|
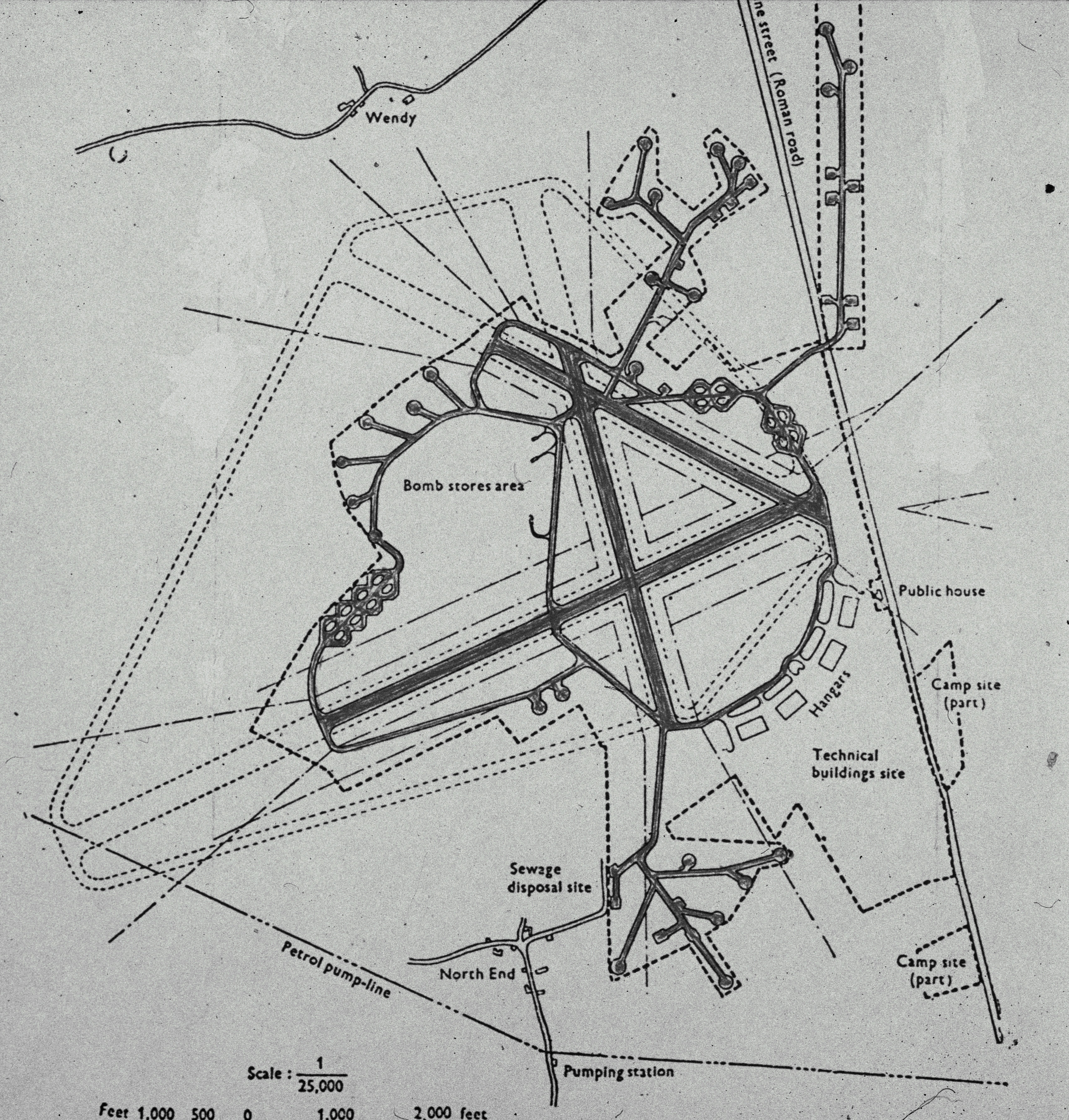
RAF Tatenhill
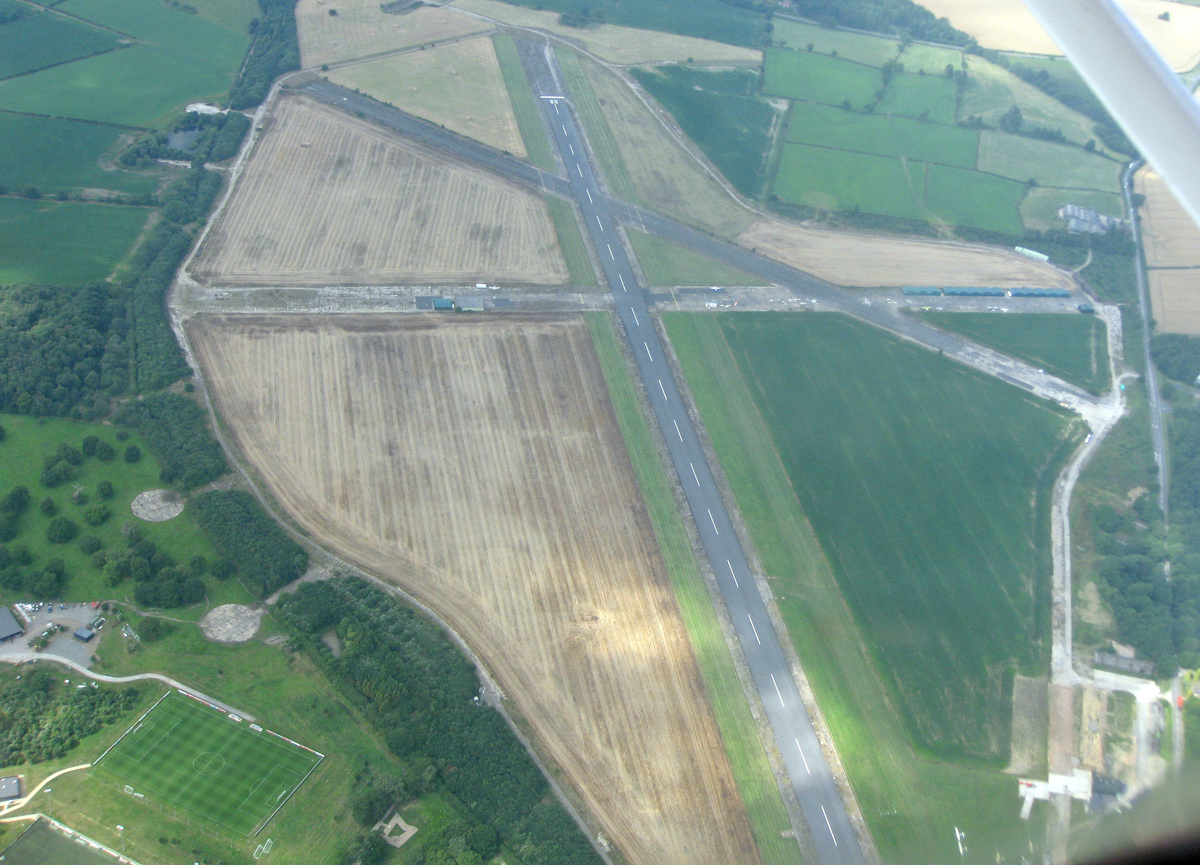
RAF Tatenhill is a former Royal Air Force satellite airfield in Tatenhill, Staffordshire, England, west of Burton on Trent. It was originally known as ''RAF Crossplains''. History The field was built in 1941 as a satellite for No. 27 Operational Training Unit RAF (OTU) at RAF Lichfield later becoming a satellite airfield for RAF Wheaton Aston. The design was the wartime RAF standard of three co-intersecting runways, east-west, north-south diagonal. The east-west runway was the only one suitable to safely accommodate bomber take off and landings () which hampered its operability. It was used as a bomber crew training field, which continued in varied training functions until 1944 with Vickers Wellington, Airspeed Oxford and Avro Anson aircraft for RAF Bomber Command. Later a single engine training unit arrived using the Miles Master aircraft. It was then used by the RAF School of Explosives after the disastrous explosion at nearby RAF Fauld, from October 1945 until January ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensign Of The Royal Air Force
An ensign is the national flag flown on a vessel to indicate nationality. The ensign is the largest flag, generally flown at the stern (rear) of the ship while in port. The naval ensign (also known as war ensign), used on warships, may be different from the civil ensign (merchant ships) or the yacht ensign (recreational boats). Large versions of naval ensigns called battle ensigns are used when a warship goes into battle. The ensign differs from the jack (flag), jack, which is flown from a jackstaff at the bow of a vessel. In its widest sense, an ensign is just a flag or other standard. The European military rank of Ensign (rank), ensign, once responsible for bearing a unit's standard (whether national or regimental), derives from it (in the cavalry, the equivalent rank was Cornet (rank), cornet, named after a type of flag). Ensigns, such as the ancient Roman ensigns in the Arch of Constantine, are not always flags. National ensigns In nautical use, the ensign is flown on a shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspeed Oxford
The Airspeed AS.10 Oxford is a twin-engine monoplane aircraft developed and manufactured by Airspeed. It saw widespread use for training British Commonwealth aircrews in navigation, radio-operating, bombing and gunnery roles throughout the Second World War. The Oxford was developed by Airspeed during the 1930s in response to a requirement for a capable trainer aircraft that conformed with Specification T.23/36, which had been issued by the British Air Ministry. Its basic design is derived from the company's earlier AS.6 Envoy, a commercial passenger aircraft. Performing its maiden flight on 19 June 1937, it was quickly put into production as part of a rapid expansion of the Royal Air Force (RAF) in anticipation of a large-scale conflict. As a consequence of the outbreak of war, many thousands of Oxfords were ordered by Britain and its allies, including Australia, Canada, France, New Zealand, Poland, and the United States. Following the end of the conflict, the Oxford continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatenhill Airfield
Tatenhill Airfield is a licensed airfield operated by Tatenhill Aviation Ltd. Its CAA Ordinary Licence (Number P813) allows flights for the public transport of passengers and for flying instruction as authorised by the licensee, Tatenhill Aviation. and is an ANSP The three runways are paved, but one is no longer operational, and a second is used only occasionally. Running east-west, the main runway is the longest. The airfield is part of the Needwood Survey, a 3000 hectare (12 sq miles) estate held by the in the area of the former |
RAF Fauld
Royal Air Force Fauld is a former Royal Air Force underground munitions storage depot located south west of Tutbury, Staffordshire and north east of Rugeley, Staffordshire, England. The site was controlled by No. 21 Maintenance Unit RAF which stored munitions underground. The explosion At 11:11 am on Monday, 27 November 1944 an explosion destroyed a large part of the site and killed about 70 people. Post 1944 The depot was used until 1966 when the site was closed. However, in late 1966 when France withdrew from NATO's integrated military structure the site was briefly used between 1967 and 1973.Reed, John, (1977). "Largest Wartime Explosions: 21 Maintenance Unit, RAF Fauld, Staff. November 27, 1944", ''After the Battle'', 18, Pp 35 - 40. ISSN 0306-154X. See also *List of former Royal Air Force stations This list of former RAF stations includes most of the stations, airfields and administrative headquarters previously used by the Royal Air Force. The station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF School Of Explosives
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miles Master
The Miles M.9 Master was a British two-seat monoplane advanced trainer designed and built by aviation company Miles Aircraft Ltd. It was inducted in large numbers into both the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Fleet Air Arm (FAA) during the Second World War. The Master can trace its origins back to the earlier M.9 Kestrel demonstrator aircraft. Following the failure of the rival de Havilland Don as a satisfactory trainer aircraft, the RAF ordered 500 ''M9A Master'' advanced trainers to meet its needs. Once in service, it provided a fast, strong and fully aerobatic aircraft that functioned as an excellent introduction to the high performance British fighter aircraft of the day: the Spitfire and Hurricane. Throughout its production life, thousands of aircraft and various variants of the Master were produced, the latter being largely influenced by engine availability. Numerous Masters were modified to enable their use as glider tows. The Master also served as the basis for the Miles M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Bomber Command
RAF Bomber Command controlled the Royal Air Force's bomber forces from 1936 to 1968. Along with the United States Army Air Forces, it played the central role in the strategic bombing of Germany in World War II. From 1942 onward, the British bombing campaign against Germany became less restrictive and increasingly targeted industrial sites and the civilian manpower base essential for German war production. In total 364,514 operational sorties were flown, 1,030,500 tons of bombs were dropped and 8,325 aircraft lost in action. Bomber Command crews also suffered a high casualty rate: 55,573 were killed out of a total of 125,000 aircrew, a 44.4% death rate. A further 8,403 men were wounded in action, and 9,838 became prisoners of war. Bomber Command stood at the peak of its post-war military power in the 1960s, the V bombers holding the United Kingdom's nuclear deterrent and a supplemental force of Canberra light bombers. In August 2006, a memorial was unveiled at Lincoln Cathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro Anson
The Avro Anson is a British twin-engined, multi-role aircraft built by the aircraft manufacturer Avro. Large numbers of the type served in a variety of roles for the Royal Air Force (RAF), Fleet Air Arm (FAA), Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and numerous other air forces before, during, and after the Second World War. Initially known as the ''Avro 652A'', the Anson was developed during the mid-1930s from the earlier Avro 652 airliner in response to a request for tenders issued by the British Air Ministry for a maritime reconnaissance aircraft. Having suitably impressed the Ministry, a single prototype was ordered, which conducted its maiden flight on 24 March 1935. Following an evaluation in which the Type 652A bettered the competing de Havilland DH.89, it was selected as the winner, leading to Air Ministry Specification 18/35 being written around the type and an initial order for 174 aircraft being ordered in July 1935. The Type 652A was promptly named after British Admira ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Wellington
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson; a key feature of the aircraft is its geodetic airframe fuselage structure, which was principally designed by Barnes Wallis. Development had been started in response to Air Ministry Specification B.9/32, issued in the middle of 1932, for a bomber for the Royal Air Force. This specification called for a twin-engined day bomber capable of delivering higher performance than any previous design. Other aircraft developed to the same specification include the Armstrong Whitworth Whitley and the Handley Page Hampden. During the development process, performance requirements such as for the tare weight changed substantially, and the engine used was not the one originally intended. The Wellington was used as a night bomber in the early years of the Second World War, performing as one o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964. It was under the political authority of the Secretary of State for Air. Organisations before the Air Ministry The Air Committee On 13 April 1912, less than two weeks after the creation of the Royal Flying Corps (which initially consisted of both a naval and a military wing), an Air Committee was established to act as an intermediary between the Admiralty and the War Office in matters relating to aviation. The new Air Committee was composed of representatives of the two war ministries, and although it could make recommendations, it lacked executive authority. The recommendations of the Air Committee had to be ratified by the Admiralty Board and the Imperial General Staff and, in consequence, the Committee was not particularly effective. The increasing separation of army and naval aviation from 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class A Airfield
Class A airfields were World War II military installations constructed to specifications laid down by the British Air Ministry Directorate-General of Works (AMDGW). Intended for use by heavy bombers and transports, they were the standard air base design for the Royal Air Force as well as U.S. Army Air Forces units operating from the UK. Upon the entry of the US into the war a number of RAF Class A bases were transferred to the U.S. Eighth Air Force for use as heavy bomber bases with the RAF units formerly occupying them being redeployed to other RAF bomber airfields, and U.S. Army Engineer Units constructed more airfields to this standard or brought earlier airfields up to this specification by lengthening runways, etc. Many units of the U.S. Ninth Air Force also flew from Class A airfields. The term Class 'A' came about because, quite often, the resultant aerial shot of the crossed runways would look like the letter A. Design The specifications set by the British Air Ministry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |