|
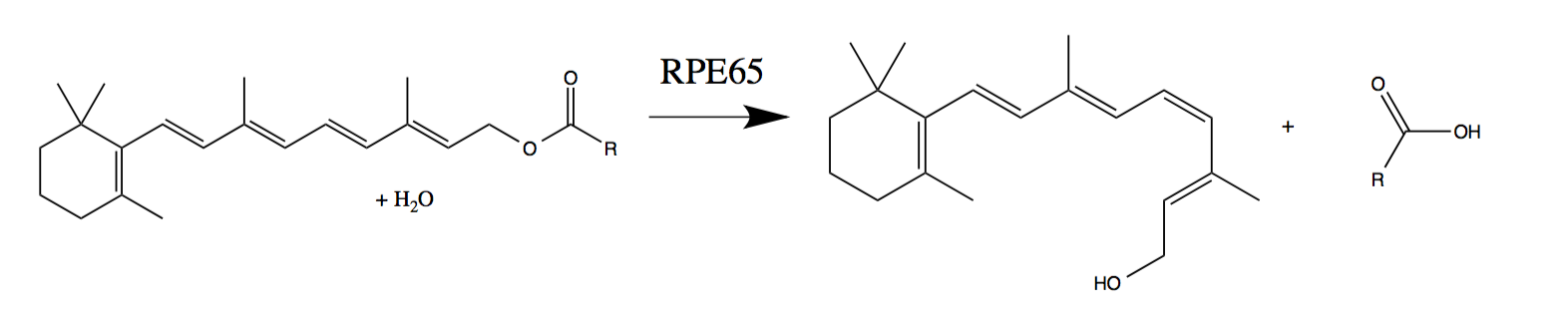
RPE65
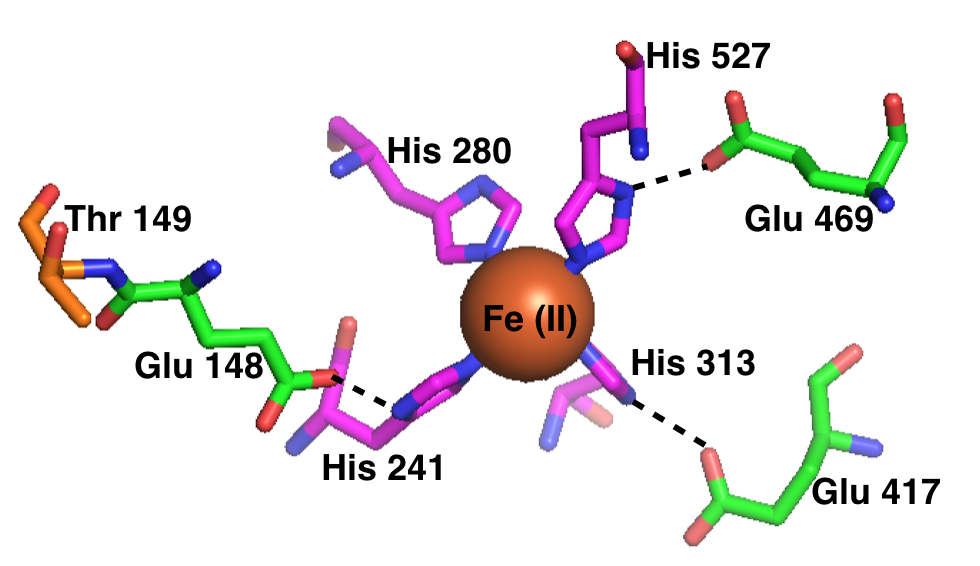
Retinal pigment epithelium-specific 65 kDa protein, also known as retinoid isomerohydrolase, is an enzyme of the vertebrate visual cycle that is encoded in humans by the ''RPE65'' gene. RPE65 is expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE, a layer of epithelial cells that nourish the photoreceptor cells) and is responsible for the conversion of all-trans- retinyl esters to 11-cis-retinol during phototransduction. 11-cis-retinol is then used in visual pigment regeneration in photoreceptor cells. RPE65 belongs to the carotenoid oxygenase family of enzymes. Function RPE65 is a critical enzyme in the vertebrate visual cycle found in the retinal pigmented epithelium. It is also found in rods and cones. The photoisomerization of 11-cis-retinal to all-trans-retinal initiates the phototransduction pathway through which the brain detects light. All-trans-retinol is not photoactive and therefore must be reconverted to 11-cis-retinal before it can recombine with opsin to form an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotenoid Oxygenase
__NOTOC__ Carotenoid oxygenases are a family of enzymes involved in the cleavage of carotenoids to produce, for example, retinol, commonly known as vitamin A. This family includes an enzyme known as RPE65 which is abundantly expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium where it catalyzed the formation of 11-cis-retinol from all-trans-retinyl esters. Carotenoids such as beta-carotene, lycopene, lutein and beta-cryptoxanthin are produced in plants and certain bacteria, algae and fungi, where they function as accessory photosynthetic pigments and as scavengers of oxygen radicals for photoprotection. They are also essential dietary nutrients in animals. Carotenoid oxygenases cleave a variety of carotenoids into a range of biologically important products, including apocarotenoids in plants that function as hormones, pigments, flavours, floral scents and defence compounds, and retinoids in animals that function as vitamins, chromophores for opsins and signalling molecules. Examples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Phototransduction
Visual phototransduction is the sensory transduction process of the visual system by which light is detected to yield nerve impulses in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye in humans and other vertebrates. It relies on the visual cycle, a sequence of biochemical reactions in which a molecule of retinal bound to opsin undergoes photoisomerization, initiates a cascade that signals detection of the photon, and is indirectly restored to its photosensitive isomer for reuse. Phototransduction in some invertebrates such as fruit flies relies on similar processes. Photoreceptors The photoreceptor cells involved in vertebrate vision are the rods, the cones, and the photosensitive ganglion cells (ipRGCs). These cells contain a chromophore ( 11-''cis''-retinal, the aldehyde of vitamin A1 and light-absorbing portion) that is bound to a cell membrane protein, opsin. Rods deal with low light level and do not mediate color vision. Cones, on the other hand, can code th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinol Isomerase
In enzymology, a retinol isomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :all-trans-retinol \rightleftharpoons 11-cis-retinol Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, all-trans-retinol, and one product, 11-cis-retinol. These enzymes are alternatively referred to as retinoid isomerases. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically cis-trans isomerases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is all-trans-retinol 11-cis-trans-isomerase. This enzyme is also called all-trans-retinol isomerase. This enzyme participates in retinol metabolism. In vertebrates, RPE65 is the active retinol isomerase in the visual cycle. A lack of RPE65 function results in congenital blindness in children (specifically Leber congenital amaurosis). Emixustat, a partial inhibitor of RPE65, is currently in FDA clinical trials for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototransduction
Visual phototransduction is the sensory transduction process of the visual system by which light is detected to yield nerve impulses in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye in humans and other vertebrates. It relies on the visual cycle, a sequence of biochemical reactions in which a molecule of retinal bound to opsin undergoes photoisomerization, initiates a cascade that signals detection of the photon, and is indirectly restored to its photosensitive isomer for reuse. Phototransduction in some invertebrates such as fruit flies relies on similar processes. Photoreceptors The photoreceptor cells involved in vertebrate vision are the rods, the cones, and the photosensitive ganglion cells (ipRGCs). These cells contain a chromophore ( 11-''cis''-retinal, the aldehyde of vitamin A1 and light-absorbing portion) that is bound to a cell membrane protein, opsin. Rods deal with low light level and do not mediate color vision. Cones, on the other hand, can code the color of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinol
Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent vitamin A deficiency, especially that which results in xerophthalmia. In regions where deficiency is common, a single large dose is recommended to those at high risk twice a year. It is also used to reduce the risk of complications in measles patients. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle. Retinol at normal doses is well tolerated. High doses may cause enlargement of the liver, dry skin, and hypervitaminosis A. High doses during pregnancy may harm the fetus. The body converts retinol to retinal and retinoic acid, through which it acts. Dietary sources include fish, dairy products, and meat. Retinol was discovered in 1909, isolated in 1931, and first made in 1947. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Retinol is available as a generic medication and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinyl Palmitate
Retinyl palmitate, or vitamin A palmitate, is the ester of retinol (vitamin A) and palmitic acid, with formula C36H60O2. It is the most abundant form of vitamin A storage in animals. An alternate spelling, retinol palmitate, which violates the -yl organic chemical naming convention for esters, is also frequently seen. Biology Animals use long-chain esters of vitamin A, most abundantly the palmitate form, as a form of vitamin A storage. The storage reaction is catalyzed by LRAT, and the inverse is catalyzed by REH. The esters are also intermediates in the visual cycle: RPE65 isomerizes the retinyl part to 11-cis-retinal. Uses Vitamin A palmitate is a common vitamin supplement, available in both oral and injectable forms for treatment of vitamin A deficiency, under the brand names Aquasol A, Palmitate A and many others. It is a constituent of intra ocular treatment for dry eyes at a concentration of 138 μg/g (VitA-Pos) by Ursapharm. It is a pre-formed version of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABA-ergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in three optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedral Molecular Geometry
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry, also called square bipyramidal, describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix ''octa''. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compounds are sulfur hexafluoride SF6 and molybdenum hexacarbonyl Mo(CO)6. The term "octahedral" is used somewhat loosely by chemists, focusing on the geometry of the bonds to the central atom and not considering differences among the ligands themselves. For example, , which is not octahedral in the mathematical sense due to the orientation of the bonds, is referred to as octahedral. The concept of octahedral coordination geometry was developed by Alfred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' Chemical specificity, specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoid
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth. Retinoids have many important functions throughout the body including roles in vision, regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation, growth of bone tissue, immune function, and activation of tumor suppressor genes. Research is also being done into their ability to treat skin cancers. Currently, alitretinoin (9-''cis''-retinoic acid) may be used topically to help treat skin lesions from Kaposi's sarcoma, and tretinoin (all-''trans''- retinoic acid) is used to treat acute promyelocytic leukemia. Types There are four generations of retinoids: * First generation include retinol, retinal, tretinoin (retinoic acid), isotretinoin, and alitretinoin * Second generation include etretinate and its metabolite acitretin * Third generation include adapalene, bexarotene, and tazarote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |