|
Race Game
Race game is a large category of board games, in which the object is to be the first to move all one's pieces to the end of a track. This is both the earliest type of board game known, with implements and representations dating back to at least the 3rd millennium BC in Egypt, Iraq, and Iran; and also the most widely dispersed: "all cultures that have games at all have race games". Race games often use dice to decide game options and how far to move pieces. Types of race games Race games may be categorized by their ratio of luck to skill. Other classifications include geographical distribution or derivation; and shape of track (including spiral, cross and circle, and square—either boustrophedon as in Snakes and Ladders or "labyrinthine" as in Thaayam). Simple Simple race games involve pure luck. Each player has only one piece to move, and the outcome of the game thus depends solely on chance. The Game of the Goose is the progenitor of most simple Western race games, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Games
Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well. Many board games feature a competition between two or more players. To show a few examples: in checkers (British English name 'draughts'), a player wins by capturing all opposing pieces, while Eurogames often end with a calculation of final scores. ''Pandemic'' is a cooperative game where players all win or lose as a team, and peg solitaire is a puzzle for one person. There are many varieties of board games. Their representation of real-life situations can range from having no inherent theme, such as checkers, to having a specific theme and narrative, such as ''Cluedo''. Rules can range from the very simple, such as in snakes and ladders; to deeply complex, as in ''Advanced Squad Leader''. Play components now often include custom figures or shaped counters, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trictrac
Trictrac is a French board game of skill and chance for two players that is played with dice on a game board similar, but not identical, to that of backgammon. It was "the classic tables game" of France in the way that backgammon is in the English-speaking world.Parlett (1999), p. 86. Trictrac's gaming interest lies in its multiple combinations, the importance of decision-making and its comprehensive rules which have been well documented and remained stable since the early 17th century. It requires constant attention from the players whether or not it is their turn. Its vocabulary, which is very rich, frequently occurs in French literature. The object of the game is not to get out the men as quickly as possible as in jacquet or backgammon, but to score as many points as possible. The game usually ends before all the men have been borne off. The name is sometimes spelt tric trac or tric-trac. History Trictrac was very popular in France at the royal court and in aristocrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agon (game)
Agon (or Queen's Guards or Royal Guards) is a strategy game invented by Anthony Peacock of London, and first published in 1842. It is a two-player game played on a 6×6×6 hexagonal gameboard, and is notable for being the oldest known board game played on a board of hexagonal cells. Rules Each player has one ''queen'' and six ''guards''. Players determine who moves first, then turns alternate. On each turn, a player moves one of his pieces. The object of the game is to be first to maneuver one's queen to the central hex (the ''throne'') at the center of the board, and surround her with all six of her guards. Moves The gameboard may be thought of as a series of concentric rings of hex cells (highlighted by rings of alternating colors). Pieces move one step at a time to an adjacent cell, either sideways in the same ring, or towards the throne to the next ring. The cell moved to must be vacant. Only the queen may move to the throne. Captures A piece is captured when two enemy pie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hex (board Game)
Hex is a two player abstract strategy board game in which players attempt to connect opposite sides of a rhombus-shaped board made of hexagonal cells. Hex was invented by mathematician and poet Piet Hein in 1942 and later rediscovered and popularized by John Nash. It is traditionally played on an 11×11 rhombus board, although 13×13 and 19×19 boards are also popular. The board is composed of hexagons called ''cells'' or ''hexes''. Each player is assigned a pair of opposite sides of the board, which they must try to connect by alternately placing a stone of their color onto any empty hex. Once placed, the stones are never moved or removed. A player wins when they successfully connect their sides together through a chain of adjacent stones. Draws are impossible in Hex due to the topology of the game board. Despite the simplicity of its rules, the game has deep strategy and sharp tactics. It also has profound mathematical underpinnings. The game was first published under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trivial Pursuit
''Trivial Pursuit'' is a board game Board games are tabletop games that typically use . These pieces are moved or placed on a pre-marked board (playing surface) and often include elements of table, card, role-playing, and miniatures games as well. Many board games feature a co ... in which winning is determined by a player's ability to answer trivia and popular culture questions. Players move their pieces around a board, the squares they land on determining the subject of a question they are asked from a card (from six categories including "history" and "science and nature"). Each correct answer allows the player's turn to continue; a correct answer on one of the six "category headquarters" spaces earns a plastic wedge which is slotted into the answerer's playing piece. The object of the game is to collect all six wedges from each "category headquarters" space, and then return to the center "hub" space to answer a question in a category selected by the other players. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
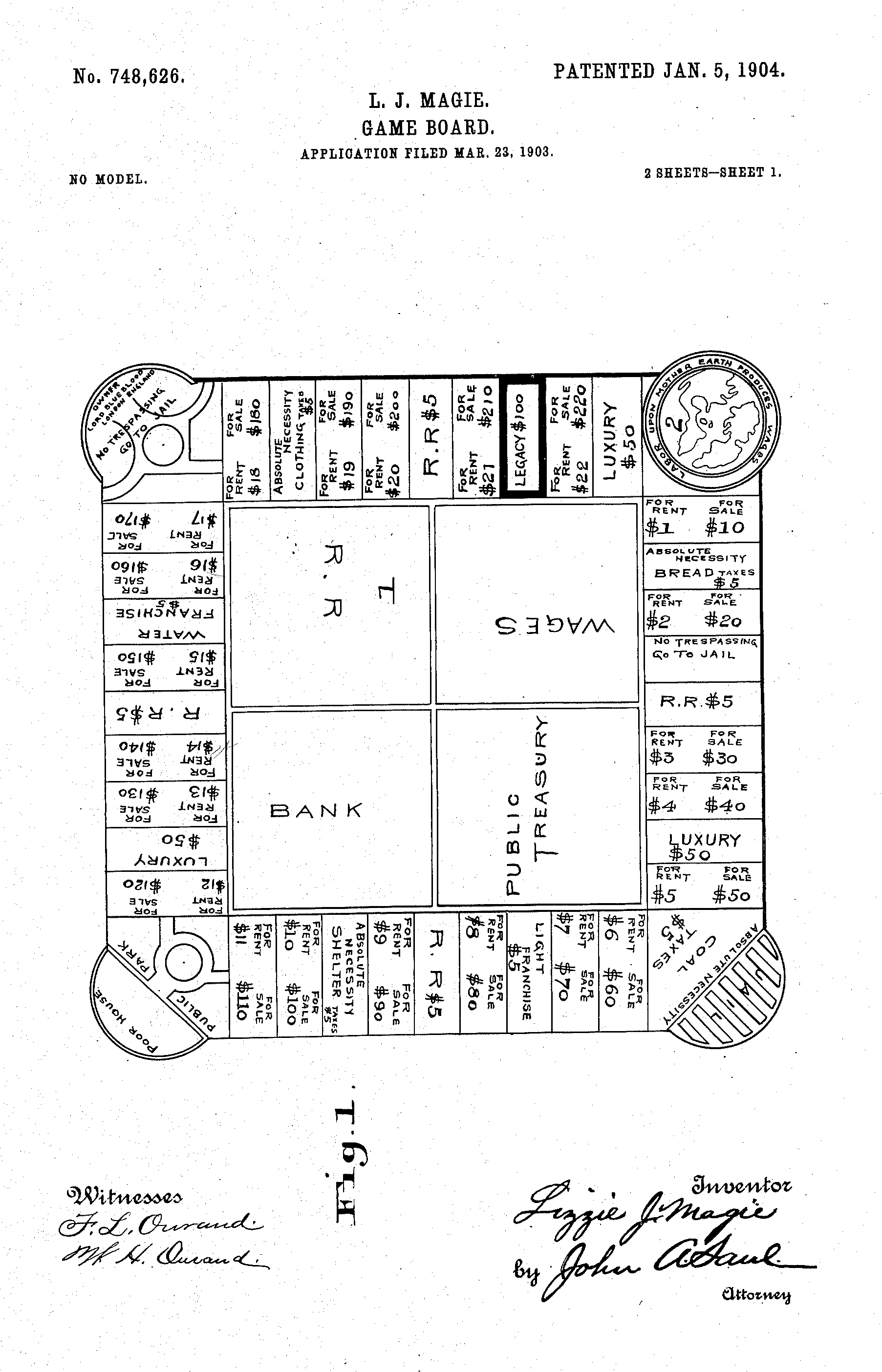
Monopoly (game)
''Monopoly'' is a multi-player economics-themed board game. In the game, players roll two dice to move around the game board, buying and trading properties and developing them with houses and hotels. Players collect rent from their opponents, aiming to drive them into bankruptcy. Money can also be gained or lost through ''Chance'' and ''Community Chest'' cards and tax squares. Players receive a stipend every time they pass "Go" and can end up in jail, from which they cannot move until they have met one of three conditions. House rules, hundreds of different editions, many spin-offs, and related media exist. ''Monopoly'' has become a part of international popular culture, having been licensed locally in more than 103 countries and printed in more than 37 languages. , it was estimated that the game had sold 275 million copies worldwide. ''Monopoly'' is derived from '' The Landlord's Game'', created by Lizzie Magie in the United States in 1903 as a way to demonstrate that an econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppit
Coppit is a running-fight board game created in 1927 by Otto Maier Verlag which was originally called in german: Fang den Hut (or Capture The Hat in English). It was renamed and has been re-released several times, most notably by the Spear's Games company in 1964. It is a game for two to six players and is based partly on luck with a die and partly on strategy. It is similar to the game Ludo and is nominally a children's game. The emblem on U-995, the world's only remaining German Type VIIC/41 Type VII U-boats were the most common type of German World War II U-boat. 703 boats were built by the end of the war. The lone surviving example, , is on display at the Laboe Naval Memorial located in Laboe, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. C ... submarine, features two ''Fang den Hut'' characters, as seen on the game's board. The game Each player has four conical, or hat-shaped, playing pieces all of the same colour that start off in their home 'base'. The object is to move out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Running-fight Game
Running-fight games are board games that essentially combine the ''method'' of race games (such as backgammon or pachisi) and the ''goal'' of elimination-based games such as chess or draughts. Like race games, pieces are moved along linear tracks based on the fall of dice or other lots; but like chess, the object is to capture opponent pieces. They might be most easily conceptualized as race games with two main differences: First, when a piece lands on a space or point occupied by an opponent, instead of sending it back to the beginning to start over, the opponent piece is '' captured'', permanently removed from the game. Second, there is typically no "end" to the track; pieces keep moving around their circuits, gradually capturing more and more enemy pieces. A player wins and ends the game by capturing the last of the opponent pieces. Running-fight games are found almost exclusively in Islamic-influenced cultures, ranging from West Africa to India, often bearing the names T� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hare And Tortoise
''Hare and Tortoise'' is a Eurogame designed by David Parlett in 1974 and first published by Intellect Games. In 1978 it was released by Ravensburger in Germany, and received generally positive reviews critically and won the 1979 Spiel des Jahres. It has since sold some 2 million units in at least ten languages. The current editions are published by Gibsons Games in the UK, Ravensburger in Germany and Rio Grande Games in the United States. Theme The game is based on Aesop's fable "The Tortoise and the Hare", in which the hare and tortoise decide to race. The tortoise wins the race by cunning while the hare fails because he overestimates himself and takes a nap during the race. The moral of the story is "slow and steady wins the race" which is incorporated in the game mechanic. In Germany, there is another fable by a similar name, ''Hase und Igel'' ( Hare and hedgehog), made popular by the Brothers Grimm, in which the hedgehog wins because his wife is at the finish line, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BoardGameGeek
BoardGameGeek (BGG) is an online forum for board gaming hobbyists and a game database that holds reviews, images and videos for over 125,600 different tabletop games, including European-style board games, wargames, and card games. In addition to the game database, the site allows users to rate games on a 1–10 scale and publishes a ranked list of board games. As of , boardgamegeek.com has an Alexa rank of . History BoardGameGeek was founded in January 2000 by Scott Alden and Derk Solko, and marked its 20th anniversary on 20 January 2020. Since 2005, BoardGameGeek hosts an annual board game convention, BGG.CON, that has a focus on playing games, and where winners of the Golden Geek Awards are announced. New games are showcased and convention staff is provided to teach rules. There is also an annual Spring BGG.CON which is family friendly, and an annual BGG@Sea which is held on a cruise. In 2010, BoardGameGeek received the Diana Jones Award, which recognized it as "a resourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Game Of Ur
The Royal Game of Ur is a two-player strategy race board game of the tables family that was first played in ancient Mesopotamia during the early third millennium BC. The game was popular across the Middle East among people of all social strata and boards for playing it have been found at locations as far away from Mesopotamia as Crete and Sri Lanka. It closely resembles another ancient game called the Game of Twenty Squares or Game of Twenty (see below). At the height of its popularity, the game acquired spiritual significance, and events in the game were believed to reflect a player's future and convey messages from deities or other supernatural beings. The Game of Ur remained popular until late antiquity, when it stopped being played, possibly evolving into, or being displaced by, a later form of tables game. It was eventually forgotten everywhere except among the Jewish population of the Indian city of Kochi, who continued playing a version of it called 'Asha' until the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)