|
RDNS SA Historical
In computer networks, a reverse DNS lookup or reverse DNS resolution (rDNS) is the querying technique of the Domain Name System (DNS) to determine the domain name associated with an IP address – the reverse of the usual "forward" DNS lookup of an IP address from a domain name. The process of reverse resolving of an IP address uses PTR records. rDNS involves searching domain name registry and registrar tables. The reverse DNS database of the Internet is rooted in the .arpa top-level domain. Although the informational RFC 1912 (Section 2.1) recommends that "every Internet-reachable host should have a name" and that "for every IP address, there should be a matching PTR record," it is not an Internet Standard requirement, and not all IP addresses have a reverse entry. Historical usage The modern "reverse DNS lookup" should not be confused with the now-obsolete "inverse query" (IQUERY) mechanism specified in : The IQUERY message type was always "optional" and "never achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) is the most recent version of the Internet Protocol (IP), the communication protocol, communications protocol that provides an identification and location system for computers on networks and routes traffic across the Internet. IPv6 was developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to deal with the long-anticipated problem of IPv4 address exhaustion, and is intended to replace IPv4. In December 1998, IPv6 became a Draft Standard for the IETF, which subsequently ratified it as an Internet Standard on 14 July 2017. Devices on the Internet are assigned a unique IP address for identification and location definition. With the rapid growth of the Internet after commercialization in the 1990s, it became evident that far more addresses would be needed to connect devices than the IPv4 address space had available. By 1998, the IETF had formalized the successor protocol. IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, theoretically allowing 2128, or approximatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Forum
An Internet forum, or message board, is an online discussion site where people can hold conversations in the form of posted messages. They differ from chat rooms in that messages are often longer than one line of text, and are at least temporarily archived. Also, depending on the access level of a user or the forum set-up, a posted message might need to be approved by a moderator before it becomes publicly visible. Forums have a specific set of jargon associated with them; example: a single conversation is called a " thread", or ''topic''. A discussion forum is hierarchical or tree-like in structure: a forum can contain a number of subforums, each of which may have several topics. Within a forum's topic, each new discussion started is called a thread and can be replied to by as many people as so wish. Depending on the forum's settings, users can be anonymous or have to register with the forum and then subsequently log in to post messages. On most forums, users do not have to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMTP
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages. User-level email clients typically use SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for relaying, and typically submit outgoing email to the mail server on port 587 or 465 per . For retrieving messages, IMAP (which replaced the older POP3) is standard, but proprietary servers also often implement proprietary protocols, e.g., Exchange ActiveSync. SMTP's origins began in 1980, building on concepts implemented on the ARPANET since 1971. It has been updated, modified and extended multiple times. The protocol version in common use today has extensible structure with various extensions for authentication, encryption, binary data transfer, and internationalized email addresses. SMTP servers commonly use the Transmission Control Protocol on port number 25 (for plaintext) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
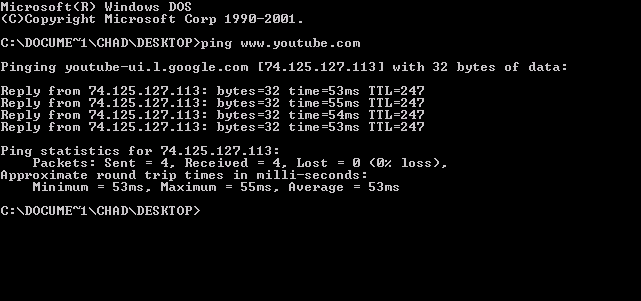
Ping (networking Utility)
ping is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. It is available for virtually all operating systems that have networking capability, including most embedded network administration software. Ping measures the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer that are echoed back to the source. The name comes from active sonar terminology that sends a pulse of sound and listens for the echo to detect objects under water. Ping operates by means of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) packets. ''Pinging'' involves sending an ICMP echo request to the target host and waiting for an ICMP echo reply. The program reports errors, packet loss, and a statistical summary of the results, typically including the minimum, maximum, the mean round-trip times, and standard deviation of the mean. The command-line options of the ping utility and its output vary between t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traceroute
In computing, traceroute and tracert are computer network diagnostic commands for displaying possible routes (paths) and measuring transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol (IP) network. The history of the route is recorded as the round-trip times of the packets received from each successive host (remote node) in the route (path); the sum of the mean times in each hop is a measure of the total time spent to establish the connection. Traceroute proceeds unless all (usually three) sent packets are lost more than twice; then the connection is lost and the route cannot be evaluated. Ping, on the other hand, only computes the final round-trip times from the destination point. For Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) the tool sometimes has the name traceroute6 and tracert6. Implementations The command traceroute is available on many modern operating systems. On Unix-like systems such as FreeBSD, macOS, and Linux it is available as a command line tool. Traceroute is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LOC Record
In the Domain Name System, a LOC record (experimental ) is a means for expressing geographic location information for a domain name. It contains WGS84 Latitude, Longitude and Altitude (ellipsoidal height) information together with host/subnet physical size and location accuracy. This information can be queried by other computers connected to the Internet. Record format The LOC record is expressed in a master file in the following format: LOC ( d1 1.html"_;"title="1_[s1">1_[s1__d2_[m2_[s2 _____________________________alt["m".html" ;"title="1">1_[s1__d2_[m2_[s2.html" ;"title="1.html" ;"title="1 [s1">1 [s1 d2 [m2 [s2">1.html" ;"title="1 [s1">1 [s1 d2 [m2 [s2 alt["m"">1">1_[s1__d2_[m2_[s2.html" ;"title="1.html" ;"title="1 [s1">1 [s1 d2 [m2 [s2">1.html" ;"title="1 [s1">1 [s1 d2 [m2 [s2 alt["m"[siz["m"] [hp["m"] [vp["m" ) (The parentheses are used for multi-line data as specified in RF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TXT Record
A TXT record (short for text record) is a type of resource record in the Domain name system (DNS) used to provide the ability to associate arbitrary text with a host or other name, such as human readable information about a server, network, data center, or other accounting information. It is also often used in a more structured fashion to record small amounts of machine-readable data into the DNS. Background A domain may have multiple TXT records associated with it, provided the DNS server implementation supports this. Each record can in turn have one or more character strings. Traditionally these text fields were used for a variety of non-standardised uses, such as a full company or organisation name, or the address of a host. In 1993 RFC 1464 proposed a simple approach to storing attributes and their values in these text fields. This is now used extensively in: * Verification of domain ownership * Implementation of Sender Policy Framework (SPF) * DomainKeys Identified Mail (DK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-configuration Networking
Zero-configuration networking (zeroconf) is a set of technologies that automatically creates a usable computer network based on the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) when computers or network peripherals are interconnected. It does not require manual operator intervention or special configuration servers. Without zeroconf, a network administrator must set up network services, such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS), or configure each computer's network settings manually. Zeroconf is built on three core technologies: automatic assignment of numeric network addresses for networked devices, automatic distribution and resolution of computer hostnames, and automatic location of network services, such as printing devices. Background Computer networks use numeric network addresses to identify communications endpoints in a network of participating devices. This is similar to the telephone network which assigns a string of digits to identify each t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Key Exchange
In computing, Internet Key Exchange (IKE, sometimes IKEv1 or IKEv2, depending on version) is the protocol used to set up a security association (SA) in the IPsec protocol suite. IKE builds upon the Oakley protocol and ISAKMP.The Internet Key Exchange (IKE), RFC 2409, §1 Abstract IKE uses X.509 certificates for authentication ‒ either pre-shared or distributed using DNS (preferably with DNSSEC) ‒ and a Diffie–Hellman key exchange to set up a shared session secret from which cryptographic keys are derived. In addition, a security policy for every peer which will connect must be manually maintained. History The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) originally defined IKE in November 1998 in a series of publications (Request for Comments) known as RFC 2407, RFC 2408 and RFC 2409: * defined the Internet IP Security Domain of Interpretation for ISAKMP. * defined the Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP). * defined the Internet Key Exchange ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
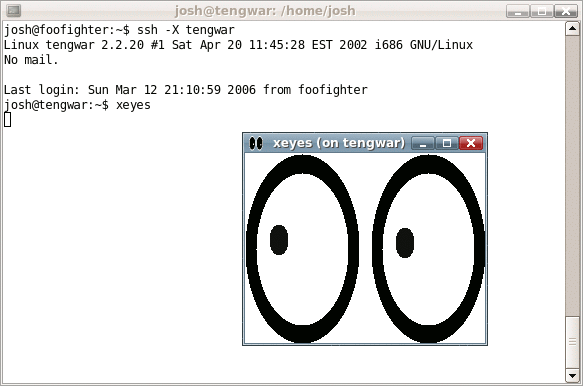
Secure Shell
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution. SSH applications are based on a client–server architecture, connecting an SSH client instance with an SSH server. SSH operates as a layered protocol suite comprising three principal hierarchical components: the ''transport layer'' provides server authentication, confidentiality, and integrity; the ''user authentication protocol'' validates the user to the server; and the ''connection protocol'' multiplexes the encrypted tunnel into multiple logical communication channels. SSH was designed on Unix-like operating systems, as a replacement for Telnet and for unsecured remote Unix shell protocols, such as the Berkeley Remote Shell (rsh) and the related rlogin and rexec protocols, which all use insecure, plaintext transmission of authentication tokens. SSH was first de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPsec
In computing, Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a secure network protocol suite that authenticates and encrypts packets of data to provide secure encrypted communication between two computers over an Internet Protocol network. It is used in virtual private networks (VPNs). IPsec includes protocols for establishing mutual authentication between agents at the beginning of a session and negotiation of cryptographic keys to use during the session. IPsec can protect data flows between a pair of hosts (''host-to-host''), between a pair of security gateways (''network-to-network''), or between a security gateway and a host (''network-to-host''). IPsec uses cryptographic security services to protect communications over Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It supports network-level peer authentication, data origin authentication, data integrity, data confidentiality (encryption), and replay protection (protection from replay attacks). The initial IPv4 suite was developed with few secur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |