|
RF Fingerprint
RF is an abbreviation for radio frequency. Rf or RF may also mean: Arts and entertainment * ''Red Faction (series)'', a series of revolution video games * Rinforzando, , in music notation * ''RF Online'', an online RPG made by CCR Businesses * Aero K, IATA code (2020—present) * Florida West International Airways, IATA code (1984—2017) * Regions Financial Corporation, NYSE stock symbol Government and military * France (''République française'') * Russian Federation * Rhodesian Front, former political party in Rhodesia Biology and medicine * Rheumatic fever, an inflammatory disease * Release factors RF1, RF2, RF3, proteins * Reticular formation, in the brainstem * Rheumatoid factor, an antibody * Receptive field, the response characteristic of a neuron * Respiratory failure * Risk factor Other uses in science and technology * Representative fraction * Retardation factor in a chromatographic system * Radiative forcing, the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Frequency
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies and the lower limit of infrared frequencies; these are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Electric current Electric currents that oscillate at radio frequencies (RF currents) have special properties not shared by direct current or lower audio frequency alternating current, such as the 50 or 60 Hz current used in electrical power distribution. * Energy from RF currents in conductors can radiate into space as electromagnetic waves ( radio waves). This is the basis of radio technology. * RF current does not penetrate deeply into electrica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
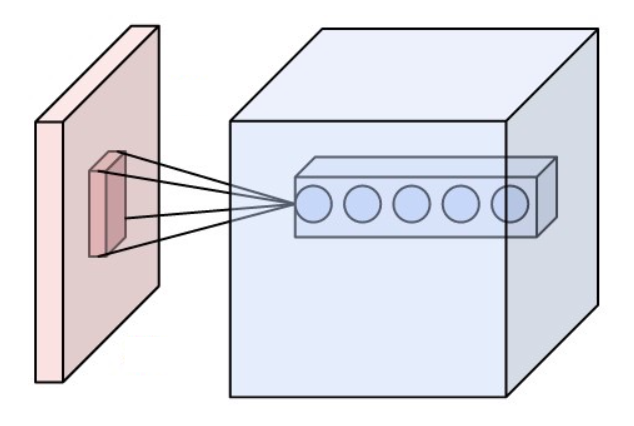
Receptive Field
The receptive field, or sensory space, is a delimited medium where some physiological stimuli can evoke a sensory neuronal response in specific organisms. Complexity of the receptive field ranges from the unidimensional chemical structure of odorants to the multidimensional spacetime of human visual field, through the bidimensional skin surface, being a receptive field for touch perception. Receptive fields can positively or negatively alter the membrane potential with or without affecting the rate of action potentials. A sensory space can be dependent of an animal's location. For a particular sound wave traveling in an appropriate transmission medium, by means of sound localization, an auditory space would amount to a reference system that continuously shifts as the animal moves (taking into consideration the space inside the ears as well). Conversely, receptive fields can be largely independent of the animal's location, as in the case of place cells. A sensory space can also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Sports Confederation
The Swedish Sports Confederation ( sv, Riksidrottsförbundet, RF) is the umbrella organisation of the Swedish sports movement. Through its member organisations, it has three million members in 22,000 clubs. The Confederation was formed on 31 May 1903. Its present chairman, since 2015, is Björn Eriksson. Tasks According to the website, their tasks are to: *Speak on behalf of the united sports movement in contacts with politicians, the government and other institutions/organisations *Coordinate the sports movement in fields like research and development *Provide service in areas where these cannot or don't want to build up their own competence *In certain areas act in place of the government, e g through distributing governmental grants to sports Member organisations Specialised sports federations affiliated to the Swedish Sports Confederation: * Also member of the Swedish Olympic Committee List of presidents The Confederation has had the following presidents: *Crown P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Fielder
A right fielder, abbreviated RF, is the outfielder in baseball or softball who plays defense in right field. Right field is the area of the outfield to the right of a person standing at home plate and facing towards the pitcher's mound. In the numbering system used to record defensive plays, the right fielder is assigned the number 9. Position description Outfielders must cover large distances, so speed, instincts and quickness to react to the ball are key. They must be able to catch fly balls above their head and on the run, as well as prevent balls hit down the right field foul line from getting past them. Being situated 250–300 feet from home plate, they must be able to throw the ball accurately over a long distance to be effective. Of all outfield positions, the right fielder often has the strongest arm, because they are the farthest from third base. As well as the requirements above, the right fielder backs up first base on all throws from the catcher and pitch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon RF Mount
The Canon RF lens mount is an interchangeable- lens mount developed by Canon for its full-frame mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras, and featured first by the EOS R, followed by the EOS RP. The RF mount was announced in September 2018. In May 2022, Canon announced APS-C EOS R cameras (the EOS R10 and EOS R7) and RF-S lenses designed for these cameras. The RF mount allows for the use of Canon EF and EF-S mount lenses using one of three Canon-made lens adapters. When an RF-S or EF-S lens is attached, however, the camera will only function as an APS-C camera, not a full-frame camera. Details Canon full-frame cameras have used the EF lens mount since 1987. In comparison with that mount, the RF mount's inner diameter is the same at 54 mm. The RF mount's flange focal distance at 20 mm is much shorter than that of the Canon EF and EF-S mounts at 44 mm. The EF-M mount has a flange focal distance of 18 mm. An EF-EOS R lens adapter enables Canon EF, EF- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherfordium
Rutherfordium is a chemical element with the symbol Rf and atomic number 104, named after New Zealand-born British physicist Ernest Rutherford. As a synthetic element, it is not found in nature and can only be made in a laboratory. It is radioactive; the most stable known isotope, 267Rf, has a half-life of about 48 minutes. In the periodic table, it is a d-block element and the second of the fourth-row transition elements. It is in period 7 and is a group 4 element. Chemistry experiments have confirmed that rutherfordium behaves as the heavier homolog to hafnium in group 4. The chemical properties of rutherfordium are characterized only partly. They compare well with the other group 4 elements, even though some calculations had indicated that the element might show significantly different properties due to relativistic effects. In the 1960s, small amounts of rutherfordium were produced at Joint Institute for Nuclear Research in the Soviet Union and at Lawrence Berkeley Nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Forest
Random forests or random decision forests is an ensemble learning method for classification, regression and other tasks that operates by constructing a multitude of decision trees at training time. For classification tasks, the output of the random forest is the class selected by most trees. For regression tasks, the mean or average prediction of the individual trees is returned. Random decision forests correct for decision trees' habit of overfitting to their training set. Random forests generally outperform decision trees, but their accuracy is lower than gradient boosted trees. However, data characteristics can affect their performance. The first algorithm for random decision forests was created in 1995 by Tin Kam Ho using the random subspace method, which, in Ho's formulation, is a way to implement the "stochastic discrimination" approach to classification proposed by Eugene Kleinberg. An extension of the algorithm was developed by Leo Breiman and Adele Cutler, who r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiative Forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external drivers of change to Earth's energy balance. System feedbacks and internal variability are related concepts, encompassing other factors that also influence the direction and magnitude of imbalance. Positive radiative forcing means Earth receives more incoming energy from sunlight than it radiates to space. This net gain of energy will cause warming. Conversely, negative radiative forcing means that Earth loses more energy to space than it receives from the sun, which produces cooling. A planet in radiative equilibrium with its parent star and the rest of space can be characterized by net zero radiative forcing and by a planetary equilibrium temperature. Radiative forcing on Earth is meaningfully evaluated at the tropopause and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retardation Factor
In chromatography, the retardation factor (''R'') is the fraction of an analyte in the mobile phase of a chromatographic system. In planar chromatography in particular, the retardation factor ''R''F is defined as the ratio of the distance traveled by the center of a spot to the distance traveled by the solvent front. Ideally, the values for ''RF'' are equivalent to the R values used in column chromatography. Although the term retention factor is sometimes used synonymously with retardation factor in regard to planar chromatography the term is not defined in this context. However, in column chromatography, the retention factor or capacity factor (''k'') is defined as the ratio of time an analyte is retained in the stationary phase to the time it is retained in the mobile phase, which is inversely proportional to the retardation factor. General definition In chromatography, the retardation factor, ''R'', is the fraction of the sample in the mobile phase at equilibrium, defined as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Representative Fraction
Spatial scale is a specific application of the term scale for describing or categorizing (e.g. into orders of magnitude) the size of a space (hence ''spatial''), or the extent of it at which a phenomenon or process occurs. For instance, in physics an object or phenomenon can be called microscopic if too small to be visible. In climatology, a micro-climate is a climate which might occur in a mountain, valley or near a lake shore. In statistics, a megatrend is a political, social, economical, environmental or technological trend which involves the whole planet or is supposed to last a very large amount of time. The concept is also used in geography, astronomy, and meteorology. These divisions are somewhat arbitrary; where, on this table, ''mega-'' is assigned global scope, it may only apply continentally or even regionally in other contexts. The interpretations of ''meso-'' and ''macro-'' must then be adjusted accordingly. See also * Astronomical units of length * Cosm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection. Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often used as a synonym. The main difference lies in the realm of practice: medicine ( clinical practice) versus public health. As an example from clinical practice, low ingestion of dietary sources of vitamin C is a known risk factor for developing scurvy. Specific to public health policy, a determinant is a health risk that is general, abstract, related to inequalities, and difficult for an individual to control. For example, poverty is known to be a determinant of an individual's standard of health. Correlation vs causation Risk factors or determinants are correlational and not necessarily causal, because correlation does not prove causation. For example, being young cannot be said to cause measles, but young people have a higher rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |