|
RELA
Transcription factor p65 also known as nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p65 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RELA'' gene. RELA, also known as p65, is a REL-associated protein involved in NF-κB heterodimer formation, nuclear translocation and activation . NF-κB is an essential transcription factor complex involved in all types of cellular processes, including cellular metabolism, chemotaxis, etc. Phosphorylation and acetylation of RELA are crucial post-translational modifications required for NF-κB activation. RELA has also been shown to modulate immune responses, and activation of RELA is positively associated with multiple types of cancer. Gene and expression RELA, or v-rel avian reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A, is also known as p65 or NFKB3. It is located on chromosome 11 q13, and its nucleotide sequence is 1473 nucleotide long. RELA protein has four isoforms, the longest and the predominant one being 551 amino acids. RELA is expressed along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular responses to stimuli such as stress, cytokines, free radicals, heavy metals, ultraviolet irradiation, oxidized LDL, and bacterial or viral antigens. NF-κB plays a key role in regulating the immune response to infection. Incorrect regulation of NF-κB has been linked to cancer, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, septic shock, viral infection, and improper immune development. NF-κB has also been implicated in processes of synaptic plasticity and memory. Discovery NF-κB was discovered by Ranjan Sen in the lab of Nobel laureate David Baltimore via its interaction with an 11-base pair sequence in the immunoglobulin light-chain enhancer in B cells. Later work by Alexander Poltorak and Bruno Lemaitre in mice and ''Drosophila'' frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDK9
Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 or CDK9 is a cyclin-dependent kinase associated with P-TEFb. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) family. CDK family members are highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28, and S. pombe cdc2, and known as important cell cycle regulators. This kinase was found to be a component of the multiprotein complex TAK/P-TEFb, which is an elongation factor for RNA polymerase II-directed transcription and functions by phosphorylating the C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. This protein forms a complex with and is regulated by its regulatory subunit cyclin T or cyclin K. HIV-1 Tat protein was found to interact with this protein and cyclin T, which suggested a possible involvement of this protein in AIDS. CDK9 is also known to associate with other proteins such as TRAF2, and be involved in differentiation of skeletal muscle. Inhibitors Based on molecular docking resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IκBα
IκBα (nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha) is one member of a family of cellular proteins that function to inhibit the NF-κB transcription factor. IκBα inhibits NF-κB by masking the nuclear localization signals (NLS) of NF-κB proteins and keeping them sequestered in an inactive state in the cytoplasm. In addition, IκBα blocks the ability of NF-κB transcription factors to bind to DNA, which is required for NF-κB's proper functioning. Disease linkage The gene encoding the IκBα protein is mutated in some Hodgkin's lymphoma cells; such mutations inactivate the IκBα protein, thus causing NF-κB to be chronically active in the lymphoma tumor cells and this activity contributes to the malignant state of these tumor cells. Interactions IκBα has been shown to interact with: * BTRC, * C22orf25, * CHUK, * DYNLL1, * G3BP2, * Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1, * IKK2, * NFKB1, * P53, * RELA, * RPS6KA1, * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C22orf25
Transport and golgi organization 2 homolog (TANGO2) also known as chromosome 22 open reading frame 25 (C22orf25) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TANGO2 gene. The function of C22orf25 is not currently known. It is characterized by the NRDE superfamily domain (DUF883), which is strictly known for the conserved amino acid sequence of (N)-Asparagine (R)-Arginine (D)-Aspartic Acid (E)-Glutamic Acid. This domain is found among distantly related species from the six kingdoms: Eubacteria Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ..., Archaebacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia and is known to be involved in Golgi apparatus, Golgi organization and protein secretion. It is likely that it localizes in the cytoplasm but is anchored in the cell membrane by the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Jun
Transcription factor Jun is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUN'' gene. c-Jun, in combination with protein c-Fos, forms the AP-1 early response transcription factor. It was first identified as the Fos-binding protein p39 and only later rediscovered as the product of the JUN gene. c-jun was the first oncogenic transcription factor discovered. The proto-oncogene c-Jun is the cellular homolog of the viral oncoprotein v-jun (). The viral homolog v-jun was discovered in avian sarcoma virus 17 and was named for ''ju-nana'', the Japanese word for 17. The human JUN encodes a protein that is highly similar to the viral protein, which interacts directly with specific target DNA sequences to regulate gene expression. This gene is intronless and is mapped to 1p32-p31, a chromosomal region involved in both translocations and deletions in human malignancies. Function Regulation Both Jun and its dimerization partners in AP-1 formation are subject to regulation by diverse extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Fos
Protein c-Fos is a proto-oncogene that is the human homolog of the retroviral oncogene v-fos. It is encoded in humans by the ''FOS'' gene. It was first discovered in rat fibroblasts as the transforming gene of the FBJ MSV (Finkel–Biskis–Jinkins murine osteogenic sarcoma virus) (Curran and Tech, 1982). It is a part of a bigger Fos family of transcription factors which includes c-Fos, FosB, Fra-1 and Fra-2. It has been mapped to chromosome region 14q21→q31. c-Fos encodes a 62 kDa protein, which forms heterodimer with c-jun (part of Jun family of transcription factors), resulting in the formation of AP-1 (Activator Protein-1) complex which binds DNA at AP-1 specific sites at the promoter and enhancer regions of target genes and converts extracellular signals into changes of gene expression. It plays an important role in many cellular functions and has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers. Structure and function c-Fos is a 380 amino acid protein with a basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BTRC (gene)
F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 1A (FBXW1A) also known as βTrCP1 or Fbxw1 or hsSlimb or pIkappaBalpha-E3 receptor subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BTRC'' (beta-transducin repeat containing) gene. This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 residue structural motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs ( Skp1-Cul1-F-box protein), which often, but not always, recognize substrates in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: * Fbxws containing WD40 repeats, * Fbxls containing leucine-rich repeats, * and Fbxos containing either "other" protein–protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbxw class as, in addition to an F-box, this protein contains multiple WD40 repeats. This protein is homologous to Xenopus βTrCP, yeast Met30, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
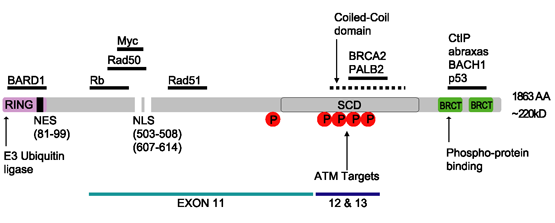
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and '' BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASCC3
Activating signal cointegrator 1 complex subunit 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ASCC3'' gene. Interactions ASCC3 has been shown to interact with RELA, C-jun and Serum response factor Serum response factor, also known as SRF, is a transcription factor protein. Function Serum response factor is a member of the MADS (MCM1, Agamous, Deficiens, and SRF) box superfamily of transcription factors. This protein binds to the serum .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (also known as AhR, AHR, ahr, ahR, or dioxin receptor) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AHR gene. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a transcription factor that regulates gene expression. It was originally thought to function primarily as a sensor of xenobiotic chemicals and also as the regulator of enzymes such as cytochrome P450s that metabolize these chemicals. The most notable of these xenobiotic chemicals are aromatic (aryl) hydrocarbons from which the receptor derives its name. More recently, it has been discovered that AhR is activated (or deactivated) by a number of endogenous indole derivatives such as kynurenine. In addition to regulating metabolism enzymes, the AhR has roles in regulating immunity, stem cell maintenance, and cellular differentiation. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a member of the family of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors. AHR binds several exogenous ligands such as natural plant flavonoids, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APBA2
Amyloid beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APBA2'' gene. Structure This protein has phosphotyrosine-binding domain (PTB domain or PID) in the middle and two PDZ domains at C-terminal. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the X11 protein family. It is a neuronal adaptor protein that interacts with the Alzheimer's disease amyloid precursor protein (APP). It stabilises APP and inhibits production of proteolytic APP fragments including the A beta peptide that is deposited in the brains of Alzheimer's disease patients. This gene product is believed to be involved in signal transduction processes. It is also regarded as a putative vesicular trafficking protein in the brain that can form a complex with the potential to couple synaptic vesicle exocytosis to neuronal cell adhesion. Interactions APBA2 has been shown to interact with CLSTN1, RELA Transcription factor p65 also known as nuclear f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 9
Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 or CDK9 is a cyclin-dependent kinase associated with P-TEFb. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) family. CDK family members are highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28, and S. pombe cdc2, and known as important cell cycle regulators. This kinase was found to be a component of the multiprotein complex TAK/P-TEFb, which is an elongation factor for RNA polymerase II-directed transcription and functions by phosphorylating the C-terminal domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. This protein forms a complex with and is regulated by its regulatory subunit cyclin T or cyclin K. HIV-1 Tat protein was found to interact with this protein and cyclin T, which suggested a possible involvement of this protein in AIDS. CDK9 is also known to associate with other proteins such as TRAF2, and be involved in differentiation of skeletal muscle. Inhibitors Based on molecular docking results ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |