|
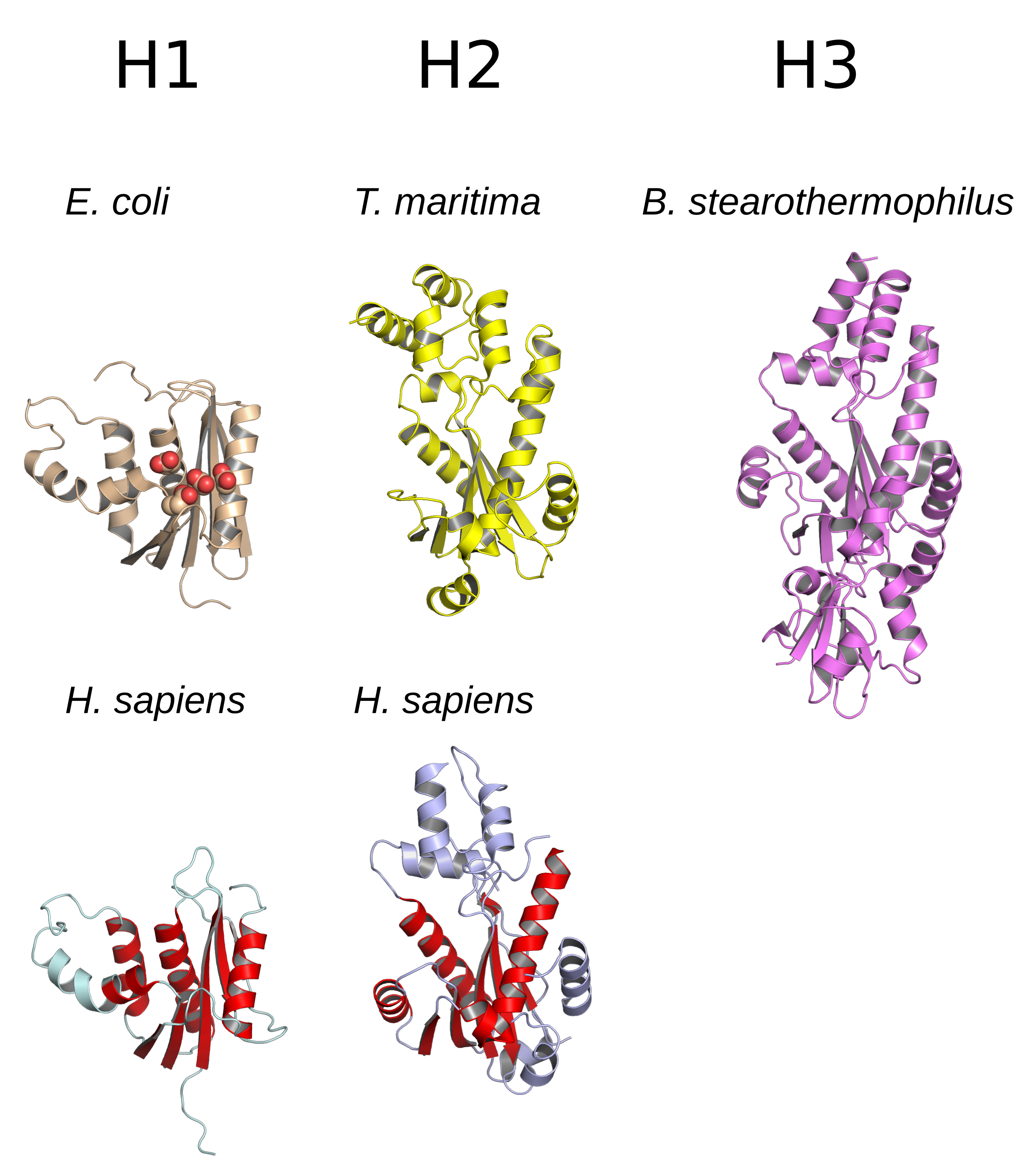
RNASEH2C
Ribonuclease H2 subunit C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2C gene. Ribonuclease H, RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit (RNASEH2A, A) and two non-catalytic subunits (RNASEH2B, B and C), and degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. Mutations in this gene are a cause of Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome type 3 (AGS3). Function This gene encodes a ribonuclease H subunit that can cleave ribonucleotides from RNA:DNA duplexes. Mutations in this gene cause Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome-3, a disease that causes severe neurologic dysfunction. A pseudogene for this gene has been identified on chromosome Y, near the sex determining region Y (SRY) gene. References Further reading * * External links * {{NLM content ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribonuclease H
Ribonuclease H (abbreviated RNase H or RNH) is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/ DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly all organisms, from bacteria to archaea to eukaryotes. The family is divided into evolutionarily related groups with slightly different substrate preferences, broadly designated ribonuclease H1 and H2. The human genome encodes both H1 and H2. Human ribonuclease H2 is a heterotrimeric complex composed of three subunits, mutations in any of which are among the genetic causes of a rare disease known as Aicardi–Goutières syndrome. A third type, closely related to H2, is found only in a few prokaryotes, whereas H1 and H2 occur in all domains of life. Additionally, RNase H1-like retroviral ribonuclease H domains occur in multidomain reverse transcriptase proteins, which are encoded by retroviruses such as HIV and are required for vira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNASEH2A
Ribonuclease H2 subunit A, also known as RNase H2 subunit A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEH2A'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the heterotrimeric type II ribonuclease H enzyme (RNaseH2). The other two subunits are the non-catalytic RNASEH2B and RNASEH2C. RNaseH2 is the major source of ribonuclease H activity in mammalian cells and endonucleolytically cleaves ribonucleotides. It is predicted to remove Okazaki fragment RNA primers during lagging strand DNA synthesis and to excise single ribonucleotides from DNA-DNA duplexes. Clinical significance Mutations in this gene cause Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), an autosomal recessive neurological disorder characterized by progressive microcephaly and psychomotor retardation, intracranial calcifications, elevated levels of interferon-alpha and white blood cells in the cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNASEH2B
Ribonuclease H2, subunit B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEH2B'' gene. RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit ( A) and two non-catalytic subunits (B and C), and degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. The non-catalytic B subunit of RNase H2 is thought to play a role in DNA replication. Mutations in this gene are a cause of Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome type 2 (AGS2). Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of RNASEH2B function. A conditional knockout mouse line, called ''Rnaseh2btm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi'' was generated as part of the International Knockout Mouse Consortium program — a high-throughput mutagenesis project to generate and distribute animal models of disease to interested scientists. Male and female animals underwent a standardized phenotypic screen to determine the effects of deletion. Twenty four tests were carried out on mutant mice and three significant abnormalities were observed. No homozygous mutant embryos wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some stag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |