|
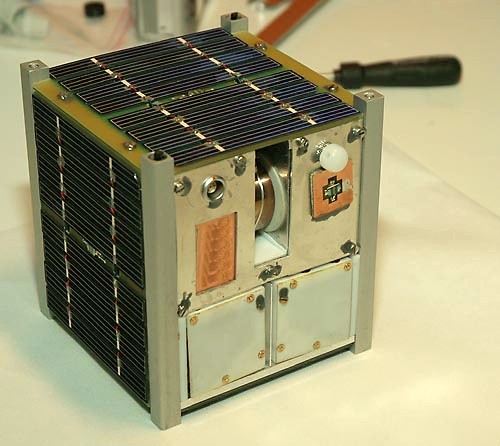
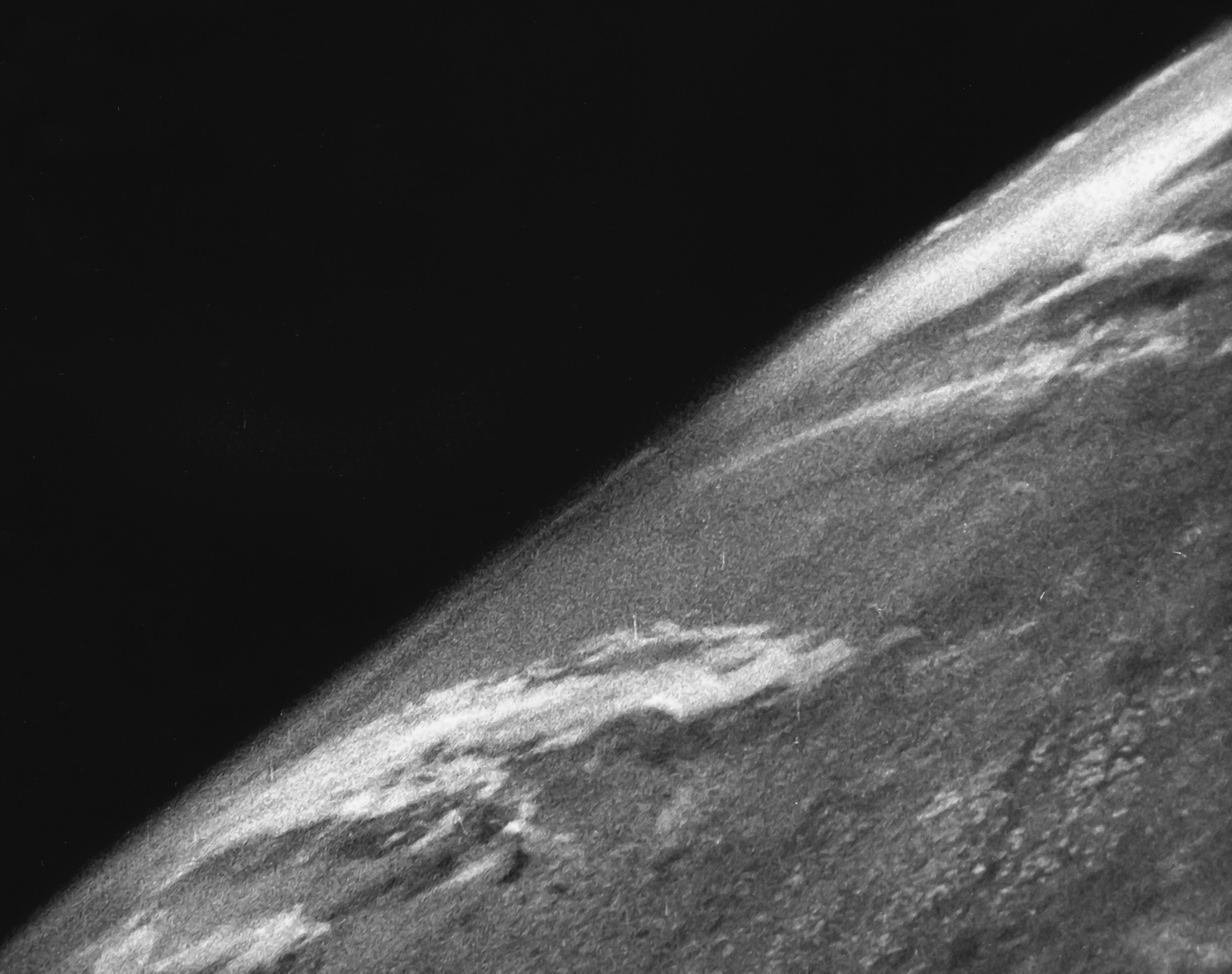
RAIKO (satellite)
RAIKO ( ja, 雷鼓, literally ''thunder drum'') is a Japanese satellite which was built and operated by Tohoku and Wakayama Universities. A two-unit CubeSat, RAIKO was deployed from the International Space Station (ISS) on 4 October 2012, having been launched on 21 July 2012. RAIKO was launched aboard the Kounotori 3 (HTV-3) spacecraft, atop an H-IIB launch vehicle flying from pad LC-Y2 of the Yoshinobu Launch Complex at the Tanegashima Space Center. The launch occurred at 02:06:18 UTC on 21 July 2012. Four other CubeSats were launched with RAIKO; WE WISH, FITSAT-1, TechEdSat-1 and F-1. The five CubeSats was delivered to the International Space Station for deployment. CubeSats were deployed from Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) '' Kibō'' via the J-SSOD system on 4 October 2012. Named after a Japanese god of thunder, RAIKO is a spacecraft, which was used for technology demonstration. It carries a camera with a fish-eye lens for Earth imaging, a prototype star tracker, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology Demonstration
A technology demonstration (or tech demo), also known as demonstrator model, is a prototype, rough example or an otherwise incomplete version of a conceivable product or future system, put together as proof of concept with the primary purpose of showcasing the possible applications, feasibility, performance and method of an idea for a new technology. They can be used as demonstrations to the investors, partners, journalists or even to potential customers in order to convince them of the viability of the chosen approach, or to test them on ordinary users. Computers and gaming Technology demonstrations are often used in the computer industry, emerging as an important tool in response to short development cycles, in both software and hardware development. * Computer game developers use tech demos to rouse and maintain interest to titles still in development (because game engines are usually ready before the art is finished) and to ensure functionality by early testing. Short segmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WE WISH
WE WISH (World Environmental Watching and Investigation from Space Height) was a small commercial CubeSat which was deployed from the International Space Station (ISS) in October 2012 and which deorbited in March 2013. It was built by the Japanese technology company Meisei Electric"WE WISH" Space.skyrocket.de Retrieved 12 January 2021 and the Meisei Amateur Radio Club, and could transmit pictures taken by a small infrared camera via radio at 437.515 ."Tag Archives: WE WISH" Amsat-uk.org Retrieved 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CubeSats
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that perform a number of scientific research functions and explore new space technologies. Academia accounted for the majority of CubeSat launches until 2013, when more than half of launches were for non-academic purposes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 2012
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FITSat 1
Niwaka or FITSAT-1 is a 1U CubeSat satellite deployed from the International Space Station (ISS) on 4 October 2012. The Niwaka satellite includes high power LEDs which are driven by 200 watts pulses, allowing Morse code style communication from the sky to the ground. FITSAT-1 (Niwaka) communicates with ground by means of 5.8 GHz high-speed (115200 bit/s) transmitter. It also has a 437 MHz (amateur band) beacon and transmitter with data rate 1200 bit/s for telemetry downlink. The name Niwaka derives from "Hakata Niwaka", which is traditional impromptu comical talking with masks. It is also the old name of the city Fukuoka, site of the Fukuoka Institute of Technology in Japan which created the satellite. WE WISH, RAIKO, FITSAT-1, F-1, and TechEdSat-1 travelled to orbit aboard Kounotori 3 (HTV-3). It reentered in the atmosphere of Earth on 4 July 2013. Launch See also * 2012 in spaceflight * Ginrei Ginrei or ShindaiSat was a 400x400x450mm cube-like microsatellite in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doppler Effect
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who described the phenomenon in 1842. A common example of Doppler shift is the change of pitch heard when a vehicle sounding a horn approaches and recedes from an observer. Compared to the emitted frequency, the received frequency is higher during the approach, identical at the instant of passing by, and lower during the recession. The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave. Therefore, each wave takes slightly less time to reach the observer than the previous wave. Hence, the time between the arrivals of successive wave crests at the observer is reduced, causing an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ku Band
The Ku band () is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in the microwave range of frequencies from 12 to 18 gigahertz (GHz). The symbol is short for "K-under" (originally german: Kurz-unten), because it is the lower part of the original NATO K band, which was split into three bands (Ku, K, and Ka) because of the presence of the atmospheric water vapor resonance peak at 22.24 GHz, (1.35 cm) which made the center unusable for long range transmission. In radar applications, it ranges from 12 to 18 GHz according to the formal definition of radar frequency band nomenclature in IEEE Standard 521–2002. Ku band is primarily used for satellite communications, most notably the downlink used by direct broadcast satellites to broadcast satellite television, and for specific applications such as NASA's Tracking Data Relay Satellite used for International Space Station (ISS) communications and SpaceX Starlink satellites. Ku band satellites are also used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Tracker
A star tracker is an optical device that measures the positions of stars using photocells or a camera. As the positions of many stars have been measured by astronomers to a high degree of accuracy, a star tracker on a satellite or spacecraft may be used to determine the orientation (or attitude) of the spacecraft with respect to the stars. In order to do this, the star tracker must obtain an image of the stars, measure their apparent position in the reference frame of the spacecraft, and identify the stars so their position can be compared with their known absolute position from a star catalog. A star tracker may include a processor to identify stars by comparing the pattern of observed stars with the known pattern of stars in the sky. History In the 1950s and early 1960s, star trackers were an important part of early long-range ballistic missiles and cruise missiles, in the era when inertial navigation systems (INS) were not sufficiently accurate for intercontinental ranges. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell images by licensing them to governments and businesses such as Apple Maps and Google Maps. History The first images from space were taken on Sub-orbital spaceflight, sub-orbital flights. The U.S-launched V-2 flight on October 24, 1946, took one image every 1.5 seconds. With an Apsis, apogee of 65 miles (105 km), these photos were from five times higher than the previous record, the 13.7 miles (22 km) by the Explorer II balloon mission in 1935. The first satellite (orbital) photographs of Earth were made on August 14, 1959, by the U.S. Explorer 6. The first satellite photographs of the Moon might have been made on October 6, 1959, by the Soviet satellite Luna 3, on a mission to photograph the far side of the Moon. The Blue Marble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish-eye Lens
A fisheye lens is an ultra wide-angle lens that produces strong visual distortion intended to create a wide panoramic or hemispherical image. Fisheye lenses achieve extremely wide angles of view, well beyond any rectilinear lens. Instead of producing images with straight lines of perspective ( rectilinear images), fisheye lenses use a special mapping ("distortion"; for example: equisolid angle, see below), which gives images a characteristic convex non-rectilinear appearance. The term ''fisheye'' was coined in 1906 by American physicist and inventor Robert W. Wood based on how a fish would see an ultrawide hemispherical view from beneath the water (a phenomenon known as Snell's window). Their first practical use was in the 1920s for use in meteorology to study cloud formation giving them the name "whole-sky lenses". The angle of view of a fisheye lens is usually between 100 and 180 degrees, although lenses covering up to 280 degrees exist (see below). Their focal lengths depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-1 (satellite)
F-1 is a CubeSat built by FSpace laboratory at FPT University, in Hanoi, Vietnam, in partnership with Angstrom Space Technology Center (ASTC), Uppsala University, Sweden and Nanoracks LLC, United States. Its mission is to train young engineers and students about aerospace engineering and evaluate an advanced three-axis magnetometer, Spin-Dependent Tunneling Magnetometer (SDTM) designed in Sweden by ASTC. F-1 was launched on 21 July 2012 and delivered to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard Kounotori 3 (HTV-3) along with the RAIKO, WE WISH, Niwaka and TechEdSat-1 cubesats. Then, on 4 October 2012, it was deployed into orbit from the ISS using the JEM-Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) which was attached to the Kibō module's robotic arm. As of 2 November 2012, F-1 failed to confirm communication after the orbital deployment. Hardware * Structure: aluminium alloy T-6061 * Power supply: body-mounted solar cells, rechargeable Li-Polymer battery * PIC16 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TechEdSat
Technology Education Satellite (TechEdSat) is a successful nano-sat flight series conducted from the NASA Ames Research Center in collaboration with numerous universities (San Jose State University, University of Idaho, University of California, University of Minnesota, Smith College). While one of the principal aims has been to introduce young professionals and university students to the practical realm of developing space flight hardware, considerable innovations have been introduced. In addition, this evolving flight platform has tested concepts for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) sample return, as well as planetary nano-sat class mission concepts. TechEdSat-1 The first TechEdSat (later renamed "TechEdSat-1" or "TES-1") was a 1U-Cubesat designed to evaluate Space Plug-and-play Avionics (SPA) designed in Sweden by ÅAC Microtec. It was also originally intended to perform a communications experiment utilizing the Iridium and Orbcomm satellite phone network, although this functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |