|
Rabdology
In 1617 a treatise in Latin titled ''Rabdologiæ'' and written by John Napier was published in Edinburgh. Printed three years after his treatise on the discovery of logarithms and in the same year as his death, it describes three devices to aid arithmetic calculations. The devices themselves don't use logarithms, rather they are tools to reduce multiplication and division of natural numbers to simple addition and subtraction operations. The first device, which by then was already popularly used and known as Napier's bones, was a set of rods inscribed with the multiplication table. Napier coined the word rabdology (from Greek ῥάβδος [rhabdos], rod and λόγoς [logos] calculation or reckoning) to describe this technique. The rods were used to multiply, divide and even find the square roots and cube roots of numbers. The second device was a promptuary (Latin ''promptuarium'' meaning storehouse) and consisted of a large set of strips that could multiply multidigit numbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Napier
John Napier of Merchiston ( ; Latinisation of names, Latinized as Ioannes Neper; 1 February 1550 – 4 April 1617), nicknamed Marvellous Merchiston, was a Scottish landowner known as a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer. He was the 8th Laird of Merchiston. John Napier is best known as the discoverer of logarithms. He also invented the so-called "Napier's bones" and made common the use of the decimal point in arithmetic and mathematics. Napier's birthplace, Merchiston Castle, Merchiston Tower in Edinburgh, is now part of the facilities of Edinburgh Napier University. There is a memorial to him at St Cuthbert's Parish Church, St Cuthbert's at the west side of Edinburgh.Monuments and monumental inscriptions in Scotland: The Grampian Society, 1871 Life Napier's father was Archibald Napier (landowner), Sir Archibald Napier of Merchiston Castle, and his mother was Janet Bothwell, daughter of the politician and judge Francis Bothwell, and a sister of Adam Bothwell who bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
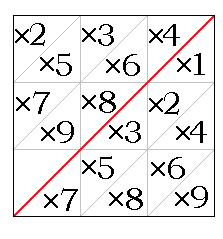
Promptuary
The promptuary, also known as the ''card abacus'' is a calculating machine invented by the 16th-century Scottish mathematician John Napier and described in his book '' Rabdologiae'' in which he also described Napier's bones. It is an extension of Napier's Bones, using two sets of rods to achieve multi-digit multiplication without the need to write down intermediate results, although some mental addition is still needed to calculate the result. The rods for the multiplicand are similar to Napier's Bones, with repetitions of the values. The set of rods for the multiplier are shutters or masks for each digit placed over the multiplicand rods. The results are then tallied from the digits showing as with other lattice multiplication methods. The final form described by Napier took advantage of symmetries to compact the rods, and used the materials of the day to hold system of metal plates, placed inside a wooden frame. Design of the Promptuary The promptuary consists of four parts: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Location Arithmetic
Location arithmetic (Latin ''arithmetica localis'') is the additive (non-positional) binary numeral systems, which John Napier explored as a computation technique in his treatise ''Rabdology'' (1617), both symbolically and on a chessboard-like grid. Napier's terminology, derived from using the positions of counters on the board to represent numbers, is potentially misleading because the numbering system is, in facts, non- positional in current vocabulary. During Napier's time, most of the computations were made on boards with tally-marks or jetons. So, unlike how it may be seen by the modern reader, his goal was not to use moves of counters on a board to multiply, divide and find square roots, but rather to find a way to compute symbolically with pen and paper. However, when reproduced on the board, this new technique did not require mental trial-and-error computations nor complex carry memorization (unlike base 10 computations). He was so pleased by his discovery that he said i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napier's Bones
Napier's bones is a manually operated calculating device created by John Napier of Merchiston, Scotland for the calculation of products and quotients of numbers. The method was based on lattice multiplication, and also called ''rabdology'', a word invented by Napier. Napier published his version in 1617. It was printed in Edinburgh and dedicated to his patron Alexander Seton, 1st Earl of Dunfermline, Alexander Seton. Using the Multiplication table, multiplication tables embedded in the rods, multiplication can be reduced to addition operations and division (mathematics), division to Subtraction, subtractions. Advanced use of the rods can extract square roots. Napier's bones are not the same as logarithms, with which Napier's name is also associated, but are based on dissected multiplication tables. The complete device usually includes a base board with a rim; the user places Napier's rods and the rim to conduct multiplication or division. The board's left edge is divided into n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , then is the logarithm of to base , written , so . As a single-variable function, the logarithm to base is the inverse of exponentiation with base . The logarithm base is called the ''decimal'' or ''common'' logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The ''natural'' logarithm has the number as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics because of its very simple derivative. The ''binary'' logarithm uses base and is widely used in computer science, information theory, music theory, and photography. When the base is unambiguous from the context or irrelevant it is often omitted, and the logarithm is written . Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal Point
FIle:Decimal separators.svg, alt=Four types of separating decimals: a) 1,234.56. b) 1.234,56. c) 1'234,56. d) ١٬٢٣٤٫٥٦., Both a comma and a full stop (or period) are generally accepted decimal separators for international use. The apostrophe and Arabic decimal separator are also used in certain contexts. A decimal separator is a symbol that separates the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form. Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The choice of symbol can also affect the choice of symbol for the #Digit grouping, thousands separator used in digit grouping. Any such symbol can be called a decimal mark, decimal marker, or decimal sign. Symbol-specific names are also used; decimal point and decimal comma refer to a dot (either Baseline dot, baseline or Middle dot, middle) and comma respectively, when it is used as a decimal separator; these are the usual terms used in English, with the aforem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andro Hart
Andro Hart (died December 1621), or Andrew Hart, was a Scottish printer, publisher, and bookseller in Edinburgh. Biography Hart occupied a shop on the north side of the High Street, opposite the mercat cross at the head of Craig's Close.Grant's Old and New Edinburgh vol.2 p.229 It is described in his will as 'the heich within his foir tenement of land upon the north syd of the Hie Streit.' The site was subsequently occupied by the shops of William Creech and Archibald Constable. Hart's printing-house was further down the close on the same side of the street. Hart was the principal printer, publisher, and bookseller of his time in Edinburgh. He published the works of Sir William Alexander and of Drummond of Hawthornden, by both of whom he was much respected. On 9 November 1618, Drayton the poet stated in a letter to Drummond that he was seeking to arrange with Hart for the publication of the last part of his 'Poly-Olbion.' Drummond was earnest with Hart 'in that particular', but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arithmetic
Arithmetic is an elementary branch of mathematics that deals with numerical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. In a wider sense, it also includes exponentiation, extraction of roots, and taking logarithms. Arithmetic systems can be distinguished based on the type of numbers they operate on. Integer arithmetic is about calculations with positive and negative integers. Rational number arithmetic involves operations on fractions of integers. Real number arithmetic is about calculations with real numbers, which include both rational and irrational numbers. Another distinction is based on the numeral system employed to perform calculations. Decimal arithmetic is the most common. It uses the basic numerals from 0 to 9 and their combinations to express numbers. Binary arithmetic, by contrast, is used by most computers and represents numbers as combinations of the basic numerals 0 and 1. Computer arithmetic deals with the specificities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Books
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of abstract objects that consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstractio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1617 Books
Events January–March * January 5 **Pocahontas and Tomocomo of the Powhatan Algonquian tribe, in the Virginia colony of America, meet King James I of England as his guests, at the Banqueting House at Whitehall. **'' The Mad Lover'', a play by John Fletcher, is given its first performance. * February 27 – The Treaty of Stolbovo ends the Ingrian War between Sweden and Russia. Sweden gains Ingria and Kexholm. * March 4 – On Shrove Tuesday, angry rioters burn down London's Cockpit Theatre because of its increase in the price of admission to its plays. Three rioters are killed when the actors at the theater defend themselves. * March 7 – Francis Bacon is appointed as Lord Keeper of the Great Seal of England and is designated by King James I to serve as regent during the time that the King of England is away from Westminster to travel to Scotland. * March 21 – Pocahontas (Rebecka Rolfe), daughter of the Chief of the Powhatan Algonquian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th-century Books In Latin
The 17th century lasted from January 1, 1601 (represented by the Roman numerals MDCI), to December 31, 1700 (MDCC). It falls into the early modern period of Europe and in that continent (whose impact on the world was increasing) was characterized by the Baroque cultural movement, the latter part of the Spanish Golden Age, the Dutch Golden Age, the French ''Grand Siècle'' dominated by Louis XIV, the Scientific Revolution, the world's first public company and megacorporation known as the Dutch East India Company, and according to some historians, the General Crisis. From the mid-17th century, European politics were increasingly dominated by the Kingdom of France of Louis XIV, where royal power was solidified domestically in the civil war of the Fronde. The semi-feudal territorial French nobility was weakened and subjugated to the power of an absolute monarchy through the reinvention of the Palace of Versailles from a hunting lodge to a gilded prison, in which a greatly expanded r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |