|
Rabinovich–Fabrikant Equations
The Rabinovich–Fabrikant equations are a set of three coupled ordinary differential equations exhibiting Chaos theory, chaotic behaviour for certain values of the parameters. They are named after Mikhail Rabinovich and Anatoly Fabrikant, who described them in 1979. System description The equations are: : \dot = y (z - 1 + x^2) + \gamma x \, : \dot = x (3z + 1 - x^2) + \gamma y \, : \dot = -2z (\alpha + xy), \, where ''α'', ''γ'' are constants that control the evolution of the system. For some values of ''α'' and ''γ'', the system is chaotic, but for others it tends to a stable periodic orbit. Danca and Chen note that the Rabinovich–Fabrikant system is difficult to analyse (due to the presence of quadratic and cubic terms) and that different attractors can be obtained for the same parameters by using different step sizes in the integration, see on the right an example of a solution obtained by two different solvers for the same parameter values and initial conditions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One Numerical Solution To The Rabinovich-Fabrikant System 01
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit (measurement), unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In Digital electronics, digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
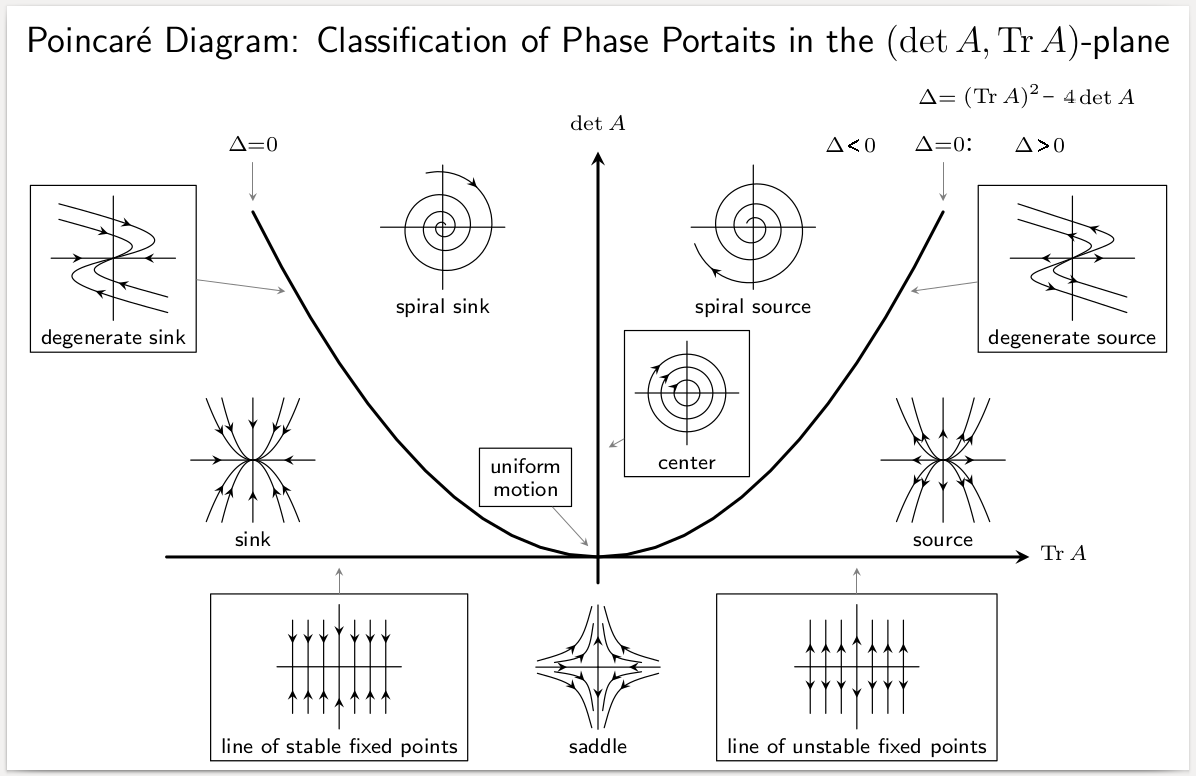
Equilibrium Points
In mathematics, specifically in differential equations, an equilibrium point is a constant solution to a differential equation. Formal definition The point \tilde\in \mathbb^n is an equilibrium point for the differential equation :\frac = \mathbf(t,\mathbf) if \mathbf(t,\tilde)=\mathbf for all t. Similarly, the point \tilde\in \mathbb^n is an equilibrium point (or fixed point) for the difference equation :\mathbf_ = \mathbf(k,\mathbf_k) if \mathbf(k,\tilde)= \tilde for k=0,1,2,\ldots. Equilibria can be classified by looking at the signs of the eigenvalues of the linearization of the equations about the equilibria. That is to say, by evaluating the Jacobian matrix at each of the equilibrium points of the system, and then finding the resulting eigenvalues, the equilibria can be categorized. Then the behavior of the system in the neighborhood of each equilibrium point can be qualitatively determined, (or even quantitatively determined, in some instances), by finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chaotic Maps
In mathematics, a chaotic map is a map (mathematics), map (an Discrete-time dynamical system, evolution function) that exhibits some sort of chaotic behavior. Maps may be parameterized by a discrete-time or a continuous-time parameter. Discrete maps usually take the form of iterated functions. Chaotic maps often occur in the study of dynamical systems. Chaotic maps and Iterated function, iterated functions often generate fractals. Some fractals are studied as objects themselves, as set (mathematics), sets rather than in terms of the maps that generate them. This is often because there are several different iterative procedures that generate the same fractal. See also Universality (dynamical systems). List of chaotic maps List of fractals * Cantor set * de Rham curve * Gravity set, or Mitchell-Green gravity set * Julia set - derived from complex quadratic map * Koch snowflake - special case of de Rham curve * Lyapunov fractal * Mandelbrot set - derived from complex quadratic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limit Cycle
In mathematics, in the study of dynamical systems with two-dimensional phase space, a limit cycle is a closed trajectory in phase space having the property that at least one other trajectory spirals into it either as time approaches infinity or as time approaches negative infinity. Such behavior is exhibited in some nonlinear systems. Limit cycles have been used to model the behavior of many real-world oscillatory systems. The study of limit cycles was initiated by Henri Poincaré (1854–1912). Definition We consider a two-dimensional dynamical system of the form x'(t)=V(x(t)) where V : \R^2 \to \R^2 is a smooth function. A ''trajectory'' of this system is some smooth function x(t) with values in \mathbb^2 which satisfies this differential equation. Such a trajectory is called ''closed'' (or ''periodic'') if it is not constant but returns to its starting point, i.e. if there exists some t_0>0 such that x(t + t_0) = x(t) for all t \in \R. An orbit (dynamics), orbit is the ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Correlation Dimension
In chaos theory, the correlation dimension (denoted by ''ν'') is a measure of the dimensionality of the space occupied by a set of random points, often referred to as a type of fractal dimension. For example, if we have a set of random points on the real number line between 0 and 1, the correlation dimension will be ''ν'' = 1, while if they are distributed on say, a triangle embedded in three-dimensional space (or ''m''-dimensional space), the correlation dimension will be ''ν'' = 2. This is what we would intuitively expect from a measure of dimension. The real utility of the correlation dimension is in determining the (possibly fractional) dimensions of fractal objects. There are other methods of measuring dimension (e.g. the Hausdorff dimension, the box-counting dimension, and the information dimension) but the correlation dimension has the advantage of being straightforwardly and quickly calculated, of being less noisy when only a small number of points is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Third Numerical Solution To The Rabinovich-Fabrikant System
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is '' a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes''. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version is often written in one of two forms: the double-storey and single-storey . The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type. In English, '' a'' is the indefinite article, with the alternative form ''an''. Name In English, the name of the letter is the ''long A'' sound, pronounced . Its name in most other languages matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The earliest known ancestor of A is ''aleph''—the first letter of the Phoenician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidden Oscillation
In the bifurcation theory, a bounded oscillation that is born without loss of stability of stationary set is called a hidden oscillation. In nonlinear control theory, the birth of a hidden oscillation in a time-invariant control system with bounded states means crossing a boundary, in the domain of the parameters, where local stability of the stationary states implies global stability (see, e.g. Kalman's conjecture). If a hidden oscillation (or a set of such hidden oscillations filling a compact subset of the phase space of the dynamical system) attracts all nearby oscillations, then it is called a hidden attractor. For a Dynamical system#Nonlinear dynamical systems and chaos, dynamical system with a unique equilibrium point that is globally attractive, the birth of a hidden attractor corresponds to a qualitative change in behaviour from monostability to bi-stability. In the general case, a dynamical system may turn out to be Multistability, multistable and have coexisting local att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatoly Fabrikant
Anatoly ( , ) is a common Russian and Ukrainian masculine given name, derived from the Greek name ''Anatolios'' (), meaning "sunrise." Saint Anatolius of Constantinople was a fifth-century saint who became the first patriarch of Constantinople in 451. Anatoly was one of the five most popular names for baby boys born in St. Petersburg, Russia, in 2004. Approximately one in every 35,110 Americans is named Anatoly, with a popularity rate of 28.48 per million. The name of Anatolia Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ... – a vast plateau that occupies a large portion of Asia Minor in modern-day Turkey – shares the same linguistic origin. People * Vladimir Shmondenko (weightlifter), Anatoly (born 1999), Ukrainian weightlifter * Anatoli Agrofenin (born 1980), Russian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |