|
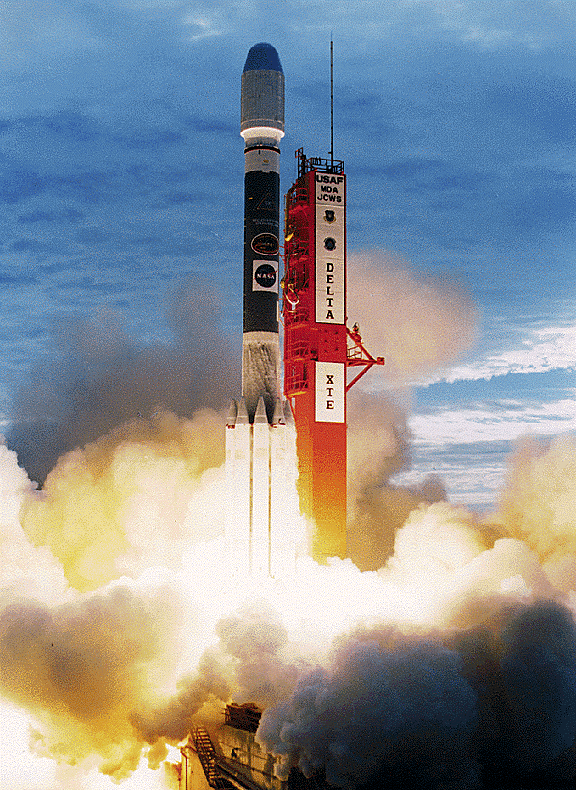
RXTE
The Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) was a NASA satellite that observed the time variation of astronomical X-ray sources, named after physicist Bruno Rossi. The RXTE had three instruments — an All Sky Monitor, the High-Energy X-ray Timing Experiment (HEXTE) and the Proportional Counter Array. The RXTE observed X-rays from black holes, neutron stars, X-ray pulsars and X-ray bursts. It was funded as part of the Explorer program, and was also called Explorer 69. RXTE had a mass of and was launched from Cape Canaveral on 30 December 1995, at 13:48:00 UTC, on a Delta II launch vehicle. Its International Designator is 1995-074A. Mission The X-Ray Timing Explorer (XTE) mission has the primary objective to study the temporal and broad-band spectral phenomena associated with stellar and galactic systems containing compact objects in the energy range 2--200 KeV, and in time scales from microseconds to years. The scientific instruments consists of two pointed instruments, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RXTE Preparations
The Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) was a NASA satellite that observed the time variation of astronomical X-ray sources, named after physicist Bruno Rossi. The RXTE had three instruments — an All Sky Monitor, the High-Energy X-ray Timing Experiment (HEXTE) and the Proportional Counter Array. The RXTE observed X-rays from black holes, neutron stars, X-ray pulsars and X-ray bursts. It was funded as part of the Explorer program, and was also called Explorer 69. RXTE had a mass of and was launched from Cape Canaveral on 30 December 1995, at 13:48:00 UTC, on a Delta II launch vehicle. Its International Designator is 1995-074A. Mission The X-Ray Timing Explorer (XTE) mission has the primary objective to study the temporal and broad-band spectral phenomena associated with stellar and galactic systems containing compact objects in the energy range 2--200 KeV, and in time scales from microseconds to years. The scientific instruments consists of two pointed instruments, the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer Program
The Explorers program is a NASA exploration program that provides flight opportunities for physics, geophysics, heliophysics, and astrophysics investigations from space. Launched in 1958, Explorer 1 was the first spacecraft of the United States to achieve orbit. Over 90 space missions have been launched since. Starting with Explorer 6, it has been operated by NASA, with regular collaboration with a variety of other institutions, including many international partners. Launchers for the Explorer program have included Juno I, Juno II, various Thor, Scout, Delta and Pegasus launch vehicles, and Falcon 9. The program has three classes: Medium-Class Explorers (MIDEX), Small Explorers (SMEX), and University-Class Explorers (UNEX), with select Missions of Opportunity operated with other agencies. History Early Explorer satellites The Explorer program began as a U.S. Army proposal ( Project Orbiter) to place a "civilian" artificial satellite into orbit during the Interna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Stars
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. white holes, quark stars, and strange stars), neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. Neutron stars have a radius on the order of and a mass of about 1.4 solar masses. They result from the supernova explosion of a massive star, combined with gravitational collapse, that compresses the core past white dwarf star density to that of atomic nuclei. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time; however, they may still evolve further through collision or accretion. Most of the basic models for these objects imply that neutron stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons (subatomic particles with no net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons); the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. It is one of ten major NASA field centers, named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.CENSUS 2000 BLOCK MAP: GODDARD CDP " U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved on September 1, 2018. 1990 Census map of Prince George's County [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has a great effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, it has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly. Objects whose gravitational fields are too strong for light to escape were first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Bursts
X-ray bursters are one class of X-ray binary stars exhibiting X-ray bursts, periodic and rapid increases in luminosity (typically a factor of 10 or greater) that peak in the X-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These astrophysical systems are composed of an accreting neutron star and a main sequence companion 'donor' star. There are two types of X-ray bursts, designated I and II. Type I bursts are caused by thermonuclear runaway, while type II arise from the release of gravitational (potential) energy liberated through accretion. For type I (thermonuclear) bursts, the mass transferred from the donor star accumulates on the surface of the neutron star until it ignites and fuses in a burst, producing X-rays. The behavior of X-ray bursters is similar to the behavior of recurrent novae. In that case the compact object is a white dwarf that accretes hydrogen that finally undergoes explosive burning. The compact object of the broader class of X-ray binaries is either a neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Vehicle
A launch vehicle or carrier rocket is a rocket designed to carry a payload (spacecraft or satellites) from the Earth's surface to outer space. Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pads, supported by a launch control center and systems such as vehicle assembly and fueling. Launch vehicles are engineered with advanced aerodynamics and technologies, which contribute to large operating costs. An orbital launch vehicle must lift its payload at least to the boundary of space, approximately and accelerate it to a horizontal velocity of at least . Suborbital vehicles launch their payloads to lower velocity or are launched at elevation angles greater than horizontal. Practical orbital launch vehicles are multistage rockets which use chemical propellants such as solid fuel, liquid hydrogen, kerosene, liquid oxygen, or Hypergolic propellants. Launch vehicles are classified by their orbital payload capacity, ranging from small-, medium-, heavy- to super-heavy lift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Designator
The International Designator, also known as COSPAR ID, is an international identifier assigned to artificial objects in space. It consists of the launch year, a three-digit incrementing launch number of that year and up to a three-letter code representing the sequential identifier of a piece in a launch. In TLE format the first two digits of the year and the dash are dropped. For example1990-037Ais the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' on mission STS-31, which carried the Hubble Space Telescope1990-037B into space. This launch was the 37th known successful launch worldwide in 1990. The designation system has been generally known as the COSPAR system, named for the Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) of the International Council for Science. COSPAR subsumed the first designation system, devised at Harvard University. That system used letters of the Greek alphabet to designate artificial satellites. This was based on the scientific naming convention for natural satellites. For example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracking And Data Relay Satellite System
The U.S. Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System (TDRSS) is a network of American communications satellites (each called a tracking and data relay satellite, TDRS) and ground stations used by NASA for space communications. The system was designed to replace an existing network of ground stations that had supported all of NASA's crewed flight missions. The prime design goal was to increase the time spacecraft were in communication with the ground and improve the amount of data that could be transferred. Many Tracking and Data Relay Satellites were launched in the 1980s and 1990s with the Space Shuttle and made use of the Inertial Upper Stage, a two-stage solid rocket booster developed for the shuttle. Other TDRS were launched by Atlas IIa and Atlas V rockets. The most recent generation of satellites provides ground reception rates of 6 Mbit/s in the S-band and 800 Mbit/s in the Ku- and Ka-bands. This is mainly used by the United States military. Origins To satisfy t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minute And Second Of Arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represented as either , but other representations such as ''true''/''false'', ''yes''/''no'', ''on''/''off'', or ''+''/''−'' are also commonly used. The relation between these values and the physical states of the underlying storage or device is a matter of convention, and different assignments may be used even within the same device or program. It may be physically implemented with a two-state device. The symbol for the binary digit is either "bit" per recommendation by the IEC 80000-13:2008 standard, or the lowercase character "b", as recommended by the IEEE 1541-2002 standard. A contiguous group of binary digits is commonly called a '' bit string'', a bit vector, or a single-dimensional (or multi-dimensional) '' bit array''. A group of eigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |