|
RM Nimbus
RM Nimbus was a range of personal computers from British company Research Machines (now RM Education) sold from 1985 until the early 1990s, after which the designation ''Nimbus'' was discontinued. The first of these computers, the RM Nimbus PC-186, was not IBM PC compatible, but its successors the PC-286 and PC-386 were. RM computers were predominantly sold to schools and colleges in the United Kingdom for use as LAN workstations in classrooms. Models PC-186 The RM Nimbus PC-186 was a 16-bit microcomputer introduced in 1985. It is one of a small number of computers based on the Intel 80186 processor, a version of the Intel 8086 (as used by the IBM PC) originally intended as a processor for embedded systems. It ran MS-DOS 3.1 but was not IBM PC compatible. The PC-186 could run Windows versions up to and including Windows 3.0, but only in real mode, as protected mode was only available on 286 or higher processors. Most PC-186 systems were used as workstations within a Local Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. Primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s, the term home computer was also used. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with the machines. While personal computer users may develop their own applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software (" freeware"), which is most often proprietary, or free and open-source software, which is provided in "ready-to-run", or binary, form. Software for personal computers is typically developed and distributed independently from the hardware or operating system ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Personal Computer
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team of engineers and designers directed by Don Estridge in Boca Raton, Florida. The machine was based on open architecture and third-party peripherals. Over time, expansion cards and software technology increased to support it. The PC had a substantial influence on the personal computer market. The specifications of the IBM PC became one of the most popular computer design standards in the world. The only significant competition it faced from a non-compatible platform throughout the 1980s was from the Apple Macintosh product line. The majority of modern personal computers are distant descendants of the IBM PC. History Prior to the 1980s, IBM had largely been known as a provider of business computer systems. As the 1980s opened, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LAN Manager
LAN Manager is a discontinued network operating system (NOS) available from multiple vendors and developed by Microsoft in cooperation with 3Com Corporation. It was designed to succeed 3Com's 3+Share network server software which ran atop a heavily modified version of MS-DOS. History The LAN Manager OS/2 operating system was co-developed by IBM and Microsoft, using the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. It originally used SMB atop either the NetBIOS Frames (NBF) protocol or a specialized version of the Xerox Network Systems (XNS) protocol. These legacy protocols had been inherited from previous products such as MS-Net for MS-DOS, Xenix-NET for MS-Xenix, and the afore-mentioned 3+Share. A version of LAN Manager for Unix-based systems called LAN Manager/X was also available. Lan Manager/X was the basis for Digital Equipment Corporation's Pathworks product for OpenVMS, Ultrix and Tru64. In 1990, Microsoft announced LAN Manager 2.0 with a host of improvements, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Program Manager
Program Manager is the shell of Windows 3.x and Windows NT 3.x operating systems. This shell exposed a task-oriented graphical user interface (GUI), consisting of ''icons'' (shortcuts for programs) arranged into ''program groups''. It replaced ''MS-DOS Executive'', a file manager, as the default Windows shell. OS/2 2.0 and later included the Program Manager as part of its Win-OS/2 compatibility layer. Win-OS/2, including the Program Manager, are still included in later derivatives of OS/2 such as ArcaOS. Overview Program Manager descends from ''Desktop Manager'' (also known as Presentation Manager), the shell for OS/2 1.2. Unlike Desktop Manager, which presents its program groups in a simple list, and opens each group in a separate window, Program Manager opens program groups in child windows using the new multiple document interface in Windows 3.x. The icons used to represent Program Manager itself, program groups, and DOS applications in Windows 3.0 are carried over from O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BNC Connector
The BNC connector (initialism of "Bayonet Neill–Concelman") is a miniature quick connect/disconnect radio frequency connector used for coaxial cable. It is designed to maintain the same characteristic impedance of the cable, with 50 ohm and 75 ohm types being made. It is usually applied for video and radio frequency connections up to about 2 GHz and up to 500 volts. The connector has a twist to lock design with two lugs in the female portion of the connector engaging a slot in the shell of the male portion. The type was introduced on military radio equipment in the 1940s and has since become widely applied in radio systems, and is a common type of video connector. Similar radio-frequency connectors differ in dimensions and attachment features, and may allow for higher voltages, higher frequencies, or three-wire connections. Description The BNC connector features two bayonet lugs on the female connector; mating is fully achieved with a quarter turn of the coupling nut. It u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micro Channel Architecture
Micro Channel architecture, or the Micro Channel bus, is a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers until the mid-1990s. Its name is commonly abbreviated as "MCA", although not by IBM. In IBM products, it superseded the ISA bus and was itself subsequently superseded by the PCI bus architecture. Background The development of Micro Channel was driven by both technical and business pressures. Technology The IBM AT bus, which later became known as the Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus, had a number of technical design limitations, including: * A slow bus speed. * A limited number of interrupts, fixed in hardware. * A limited number of I/O device addresses, also fixed in hardware. * Hardwired and complex configuration with no conflict resolution. * Deep links to the architecture of the 80x86 chip familyUse of the ISA bus outside of machines employing the 80x86 CPU family was rare. Notable non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
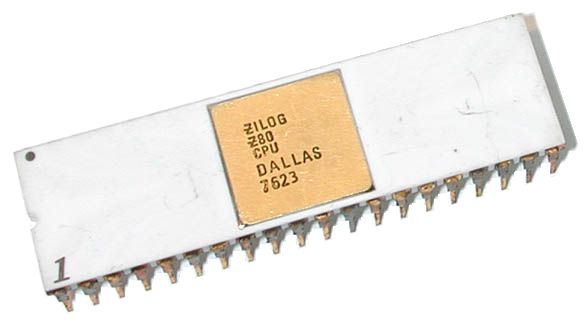
Zilog
Zilog, Inc. is an American manufacturer of microprocessors and 8-bit and 16-bit microcontrollers. It is also a supplier of application-specific embedded system-on-chip (SoC) products. Its most famous product is the Z80 series of 8-bit microprocessors that were compatible with the Intel 8080 but significantly cheaper. The Z80 was widely used during the 1980s in many popular home computers such as the TRS-80, MSX, Amstrad CPC and the ZX Spectrum, as well as arcade games such as '' Pac-Man''. The company also made 16- and 32-bit processors, but these did not see widespread use. From the 1990s, the company focused primarily on the microcontroller market. The name (pronunciation varies) is an acronym of ''Z integrated logic'', also thought of as "Z for the last word of Integrated Logic". In the oral history interview video which Federico Faggin (co-founder of Zilog) recorded for the Computer History Museum, he pronounced Zilog with a long "i" () consistently. History Zilog wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhanced Small Disk Interface
Enhanced Small Disk Interface (ESDI) is an obsolete disk interface designed by Maxtor Corporation in the early 1980s to be a follow-on to the ST-412/506 interface. ESDI improved on ST-506 by moving certain parts that were traditionally kept on the controller (such as the data separator) into the drives themselves, and also generalizing the control bus such that more kinds of devices (such as removable disks and tape drives) could be connected. ESDI uses the same cabling as ST-506 (one 34-pin common control cable, and a 20-pin data channel cable for each device), and thus could easily be retrofitted to ST-506 applications. ESDI was popular in the mid-to-late 1980s, when SCSI and IDE technologies were young and immature, and ST-506 was neither fast nor flexible enough. ESDI could handle data rates of 10, 15, or 20 Mbit/s (as opposed to ST-506's top speed of 7.5 Mbit/s), and many high-end SCSI drives of the era were actually high-end ESDI drives with SCSI bridge A bridge is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Area Network
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves leased telecommunication circuits. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies in use for local area networks. Historical network technologies include ARCNET, Token Ring and AppleTalk. History The increasing demand and usage of computers in universities and research labs in the late 1960s generated the need to provide high-speed interconnections between computer systems. A 1970 report from the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory detailing the growth of their "Octopus" network gave a good indication of the situation. A number of experimental and early commercial LAN technologies were developed in the 1970s. Cambridge Ring was developed at Cambridge University starting in 1974. Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Mode
In computing, protected mode, also called protected virtual address mode, is an operational mode of x86-compatible central processing units (CPUs). It allows system software to use features such as virtual memory, paging and safe multi-tasking designed to increase an operating system's control over application software. When a processor that supports x86 protected mode is powered on, it begins executing instructions in real mode, in order to maintain backward compatibility with earlier x86 processors. Protected mode may only be entered after the system software sets up one descriptor table and enables the Protection Enable (PE) bit in the control register 0 (CR0). Protected mode was first added to the x86 architecture in 1982, with the release of Intel's 80286 (286) processor, and later extended with the release of the 80386 (386) in 1985. Due to the enhancements added by protected mode, it has become widely adopted and has become the foundation for all subsequent enhanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Mode
Real mode, also called real address mode, is an operating mode of all x86-compatible CPUs. The mode gets its name from the fact that addresses in real mode always correspond to real locations in memory. Real mode is characterized by a 20-bit segmented memory address space (giving 1 MB of addressable memory) and unlimited direct software access to all addressable memory, I/O addresses and peripheral hardware. Real mode provides no support for memory protection, multitasking, or code privilege levels. Before the release of the 80286, which introduced protected mode, real mode was the only available mode for x86 CPUs; and for backward compatibility, all x86 CPUs start in real mode when reset, though it is possible to emulate real mode on other systems when starting on other modes. History The 286 architecture introduced protected mode, allowing for (among other things) hardware-level memory protection. Using these new features, however, required a new operating system that was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)