|
RD-701
The RD-701 (''russian: Раке́тный дви́гатель 701'', Rocket Engine 701) is a liquid-fuel rocket engine developed by Energomash, Russia (USSR at that time). It was briefly proposed to propel the reusable MAKS space plane, but the project was cancelled shortly before the end of USSR. The ''RD-701'' is a tripropellant engine that uses a staged combustion cycle with afterburning of oxidizer-rich hot turbine gas. The RD-701 has two modes. ''Mode 1'' uses three components: LOX as an oxidizer and a fuel mixture of RP-1 / LH2 which is used in the lower atmosphere. ''Mode 2'' also uses LOX, with LH2 as fuel in vacuum where atmospheric influence is negligible. The use of less dense fuel components at maximum efficiency conditions allows minimizing the volume of fuel tanks and subsequently their mass down to 30%. The ''RD-701'' was developed into the RD-704 with one combustion chamber. The RD-701 is derived from the hydrogen fueled RD-0120. It is essentially two engines wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NPO Energomash
NPO Energomash “V. P. Glushko” is a major Russian rocket engine manufacturer. The company primarily develops and produces liquid propellant rocket engines. Energomash originates from the Soviet design bureau OKB-456, which was founded in 1946. NPO Energomash acquired its current name on May 15, 1991, in honor of its former chief designer Valentin Glushko. Energomash is noted for its long history of large scale LOX/Kerosene engine development. Notable examples are the RD-107/ RD-108 engines used on the R-7, Molniya and Soyuz rocket families, and the RD-170, RD-171 and RD-180 engines used on the Energia, Zenit and Atlas V launch vehicles. , the company remained largely owned by the federal government of Russia, but RSC Energia owned approximately 14% of the total shares. , NPO Energomash employed approximately 5500 workers at its headquarters in Khimki, Moscow and its satellite facilities in Samara, Perm, and St. Petersburg. On 4 August 2016, the company announced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAKS Space Plane
The MAKS (Multipurpose aerospace system) (Russian: МАКС (Многоцелевая авиационно-космическая система)) is a Soviet air-launched orbiter reusable launch system project that was proposed in 1988, but cancelled in 1991. The MAKS orbiter was supposed to reduce the cost of transporting materials to Earth orbit by a factor of ten. The reusable orbiter and its external expendable fuel tank would have been launched by an Antonov AN-225 airplane, developed by Antonov ASTC (Kyiv, Ukraine). Had it been built, the system would have weighed and been capable of carrying a payload. Three variants of the MAKS system were conceived: MAKS-OS, the standard configuration with the orbiter on top of the fuel tank; MAKS-T, with upgraded payload capability and a configuration that involved the fuel tank above the orbiter; and MAKS-M, a version that included its fuel tank within the envelope of the orbiter. As of June of 2010, Russia was considering reviving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator.Munson, Bruce Roy, T. H. Okiishi, and Wade W. Huebsch. "Turbomachines." Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 6th ed. Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2009. Print. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels. Gas, steam, and water turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the working fluid. Credit for invention of the steam turbine is given both to Anglo-Irish engineer Sir Charles Parsons (1854–1931) for invention of the reaction turbine, and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocket Engines Of Russia
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere. Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity. Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Significant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-170
The RD-170 ( rus, РД-170, Ракетный Двигатель-170, Raketnyy Dvigatel-170) is the world's most powerful and heaviest liquid-fuel rocket engine. It was designed and produced in the Soviet Union by NPO Energomash for use with the Energia launch vehicle. The engine burns kerosene fuel and LOX oxidizer in four combustion chambers, all supplied by one single-shaft, single-turbine turbopump rated at in a staged combustion cycle. Shared turbopump Several Soviet and Russian rocket engines use the approach of clustering small combustion chambers around a single turbine and pump. During the early 1950s, many Soviet engine designers, including Valentin P. Glushko, faced problems of combustion instability while designing bigger thrust chambers. At that time, they solved the problem by using a cluster of smaller thrust chambers. Variants RD-170 The RD-170 engine featured four combustion chambers and was developed for use on the Energia launch vehicle – both the eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preburner
The staged combustion cycle (sometimes known as topping cycle, preburner cycle, or closed cycle) is a power cycle of a bipropellant rocket engine. In the staged combustion cycle, propellant flows through multiple combustion chambers, and is thus combusted in stages. The main advantage relative to other rocket engine power cycles is high fuel efficiency, measured through specific impulse, while its main disadvantage is engineering complexity. Typically, propellant flows through two kinds of combustion chambers; the first called preburner and the second called main combustion chamber. In the preburner, a small portion of propellant, usually fuel-rich, is partly combusted, and the increasing volume flow is used to drive the turbopumps that feed the engine with propellant. The gas is then injected into the main combustion chamber and combusted completely with the other propellant to produce thrust. Tradeoffs The main advantage is fuel efficiency due to all of the propellant flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX Raptor
Raptor is a family of full-flow staged-combustion-cycle rocket engines developed and manufactured by SpaceX for use on the in-development SpaceX Starship. The engine is powered by cryogenic liquid methane and liquid oxygen ("methalox") rather than the RP-1 and liquid oxygen ("kerolox") used in SpaceX's prior Merlin and Kestrel rocket engines. The Raptor engine has more than twice the thrust of SpaceX's Merlin 1D engine that powers the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles. Raptor is used in the Starship system in both the super-heavy-lift Super Heavy booster and in the Starship spacecraft which acts as the second stage when launched from Earth and as an independent spacecraft in LEO and beyond. Starship is planned to be used in various applications, including Earth-orbit satellite delivery, deployment of a large portion of SpaceX's Starlink satellite constellation, exploration, Moon landing, and colonization of Mars. History Conception and initial designs An advanced r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
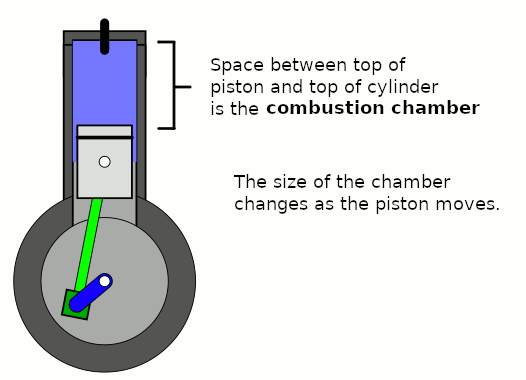
Combustion Chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process. Internal combustion engines In an internal combustion engine, the pressure caused by the burning air/fuel mixture applies direct force to part of the engine (e.g. for a piston engine, the force is applied to the top of the piston), which converts the gas pressure into mechanical energy (often in the form of a rotating output shaft). This contrasts an external combustion engine, where the combustion takes place in a separate part of the engine to where the gas pressure is converted into mechanical energy. Spark-ignition engines In spark ignition engines, such as petrol (gasoline) engines, the combustion chamber is usually located in the cylinder head. The engines are often designed such that the bottom of combustion chamber is roughly in li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RD-0120
The Soviet RD-0120 (also designated 11D122) was the Energia (rocket), Energia core rocket engine, fueled by LH2, LH/LOX, roughly equivalent to the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME). These were attached to the Energia core rather than the orbiter, so were not recoverable after a flight, but created a more modular design (the Energia core could be used for a variety of missions besides launching the shuttle). The RD-0120 and the SSME have both similarities and differences. The RD-0120 achieved a slightly higher specific impulse and combustion chamber pressure with reduced complexity and cost (but it was single-use), as compared to the SSME. It uses a fuel-rich staged combustion cycle and a single shaft to drive both the fuel and oxidizer turbopumps. Some of the Russian design features, such as the simpler and cheaper channel wall nozzles, were evaluated by Rocketdyne for possible upgrades to the SSME. It achieved combustion stability without the acoustic resonance chambers that the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Impulse
Specific impulse (usually abbreviated ) is a measure of how efficiently a reaction mass engine (a rocket using propellant or a jet engine using fuel) creates thrust. For engines whose reaction mass is only the fuel they carry, specific impulse is exactly proportional to the effective exhaust gas velocity. A propulsion system with a higher specific impulse uses the mass of the propellant more efficiently. In the case of a rocket, this means less propellant needed for a given delta-v, so that the vehicle attached to the engine can more efficiently gain altitude and velocity. In an atmospheric context, specific impulse can include the contribution to impulse provided by the mass of external air that is accelerated by the engine in some way, such as by an internal turbofan or heating by fuel combustion participation then thrust expansion or by external propeller. Jet engines breathe external air for both combustion and by-pass, and therefore have a much higher specific impulse than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but has since also been applied to other sources of heat energy, such as nuclear energy (via nuclear fission and nuclear fusion). The heat energy released by reactions of fuels can be converted into mechanical energy via a heat engine. Other times, the heat itself is valued for warmth, cooking, or industrial processes, as well as the illumination that accompanies combustion. Fuels are also used in the cells of organisms in a process known as cellular respiration, where organic molecules are oxidized to release usable energy. Hydrocarbons and related organic molecules are by far the most common source of fuel used by humans, but other substances, including radioactive metals, are also utilized. Fuels are contrasted with other substances or de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev ( Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |