|
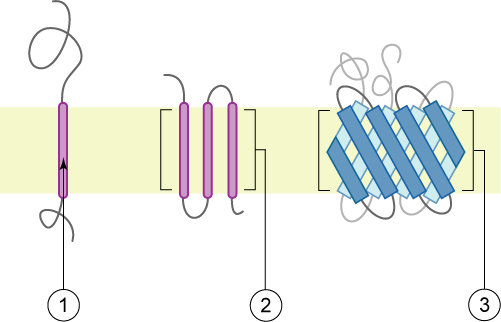
RHBDL2
Rhomboid-related protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHBDL2 gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the rhomboid protease family of integral membrane proteins. This family contains proteins that are related to Drosophila rhomboid-1. Members of this family are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes and are thought to function as intramembrane serine proteases. RHBDL2 functions as a sheddase and is localized to the plasma membrane. Known substrates of RHBDL2 include thrombomodulin and epidermal growth factor Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor, EGFR. Human EGF is 6-k Da and has 53 amino acid residues and three intramolecular disulfide bonds. EGF was originally descr ...; profiling of the substrate repertoire of RHBDL2 has identified a number of additional type I membrane proteins substrates, including BCAM, SPINT1, and CLCP1. Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhomboid Protease
The rhomboid proteases are a family of enzymes that exist in almost all species. They are proteases: they cut the polypeptide chain of other proteins. This proteolytic cleavage is irreversible in cells, and an important type of cellular regulation. Although proteases are one of the earliest and best studied class of enzyme, rhomboids belong to a much more recently discovered type: the intramembrane proteases. What is unique about intramembrane proteases is that their active sites are buried in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, and they cleave other transmembrane proteins within their transmembrane domains. About 30% of all proteins have transmembrane domains, and their regulated processing often has major biological consequences. Accordingly, rhomboids regulate many important cellular processes, and may be involved in a wide range of human diseases. Intramembrane proteases Rhomboids are intramembrane serine proteases. The other types of intramembrane protease are aspartyl- an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhomboid-1
The rhomboid proteases are a family of enzymes that exist in almost all species. They are proteases: they cut the polypeptide chain of other proteins. This proteolytic cleavage is irreversible in cells, and an important type of cellular regulation. Although proteases are one of the earliest and best studied class of enzyme, rhomboids belong to a much more recently discovered type: the intramembrane proteases. What is unique about intramembrane proteases is that their active sites are buried in the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, and they cleave other transmembrane proteins within their transmembrane domains. About 30% of all proteins have transmembrane domains, and their regulated processing often has major biological consequences. Accordingly, rhomboids regulate many important cellular processes, and may be involved in a wide range of human diseases. Intramembrane proteases Rhomboids are intramembrane serine proteases. The other types of intramembrane protease are aspartyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcellular Localization
The cells of eukaryotic organisms are elaborately subdivided into functionally-distinct membrane-bound compartments. Some major constituents of eukaryotic cells are: extracellular space, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), peroxisome, vacuoles, cytoskeleton, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, nuclear matrix and ribosomes. Bacteria also have subcellular localizations that can be separated when the cell is fractionated. The most common localizations referred to include the cytoplasm, the cytoplasmic membrane (also referred to as the inner membrane in Gram-negative bacteria), the cell wall (which is usually thicker in Gram-positive bacteria) and the extracellular environment. The cytoplasm, the cytoplasmic membrane and the cell wall are subcellular localizations, whereas the extracellular environment is clearly not. Most Gram-negative bacteria also contain an outer membrane and periplasmic space. Unlike eukaryotes, most bacteria cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Cell Adhesion Molecule
Basal cell adhesion molecule, also known as Lutheran antigen, is a plasma membrane glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCAM'' gene. BCAM has also recently been designated CD239 (cluster of differentiation 239). Function Lutheran blood group glycoprotein is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and a receptor for the extracellular matrix protein, laminin. The protein contains five, N-terminus, extracellular immunoglobulin domains, a single transmembrane domain, and a short, C-terminal cytoplasmic tail. This protein may play a role in epithelial cell cancer and in vaso-occlusion of red blood cells in sickle cell disease. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Interactions BCAM has been shown to interact with Laminin, alpha 5 Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type I Membrane Protein
A single-pass membrane protein also known as single-spanning protein or bitopic protein is a transmembrane protein that spans the lipid bilayer only once. These proteins may constitute up to 50% of all transmembrane proteins, depending on the organism, and contribute significantly to the network of interactions between different proteins in cells, including interactions via transmembrane alpha helices. They usually include one or several water-soluble domains situated at the different sides of biological membranes, for example in single-pass transmembrane receptors. Some of them are small and serve as regulatory or structure-stabilizing subunits in large multi-protein transmembrane complexes, such as photosystems or the respiratory chain. A 2013 estimate identified about 1300 single-pass membrane proteins in the human genome. Topology-based classification Bitopic proteins are classified into 4 types, depending on their transmembrane topology and location of the transmembrane heli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Growth Factor
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a protein that stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor, EGFR. Human EGF is 6-k Da and has 53 amino acid residues and three intramolecular disulfide bonds. EGF was originally described as a secreted peptide found in the submaxillary glands of mice and in human urine. EGF has since been found in many human tissues, including platelets, submandibular gland (submaxillary gland), and parotid gland. Initially, human EGF was known as urogastrone. Structure In humans, EGF has 53 amino acids (sequence NSDSECPLSHDGYCLHDGVCMYIEALDKYACNCVVGYIGERCQYRDLKWWELR), with a molecular mass of around 6 kDa. It contains three disulfide bridges (Cys6-Cys20, Cys14-Cys31, Cys33-Cys42). Function EGF, via binding to its cognate receptor, results in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Salivary EGF, which seems to be regulated by dietary inorganic iodine, also plays an important physiological role in the maintenance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombomodulin
Thrombomodulin (TM), CD141 or BDCA-3 is an integral membrane protein expressed on the surface of endothelial cells and serves as a cofactor for thrombin. It reduces blood coagulation by converting thrombin to an anticoagulant enzyme from a procoagulant enzyme. Thrombomodulin is also expressed on human mesothelial cell, monocyte and a dendritic cell subset. Genetics and structure In humans, thrombomodulin is encoded by the gene. The protein has a molecular mass of 74k Da, and consists of a single chain with six tandemly repeated EGF-like domains, a Serine/Threonine-rich spacer and a transmembrane domain. It is a member of the C-type lectin domain (CTLD) group 14 family. Function Thrombomodulin functions as a cofactor in the thrombin-induced activation of protein C in the anticoagulant pathway by forming a 1:1 stoichiometric complex with thrombin. This raises the speed of protein C activation thousandfold. Thrombomodulin-bound thrombin has procoagulant effect at the same ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine Protease
Serine proteases (or serine endopeptidases) are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 16 superfamilies (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent convergent evolution of the catalytic mechanism. The majority belong to the S1 family of the PA clan (superfamily) of proteases. For superfamilies, P: superfamily, containing a mixture of nucleophile class families, S: purely serine proteases. superfamily. Within each superfamily, families are designated by their catalytic nucleophile, (S: serine proteases). Substrate specificity Serine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheddase
Sheddases are membrane-bound enzymes that cleave extracellular portions of transmembrane proteins, releasing the soluble ectodomains from the cell surface. Many sheddases are members of the ADAM or aspartic protease (BACE) protein families. These enzymes can activate a transmembrane protein if it is a receptor (e.g., HER2), or cut off the part of the transmembrane protein which has already bound an agonist (e.g., in the case of EGFR), allowing this agonist to go and stimulate a receptor on another cell. Hence, sheddases demultiply the yield of agonists. Sheddase inhibitors active on ADAM10 and ADAM17 can potentiate anti-cancer therapy. Functions It has been postulated that the activity of sheddases occurs in relation to the amount of general enzymatic activity. Research indicates that sheddases are instead related to phosphatidylserine exposure. When PSA-3 cells' ability to synthesize phosphatidylserine was repressed, sheddase activity decreased, and the sheddase activity retu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |