a vitamin D deficiency, although hereditary genetic forms also exist. This can result from eating a diet without enough vitamin D, dark skin, too little sun exposure, exclusive breastfeeding without vitamin D supplementation, celiac disease, and certain genetic conditions. Other factors may include not enough calcium or phosphorus. The underlying mechanism involves insufficient calcification of the growth plate. Diagnosis is generally based on blood tests finding a low calcium, low phosphorus, and a high alkaline phosphatase together with X-rays. Prevention for exclusively breastfed babi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
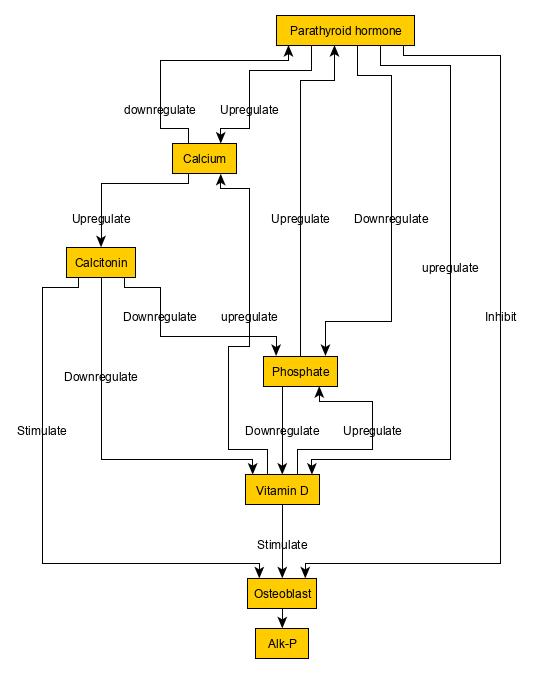
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D deficiency can also be caused by inadequate nutritional intake of vitamin D; disorders that limit vitamin D absorption; and disorders that impair the conversion of vitamin D to active metabolites, including certain liver, kidney, and hereditary disorders. Deficiency impairs bone mineralization, leading to bone-softening diseases, such as rickets in children. It can also worsen osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults, increasing the risk of bone fractures. Muscle weakness is also a common symptom of vitamin D deficiency, further increasing the risk of fall and bone fractures in adults. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with the development of schizophrenia. Vitamin D can be synthesized in the skin under the exposure of UVB from sunlight. Oily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecalciferol
Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement. Cholecalciferol is made in the skin following UVB light exposure. It is converted in the liver to calcifediol (25-hydroxyvitamin D) which is then converted in the kidney to calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D). One of its actions is to increase calcium uptake by the intestines. It is found in food such as some fish, beef liver, eggs, and cheese. Plant and cow milk, fruit juice, yogurt, and margarine also may have cholecalciferol added to them in some countries, including the United States. Cholecalciferol can be taken as an oral dietary supplement to prevent vitamin D deficiency or as a medication to treat associated diseases, including rickets. It is also used for familial hypophosphatemia, hypoparathyroidism that is causing low blood calcium, and Fanconi syndrome. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spine. Similarly, kyphosis historically refers to ''abnormal'' convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacral regions is also termed ''kyphosis'' or ''kyphotic''. The term comes from the Greek lordōsis, from ''lordos'' ("bent backward"). Lordosis in the human spine makes it easier for humans to bring the bulk of their mass over the pelvis. This allows for a much more efficient walking gait than that of other primates, whose inflexible spines cause them to resort to an inefficient forward leaning "bent-knee, bent-waist" gait. As such, lordosis in the human spine is considered one of the primary physiological adaptations of the human skeleton that allows for human gait to be as energeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticonvulsant
Anticonvulsants (also known as antiepileptic drugs or recently as antiseizure drugs) are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain. Conventional antiepileptic drugs may block sodium channels or enhance γ-aminobutyric acid ( GABA) function. Several antiepileptic drugs have multiple or uncertain mechanisms of action. Next to the voltage-gated sodium channels and components of the GABA system, their targets include GABAA receptors, the GAT-1 GABA transporter, and GABA transaminase. Additional targets include voltage-gated calcium channels, SV2A, and α2δ. By blocking sodium o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogenic Osteomalacia
Oncogenic osteomalacia, also known as oncogenic hypophosphatemic osteomalacia, is an uncommon disorder resulting in increased renal phosphate excretion, hypophosphatemia and osteomalacia. It may be caused by a phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor. Signs and symptoms Adult patients may present with worsening musculoskeletal symptoms, muscle weakness, myalgias, bone pains and fatigue which are followed by recurrent fractures. Children present with difficulty in walking, stunted growth and deformities of the skeleton (features of rickets). There can also be a significant delay between the beginning of symptoms to diagnosis, which research reflects as being between 2.5 to 28 years. Cause Tumor-induced osteomalacia is usually referred to as a paraneoplastic phenomenon, however, the tumors are usually benign and the symptomatology is due to osteomalacia or rickets. A benign mesenchymal or mixed connective tissue tumor (usually phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor and hemangiopericytoma) are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Kidney Failure
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include pedal edema, leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications can relate to hormonal dysfunction of the kidneys and include (in chronological order) Hypertension, high blood pressure (often related to activation of the renin–angiotensin system system), renal osteodystrophy, bone disease, and anemia. Additionally CKD patients have markedly increased Cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular complications with increased risks of death and hospitalization. Causes of chronic kidney disease include diabetic nephropathy, diabetes, high blood pressure, glomerulonephritis, and polycystic kidney disease. Risk factors include a family history of chronic kidney disease. Diagnosis is by blood tests to measure the estimated glomerular filtration rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypophosphatemia
Hypophosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a low level of phosphate in the blood. Symptoms may include weakness, trouble breathing, and loss of appetite. Complications may include seizures, coma, rhabdomyolysis, or softening of the bones. Causes include alcohol use disorder, refeeding in those with malnutrition, recovery from diabetic ketoacidosis, burns, hyperventilation, and certain medications. It may also occur in the setting of hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism, and Cushing syndrome. It is diagnosed based on a blood phosphate concentration of less than 0.81 mmol/L (2.5 mg/dL). When levels are below 0.32 mmol/L (1.0 mg/dL) it is deemed to be severe. Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Phosphate may be given by mouth or by injection into a vein. Hypophosphatemia occurs in about 2% of people within hospital and 70% of people in the intensive care unit (ICU). Signs and symptoms * Muscle dysfunction and weakness – This occurs in major muscles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a variety of anaemias. Normally the human gastrointestinal tract digests and absorbs dietary nutrients with remarkable efficiency. A typical Western diet ingested by an adult in one day includes approximately 100 g of fat, 400 g of carbohydrate, 100 g of protein, 2 L of fluid, and the required sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, vitamins, and other elements. Salivary, gastric, intestinal, hepatic, and pancreatic secretions add an additional 7–8 L of protein-, lipid-, and electrolyte-containing fluid to intestinal contents. This massive load is reduced by the small and large intestines to less than 200 g of stool that contains less than 8 g of fat, 1–2 g of nitrogen, and less than 20 mmol each of Na+, K+, Cl–, HCO3–, Ca2+, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An ''embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term '' fetus'' is used until birth. Signs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues and form. Malnutrition is not receiving the correct amount of nutrition. Malnutrition is increasing in children under the age of five due to providers who cannot afford or do not have access to adequate nutrition. Malnutrition is a category of diseases that includes undernutrition and overnutrition. Undernutrition is a lack of nutrients, which can result in stunted growth, wasting, and underweight. A surplus of nutrients causes overnutrition, which can result in obesity. In some developing countries, overnutrition in the form of obesity is beginning to appear within the same communities as undernutrition. Most clinical studies use the term 'malnutrition' to refer to undernutrition. However, the use of 'malnutrition' instead of 'und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Tubular Acidosis
Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is a medical condition that involves an accumulation of acid in the body due to a failure of the kidneys to appropriately acidify the urine. In renal physiology, when blood is filtered by the kidney, the filtrate passes through the tubules of the nephron, allowing for exchange of salts, acid equivalents, and other solutes before it drains into the bladder as urine. The metabolic acidosis that results from RTA may be caused either by insufficient secretion of hydrogen ions (which are acidic) into the latter portions of the nephron (the distal tubule) or by failure to reabsorb sufficient bicarbonate ions (which are alkaline) from the filtrate in the early portion of the nephron (the proximal tubule). Although a metabolic acidosis also occurs in those with chronic kidney disease, the term RTA is reserved for individuals with poor urinary acidification in otherwise well-functioning kidneys. Several different types of RTA exist, which all have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |