|
R134a
1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane (also known as norflurane ( INN), R-134a, Klea 134a, Freon 134a, Forane 134a, Genetron 134a, Green Gas, Florasol 134a, Suva 134a, HFA-134a, or HFC-134a) is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) and haloalkane refrigerant with thermodynamic properties similar to R-12 (dichlorodifluoromethane) but with insignificant ozone depletion potential and a lower 100-year global warming potential (1,430, compared to R-12's GWP of 10,900). It has the formula CFCHF and a boiling point of −26.3 °C (−15.34 °F) at atmospheric pressure. R-134a cylinders are colored light blue. A phaseout and transition to HFO-1234yf and other refrigerants, with GWPs similar to CO2, began in 2012 within the automotive market. Uses 1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane is a non-flammable gas used primarily as a "high-temperature" refrigerant for domestic refrigeration and automobile air conditioners. These devices began using 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane in the early 1990s as a replacement for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are heavily regulated because of their toxicity and flammability, as well as the contribution of CFC and HCFC refrigerants to ozone depletion and the contribution of HFC refrigerants to climate change. Refrigerants are used in a direct expansion (DX) circulating system to transfer energy from one environment to another, typically from inside a building to outside or vice versa. These can be air conditioner cooling only systems, cooling & heating reverse DX systems, or heat pump and heating only DX cycles. Refrigerants are controlled substances that are classified by several international safety regulations and, depending on their classification, may only be handled by qualified engineers due to extreme pressure, temperature, flammability, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automobile Air Conditioning
Automotive air conditioning systems use air conditioning to cool the air in a vehicle. History A company in New York City in the United States first offered the installation of air conditioning for cars in 1933. Most of their customers operated limousines and luxury cars. On 7 October 1935, Ralph Peo of Houde Engineering, Buffalo, New York, applied for a patent for an "Air Cooling Unit for Automobiles". , was granted on 16 November 1937. In 1939, Packard became the first automobile manufacturer to offer an optional air conditioning unit in its 1940 model year cars. These bulky units were manufactured by Bishop and Babcock (B&B), of Cleveland, Ohio and were ordered on approximately 2,000 cars. The "Bishop and Babcock Weather Conditioner" also incorporated a heater. Cars ordered with this option were shipped from Packard's East Grand Boulevard facility to the B&B factory where the installation was performed. Once complete, the car was shipped to a local dealer for delivery to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Hexafluoride
Sulfur hexafluoride or sulphur hexafluoride ( British spelling) is an inorganic compound with the formula SF6. It is a colorless, odorless, non-flammable, and non-toxic gas. has an octahedral geometry, consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. It is a hypervalent molecule. Typical for a nonpolar gas, is poorly soluble in water but quite soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. It has a density of 6.12 g/L at sea level conditions, considerably higher than the density of air (1.225 g/L). It is generally stored and transported as a liquefied compressed gas. has 23,500 times greater global warming potential (GWP) than as a greenhouse gas (over a 100-year time-frame) but exists in relatively minor concentrations in the atmosphere. Its concentration in Earth's troposphere reached 12.06 parts per trillion (ppt) in February 2025, rising at 0.4 ppt/year. The increase since 1980 is driven in large part by the expanding electric power sector, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryogenic Particle Detector
Cryogenic particle detectors operate at very low temperature, typically only a few degrees above absolute zero. These sensors interact with an energetic elementary particle (such as a photon) and deliver a signal that can be related to the type of particle and the nature of the interaction. While many types of particle detectors might be operated with improved performance at cryogenic temperatures, this term generally refers to types that take advantage of special effects or properties occurring only at low temperature. Introduction The most commonly cited reason for operating any sensor at low temperature is the reduction in thermal noise, which is proportional to the square root of the absolute temperature. However, at very low temperature, certain material properties become very sensitive to energy deposited by particles in their passage through the sensor, and the gain from these changes may be even more than that from reduction in thermal noise. Two such commonly used prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Hadron Collider
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle accelerator. It was built by the CERN, European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008, in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists, and hundreds of universities and laboratories across more than 100 countries. It lies in a tunnel in circumference and as deep as beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva. The first collisions were achieved in 2010 at an energy of 3.5 tera-electronvolts (TeV) per beam, about four times the previous world record. The discovery of the Higgs boson at the LHC was announced in 2012. Between 2013 and 2015, the LHC was shut down and upgraded; after those upgrades it reached 6.5 TeV per beam (13.0 TeV total collision energy). At the end of 2018, it was shut down for maintenance and further upgrades, and reopened over three years later in April 2022. The collider has four crossing points where the accelerated particles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
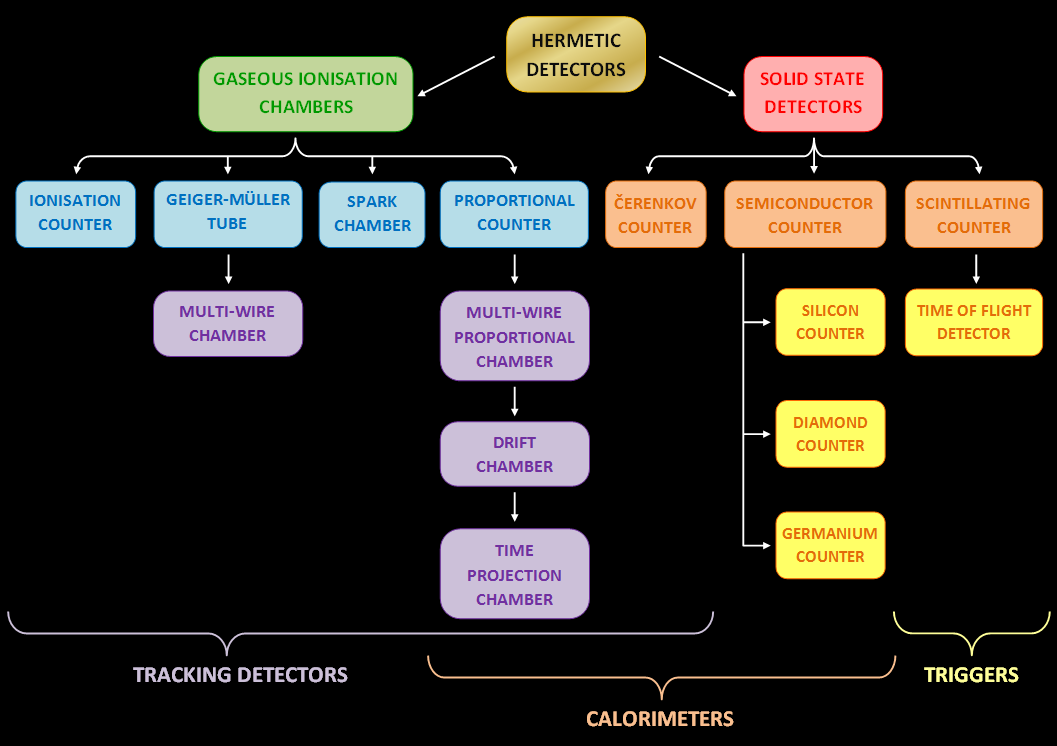
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. The operating of a nuclear radiation detector The operating principle of a nuclear radiation detector can be summarized as follows: The detector identifies high-energy particles or photons—such as alpha, beta, gamma radiation, or neutrons—through their interactions with the atoms of the detector material. These interactions generate a primary signal, which may involve ionization of gas, the creation of electron-hole pairs in semiconductors, or the emission of light in scint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistive Plate Chamber
A Resistive plate chamber (RPC) is a particle detector widely used in high energy physics. They are used for detecting muons in most of the modern experiments including ATLAS experiment, ATLAS, Compact Muon Solenoid, CMS, and BES III. References {{reflist Particle detectors Science experiments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercritical Fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is a substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous solids like a gas, overcoming the mass transfer limitations that slow liquid transport through such materials. SCFs are superior to gases in their ability to dissolve materials like liquids or solids. Near the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be "fine-tuned". Supercritical fluids occur in the atmospheres of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn, the terrestrial planet Venus, and probably in those of the ice giants Uranus and Neptune. Supercritical water is found on Earth, such as the water issuing from black smokers, a type of hydrothermal vent. SCFs are used as a substitute for organic solvents in a range of industrial and laborato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Solvent
A solvent (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for polar molecules, and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a cell are dissolved in water within the cell. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents ( citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas industries, including in chemical syntheses and purification processes Some petrochemical solvents are highly toxic and emit volatile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airsoft
Airsoft, also known as survival game () in Japan where it was popular, is a team sport, team-based shooting sport, shooting game in which participants eliminate opposing players out of play by shooting them with airsoft pellets, spherical plastic projectiles shot from airsoft guns. Although similar to paintball in concept and gameplay, airsoft pellets do not leave visible markings on their target and hits are not always apparent. Though the pellet impacts can leave small bruises or welt (bruise), welts on exposed skin (and so protective gear is still recommended), the game relies heavily on an honor system in which players who have been hit are expected to call themselves out of play in keeping with honesty, fairness and sportsmanship. The airsoft guns used are mostly magazine (firearms), magazine-fed, with some having manual/battery (electricity), battery electric motor, motor-powered spring (device), spring-piston pump powerplant, power plants similar to Nerf Blasters, or pne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overclocking
In computing, overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock rate of a computer to exceed that certified by the manufacturer. Commonly, operating voltage is also increased to maintain a component's operational stability at accelerated speeds. Semiconductor devices operated at higher frequencies and voltages increase power consumption and heat. An overclocked device may be unreliable or fail completely if the additional heat load is not removed or power delivery components cannot meet increased power demands. Many device warranties state that overclocking or over-specification voids any warranty, but some manufacturers allow overclocking as long as it is done (relatively) safely. Overview The purpose of overclocking is to increase the operating speed of a given component. Normally, on modern systems, the target of overclocking is increasing the performance of a major chip or subsystem, such as the main processor or graphics controller, but other components, such as sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |