|
RC5 Cipher
In cryptography, RC5 is a symmetric-key block cipher notable for its simplicity. Designed by Ronald Rivest in 1994, ''RC'' stands for "Rivest Cipher", or alternatively, "Ron's Code" (compare RC2 and RC4). The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) candidate RC6 was based on RC5. Description Unlike many schemes, RC5 has a variable block size (32, 64 or 128 bits), key size (0 to 2040 bits) and number of rounds (0 to 255). The original suggested choice of parameters were a block size of 64 bits, a 128-bit key and 12 rounds. A key feature of RC5 is the use of data-dependent rotations; one of the goals of RC5 was to prompt the study and evaluation of such operations as a cryptographic primitive . RC5 also consists of a number of modular additions and eXclusive OR (XOR)s. The general structure of the algorithm is a Feistel-like network. The encryption and decryption routines can be specified in a few lines of code. The key schedule, however, is more complex, expanding the key us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RC5 InfoBox Diagram
In cryptography, RC5 is a symmetric-key block cipher notable for its simplicity. Designed by Ronald Rivest in 1994, ''RC'' stands for "Rivest Cipher", or alternatively, "Ron's Code" (compare RC2 and RC4). The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) candidate RC6 was based on RC5. Description Unlike many schemes, RC5 has a variable block size (32, 64 or 128 bits), key size (0 to 2040 bits) and number of rounds (0 to 255). The original suggested choice of parameters were a block size of 64 bits, a 128-bit key and 12 rounds. A key feature of RC5 is the use of data-dependent rotations; one of the goals of RC5 was to prompt the study and evaluation of such operations as a cryptographic primitive . RC5 also consists of a number of modular additions and eXclusive OR (XOR)s. The general structure of the algorithm is a Feistel-like network. The encryption and decryption routines can be specified in a few lines of code. The key schedule, however, is more complex, expanding the key using an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-way Function
In computer science, a one-way function is a function that is easy to compute on every input, but hard to invert given the image of a random input. Here, "easy" and "hard" are to be understood in the sense of computational complexity theory, specifically the theory of polynomial time problems. Not being one-to-one is not considered sufficient for a function to be called one-way (see Theoretical definition, below). The existence of such one-way functions is still an open conjecture. Their existence would prove that the complexity classes P and NP are not equal, thus resolving the foremost unsolved question of theoretical computer science.Oded Goldreich (2001). Foundations of Cryptography: Volume 1, Basic Tools,draft availablefrom author's site). Cambridge University Press. . (see als The converse is not known to be true, i.e. the existence of a proof that P≠NP would not directly imply the existence of one-way functions. In applied contexts, the terms "easy" and "hard" are us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madryga
In cryptography, Madryga is a block cipher published in 1984 by W. E. Madryga. It was designed to be easy and efficient for implementation in software. Serious weaknesses have since been found in the algorithm, but it was one of the first encryption algorithms to make use of data-dependent rotations, later used in other ciphers, such as RC5 and RC6. In his proposal, Madryga set forth twelve design objectives that are generally considered to be good goals in the design of a block cipher. DES had already fulfilled nine of them. The three that DES did not fulfill were: # Any possible key should produce a strong cipher. (Meaning no weak keys, which DES has.) # The length of the key and the text should be adjustable to meet varying security requirements. # The algorithm should be efficiently implementable in software on large mainframes, minicomputers, and microcomputers, and in discrete logic. (DES has a large amount of bitwise permutations, which are inefficient in software implemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft ("share alike") terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston, Massachusetts, US, where it is also based. From its founding until the mid-1990s, FSF's funds were mostly used to employ software developers to write free software for the GNU Project. Since the mid-1990s, the FSF's employees and volunteers have mostly worked on legal and structural issues for the free software movement and the free software community. Consistent with its goals, the FSF aims to use only free software on its own computers. History The Free Software Foundation was founded in 1985 as a non-profit corporation supporting free software development. It continued existing GNU projects such as the sale of manuals and tapes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciphertext
In cryptography, ciphertext or cyphertext is the result of encryption performed on plaintext using an algorithm, called a cipher. Ciphertext is also known as encrypted or encoded information because it contains a form of the original plaintext that is unreadable by a human or computer without the proper cipher to decrypt it. This process prevents the loss of sensitive information via hacking. Decryption, the inverse of encryption, is the process of turning ciphertext into readable plaintext. Ciphertext is not to be confused with codetext because the latter is a result of a code, not a cipher. Conceptual underpinnings Let m\! be the plaintext message that Alice wants to secretly transmit to Bob and let E_k\! be the encryption cipher, where _k\! is a cryptographic key. Alice must first transform the plaintext into ciphertext, c\!, in order to securely send the message to Bob, as follows: : c = E_k(m). \! In a symmetric-key system, Bob knows Alice's encryption key. Once the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSA Security
RSA Security LLC, formerly RSA Security, Inc. and doing business as RSA, is an American computer security, computer and network security company with a focus on encryption and encryption standards. RSA was named after the initials of its co-founders, Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman, after whom the RSA (algorithm), RSA public key cryptography algorithm was also named. Among its products is the SecurID authentication token. The BSAFE cryptography libraries were also initially owned by RSA. RSA is known for incorporating backdoors developed by the National Security Agency, NSA in its products. It also organizes the annual RSA Conference, an information security conference. Founded as an independent company in 1982, RSA Security was acquired by EMC Corporation in 2006 for US$2.1 billion and operated as a division within EMC. When EMC was acquired by Dell Technologies in 2016, RSA became part of the Dell Technologies family of brands. On 10 March 2020, Dell Technologies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
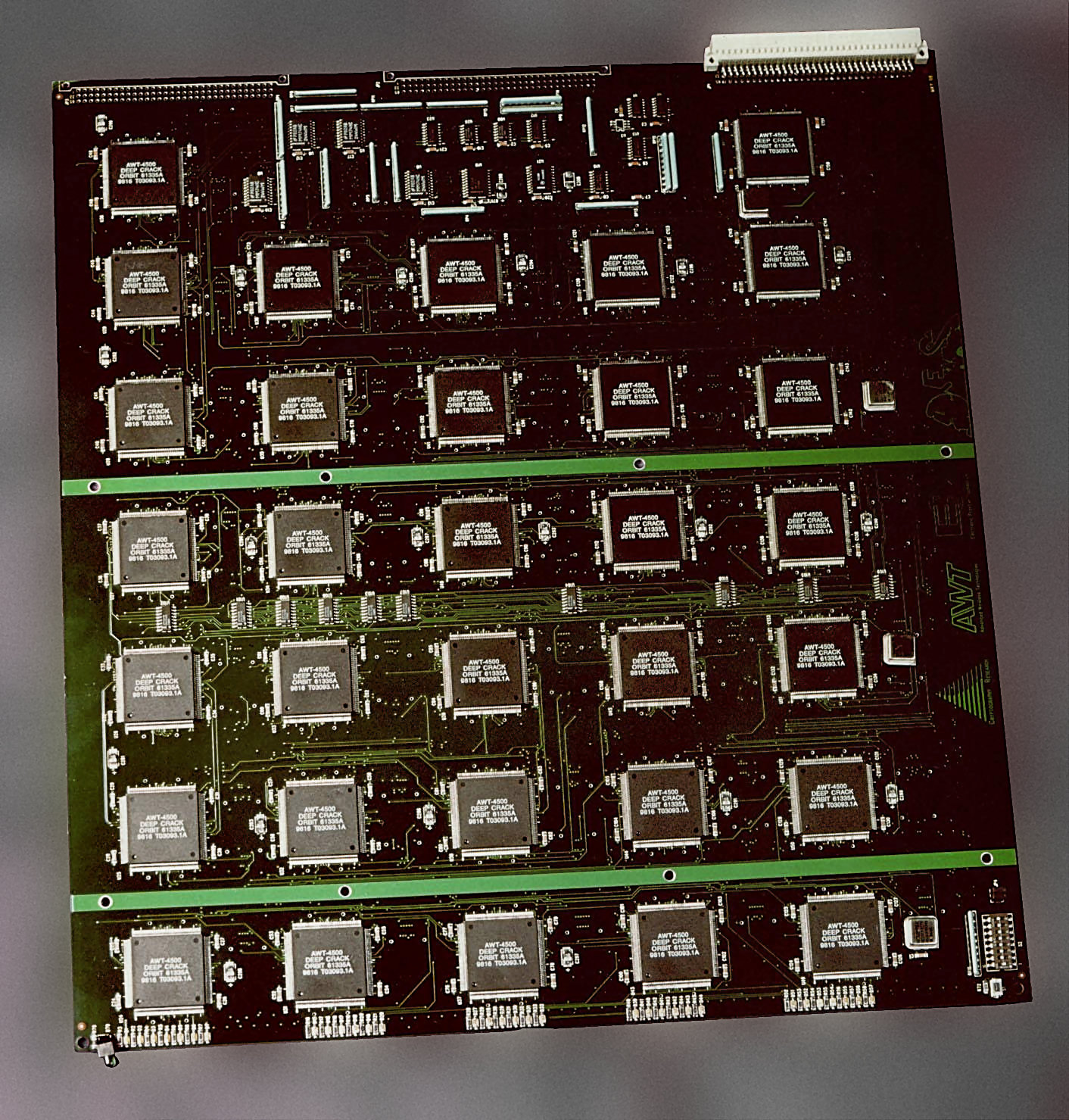
Brute Force Attack
In cryptography, a brute-force attack consists of an attacker submitting many passwords or passphrases with the hope of eventually guessing correctly. The attacker systematically checks all possible passwords and passphrases until the correct one is found. Alternatively, the attacker can attempt to guess the key which is typically created from the password using a key derivation function. This is known as an exhaustive key search. A brute-force attack is a cryptanalytic attack that can, in theory, be used to attempt to decrypt any encrypted data (except for data encrypted in an information-theoretically secure manner). Such an attack might be used when it is not possible to take advantage of other weaknesses in an encryption system (if any exist) that would make the task easier. When password-guessing, this method is very fast when used to check all short passwords, but for longer passwords other methods such as the dictionary attack are used because a brute-force sear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed
Distribution may refer to: Mathematics *Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations *Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a variable **Cumulative distribution function In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Ev ..., in which the probability of being no greater than a particular value is a function of that value *Frequency distribution, a list of the values recorded in a sample *Inner distribution, and outer distribution, in coding theory *Distribution (differential geometry), a subset of the tangent bundle of a manifold *Distributed parameter system, systems that have an infinite-dimensional state-space *Distribution of terms, a situation in which all members of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming'' is the process of writing such programs. There are many different types of implementations for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nothing Up My Sleeve Number
In cryptography, nothing-up-my-sleeve numbers are any numbers which, by their construction, are above suspicion of hidden properties. They are used in creating cryptographic functions such as hashes and ciphers. These algorithms often need randomized constants for mixing or initialization purposes. The cryptographer may wish to pick these values in a way that demonstrates the constants were not selected for a nefarious purpose, for example, to create a backdoor to the algorithm. These fears can be allayed by using numbers created in a way that leaves little room for adjustment. An example would be the use of initial digits from the number as the constants. Using digits of millions of places after the decimal point would not be considered trustworthy because the algorithm designer might have selected that starting point because it created a secret weakness the designer could later exploit. Digits in the positional representations of real numbers such as , ''e'', and irrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golden Ratio
In mathematics, two quantities are in the golden ratio if their ratio is the same as the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. Expressed algebraically, for quantities a and b with a > b > 0, where the Greek letter phi ( or \phi) denotes the golden ratio. The constant \varphi satisfies the quadratic equation \varphi^2 = \varphi + 1 and is an irrational number with a value of The golden ratio was called the extreme and mean ratio by Euclid, and the divine proportion by Luca Pacioli, and also goes by several other names. Mathematicians have studied the golden ratio's properties since antiquity. It is the ratio of a regular pentagon's diagonal to its side and thus appears in the construction of the dodecahedron and icosahedron. A golden rectangle—that is, a rectangle with an aspect ratio of \varphi—may be cut into a square and a smaller rectangle with the same aspect ratio. The golden ratio has been used to analyze the proportions of natural o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E (mathematical Constant)
The number , also known as Euler's number, is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828 that can be characterized in many ways. It is the base of the natural logarithms. It is the limit of as approaches infinity, an expression that arises in the study of compound interest. It can also be calculated as the sum of the infinite series e = \sum\limits_^ \frac = 1 + \frac + \frac + \frac + \cdots. It is also the unique positive number such that the graph of the function has a slope of 1 at . The (natural) exponential function is the unique function that equals its own derivative and satisfies the equation ; hence one can also define as . The natural logarithm, or logarithm to base , is the inverse function to the natural exponential function. The natural logarithm of a number can be defined directly as the area under the curve between and , in which case is the value of for which this area equals one (see image). There are various other character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |