|
RUNCOM
RUNCOM is a CTSS macro command (script) processor. History Louis Pouzin created RUNCOM for CTSS circa 1963. He released a paper in 1965 describing a design for the Multics shell which includes a brief description of RUNCOM followed by a second paper he released five days later describing a design for RUNCOM that added commands for control flow, conditional branching and looping. In the context of Unix-like systems, the term ''rc'' stands for the phrase "run commands". It is used for any file that contains startup information for a command. From Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie: https://www.oreilly.com/pub/au/2933 O'Reilly, Bio for Vicki Brown Tom Van Vleck, a Multics engineer, has also reminisced about the extension rc: "The idea of having the command processing shell be an ordinary slave program came from the Multics design, and a predecessor program on CTSS by Louis Pouzin called RUNCOM, the source of the '.rc' suffix on some Unix configuration files." This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Pouzin
Louis Pouzin (born 20 April 1931) is a French computer scientist and Internet pioneer. He directed the development of the CYCLADES computer network in France the early 1970s, which implemented a novel design for packet communication. He was the first to implement the end-to-end principle in a wide-area network, which became fundamental to the design of the Internet. This network was the first implementation of the pure datagram model, initially conceived and described by Donald Davies, subsequently named by Halvor Bothner-By, and seen by Louis Pouzin as his personal invention. His work, and that of his colleagues Hubert Zimmerman and Gérard Le Lann, were acknowledged by Vinton Cerf as substantial contributions to the design of TCP/IP, the protocol suite used by the Internet. Biography Louis Pouzin was born in Chantenay-Saint-Imbert, Nièvre, France on 20 April 1931. He studied at the École Polytechnique from 1950 to 1952. Having participated in the design of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
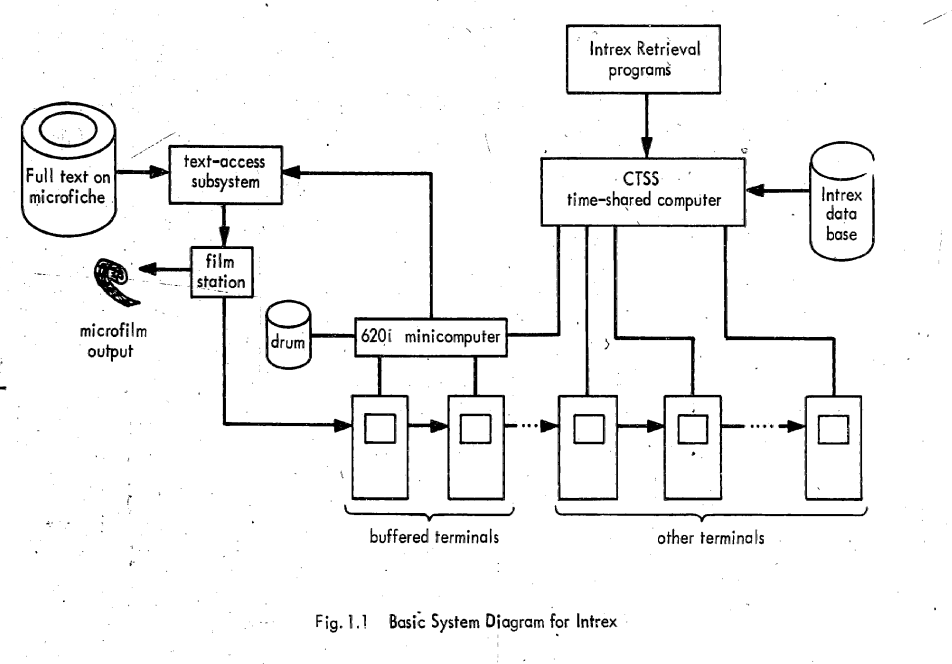
Compatible Time Sharing System
The Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) was the first general purpose time-sharing operating system. Compatible Time Sharing referred to time sharing which was compatible with batch processing; it could offer both time sharing and batch processing concurrently. CTSS was developed at the MIT Computation Center ("Comp Center"). CTSS was first demonstrated on MIT's modified IBM 709 in November 1961. The hardware was replaced with a modified IBM 7090 in 1962 and later a modified IBM 7094 called the "blue machine" to distinguish it from the Project MAC CTSS IBM 7094. Routine service to MIT Comp Center users began in the summer of 1963 and was operated there until 1968. A second deployment of CTSS on a separate IBM 7094 that was received in October 1963 (the "red machine") was used early on in Project MAC until 1969 when the red machine was moved to the Information Processing Center and operated until July 20, 1973. CTSS ran on only those two machines; however, there were remote CTS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Configuration File
A configuration file, a.k.a. config file, is a computer file, file that stores computer data, data used to configure a software system such as an application software, application, a server (computing), server or an operating system. Some applications provide a tool to create, modify, and verify the syntax of their configuration files sometimes via graphical user interface (GUI). For context, system administrators may be expected to create and modify plain text, text config files via a text editor. For server processes and operating-system settings, there is often no standard tool, but operating systems may provide graphical interfaces such as YaST or debconf. Some computer programs only read their configuration files at Booting, startup. Others periodically check the configuration files for changes. Users can instruct some programs to re-read the configuration files and apply the changes to the current process, or indeed to read arbitrary files as a configuration file. There ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Run Command
The Run command on an operating system such as Microsoft Windows and Unix-like systems is used to directly open an application or document whose Path (computing), path is known. Overview The command functions more or less like a single-line command-line interface. In the GNOME (a UNIX-like derivative) interface, the Run command is used to run applications via terminal commands. It can be accessed by pressing . KDE (a UNIX-like derivative) has similar functionality called KRunner. It is accessible via the same key binds. The Multics shell includes a run command to run a command in an isolated environment. The Digital Equipment Corporation, DEC TOPS-10 and TOPS-20 Command Processor included a RUN command (computing), command for running executable programs. In the BASIC programming language, RUN is used to start program execution from direct mode, or to start an Overlay (programming), overlay program from a loader (computing), loader program. Accessing the Run command Starting w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCD (character Encoding)
BCD (''binary-coded decimal''), also called alphanumeric BCD, alphameric BCD, BCD Interchange Code, or BCDIC, is a family of representations of numerals, uppercase Latin letters, and some special and control characters as six-bit character codes. Unlike later encodings such as ASCII, BCD codes were not standardized. Different computer manufacturers, and even different product lines from the same manufacturer, often had their own variants, and sometimes included unique characters. Other six-bit encodings with completely different mappings, such as some FIELDATA variants or Transcode, are sometimes incorrectly termed BCD. Many variants of BCD encode the characters '0' through '9' as the corresponding binary values. History Technically, '' binary-coded decimal'' describes the encoding of decimal numbers where each decimal digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four. With the introduction of the '' IBM card'' in 1928, IBM created a code capable of representing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric S
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, Eirik, or Eiríkur is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''* aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form '' Euric''. The second element ''- ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic ''* ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''* ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European root * h₃rḗǵs. The name is thus usually taken to mean "sole ruler, autocrat" or "eternal ruler, ever powerful". ''Eric'' used in the sense of a proper noun meaning "one ruler" may be the origin of '' Eriksgata'', and if so it would have meant "one ruler's journey". The tour was the medieval Swedish king's journey, when newly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Art Of Unix Programming
''The Art of Unix Programming'' by Eric S. Raymond is a book about the history and culture of Unix programming from its earliest days in 1969 to 2003 when it was published, covering both genetic derivations such as BSD and conceptual ones such as Linux. The author utilizes a comparative approach to explaining Unix by contrasting it to other operating systems including desktop-oriented ones such as Microsoft Windows and the classic Mac OS to ones with research roots such as EROS and Plan 9 from Bell Labs. The book was published by Addison-Wesley, September 17, 2003, and is also available online, under a Creative Commons license with additional clauses. Contributors The book contains many contributions, quotations and comments from UNIX gurus past and present. These include: *Ken Arnold (author of curses and co-author of '' Rogue'') * Steve Bellovin * Stuart Feldman *Jim Gettys * Stephen C. Johnson *Brian Kernighan * David Korn *Mike Lesk *Doug McIlroy * Marshall Kirk McKusick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vim (text Editor)
Vim (; : "Vim is pronounced as one word, like Jim, not vi-ai-em. It's written with a capital, since it's a name, again like Jim." ''vi improved'') is a free and open-source, screen-based text editor program. It is an improved Clone (computing), clone of Bill Joy's vi (text editor), vi. Vim's author, Bram Moolenaar, derived Vim from a port of the Stevie (text editor), Stevie editor for Amiga and released a version to the public in 1991. Vim is designed for use both from a command-line interface and as a standalone application in a graphical user interface. Since its release for the Amiga, cross-platform development has made it available on #Availability, many other systems. In 2018, it was voted the most popular editor amongst ''Linux Journal'' readers; in 2015 the Stack Overflow developer survey found it to be the third most popular text edit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rc Shell
rc (for "run commands") is the command-line interpreter for Version 10 Unix and Plan 9 from Bell Labs operating systems. It resembles the Bourne shell, but its syntax is somewhat simpler. It was created by Tom Duff, who is better known for an unusual C programming language construct (" Duff's device"). A port of the original rc to Unix is part of Plan 9 from User Space. A rewrite of rc for Unix-like operating systems by Byron Rakitzis is also available but includes some incompatible changes. Rc uses C-like control structures instead of the original Bourne shell's ALGOL-like structures, except that it uses an if not construct instead of else, and has a Bourne-like for loop to iterate over lists. In rc, all variables are lists of strings, which eliminates the need for constructs like "$@". Variables are not re-split when expanded. The language is described in Duff's paper. Influences es ''es'' (for "extensible shell") is an open source, command line interpreter developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Duff
Thomas Douglas Selkirk Duff (born December 8, 1952) is a Canadian computer programmer. Life and career Early life Duff was born in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and was named for his putative ancestor, the fifth Earl of Selkirk. He grew up in Toronto and Leaside. In 1974 he graduated from the University of Waterloo with a B.Math and, two years later, was awarded an M.Sc. from the University of Toronto. Programming career Duff worked at the New York Institute of Technology Computer Graphics Lab and the Mark Williams Company in Chicago before moving to Lucasfilm's Computer Research and Development Division. He and Thomas Porter, another Lucasfilm employee, developed a new approach to compositing images; their 1984 paper, "Compositing Digital Images", is " e seminal work on an algebra for image compositing", according to Keith Packard, and " Porter-Duff compositing" is now a key technique in computer graphics. (See, for example, XRender and Glitz.) Duff later worked for 12 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Van Vleck
Tom Van Vleck is an American computer software engineer. Life and work Van Vleck graduated from MIT in 1965 with a BS in Mathematics. He worked on CTSS at MIT, and co-authored its first email program with Noel Morris. In 1965, he joined Project MAC, the predecessor of the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory.''A Marriage of Convenience: THE FOUNDING OF THE MIT ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE LABORATORY'' Chiou, Stefanie; et al. (2001) He worked on the development of for more than 16 years at and at [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plan 9 From Bell Labs
Plan 9 from Bell Labs is a distributed operating system which originated from the Computing Science Research Center (CSRC) at Bell Labs in the mid-1980s and built on UNIX concepts first developed there in the late 1960s. Since 2000, Plan 9 has been free and open-source. The final official release was in early 2015. Under Plan 9, UNIX's '' everything is a file'' metaphor is extended via a pervasive network-centric filesystem, and the cursor-addressed, terminal-based I/O at the heart of UNIX-like operating systems is replaced by a windowing system and graphical user interface without cursor addressing, although rc, the Plan 9 shell, is text-based. The name ''Plan 9 from Bell Labs'' is a reference to the Ed Wood 1957 cult science fiction Z-movie '' Plan 9 from Outer Space''. The system continues to be used and developed by operating system researchers and hobbyists. History Plan 9 from Bell Labs was originally developed, starting in the late 1980s, by members of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |