|
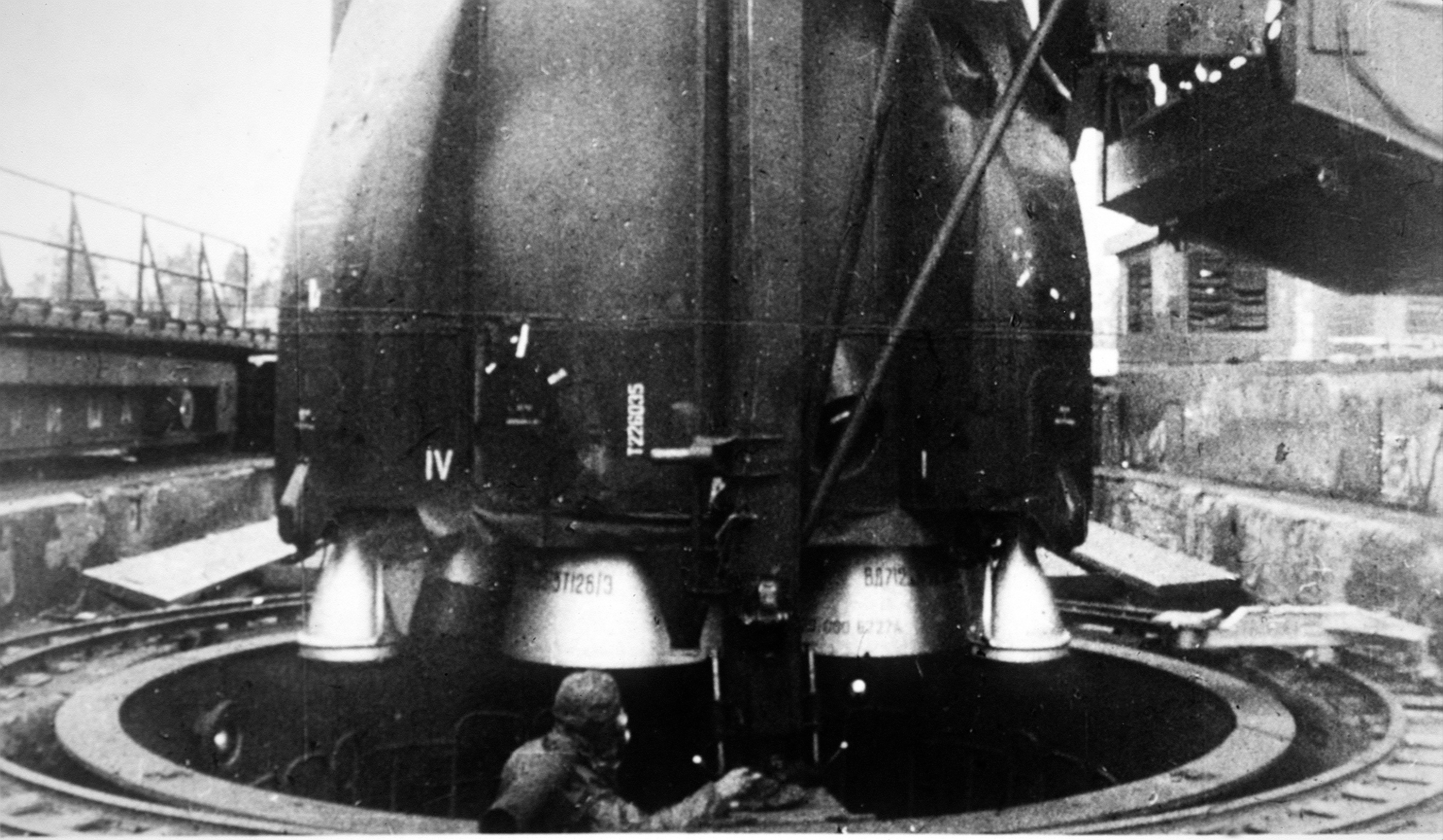
R-46 (missile)
The R-46 was an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) design by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The R-46 concept was to launch a very large hydrogen bomb into orbit as a fractional orbital bombardment system (FOBS). The existence of the system was alluded to in a speech by then Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev in 1961. The design was not developed, however, and the FOBS concept was abandoned as part of SALT II. See also * 8K69, the first Soviet fractional orbital bombardment system * List of missiles * List of rockets There are several different types of rockets. The following articles contain lists of rockets by type: * List of missiles * List of orbital launch systems * List of sounding rockets * List of military rockets * List of rocket stages See also * C ... Cold War intercontinental ballistic missiles of the Soviet Union Abandoned military projects of the Soviet Union R-046 {{Soviet-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two superpowers, but they each supported major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. The conflict was based around the ideological and geopolitical struggle for global influence by these two superpowers, following their temporary alliance and victory against Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan in 1945. Aside from the nuclear arsenal development and conventional military deployment, the struggle for dominance was expressed via indirect means such as psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race. The Western Bloc was led by the United States as well as a number of other First W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bomb
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lower mass, or a combination of these benefits. Characteristics of nuclear fusion reactions make possible the use of non-fissile depleted uranium as the weapon's main fuel, thus allowing more efficient use of scarce fissile material such as uranium-235 () or plutonium-239 (). The Ivy Mike, first full-scale thermonuclear test was carried out by the United States in 1952; the concept has since been employed by most of the world's List of states with nuclear weapons, nuclear powers in the design of their weapons. Modern fusion weapons consist essentially of two main components: a nuclear fission primary stage (fueled by or ) and a separate nuclear fusion secondary stage containing thermonuclear fuel: the heavy hydrogen isotopes deuterium and tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractional Orbital Bombardment System
A Fractional Orbital Bombardment System (FOBS) is a warhead delivery system that uses a low earth orbit towards its target destination. Just before reaching the target, it deorbits through a retrograde engine burn. Mark ZastrowHow does China’s hypersonic glide vehicle work? Astronomy, 4 November 2021. The Soviet Union first developed FOBS as a nuclear-weapons delivery system in the 1960s. It was one of the first Soviet efforts to use space to deliver nuclear weapons. In August 2021, the People's Republic of China tested a weapon that combined a FOBS with a hypersonic glide vehicle. Like a kinetic bombardment system but with nuclear weapons, FOBS had several attractive qualities: it had no range limit, its flight path would not reveal the target location, and warheads could be directed to North America over the South Pole, evading detection by NORAD's north-facing early warning systems. The maximum altitude would be around 150 km. Energetically, this would require a laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Premier
The Premier of the Soviet Union (russian: Глава Правительства СССР) was the head of government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). The office had four different names throughout its existence: Chairman of the Council of People's Commissars (1923–1946), Chairman of the Council of Ministers (1946–1991), Prime Minister (January – August 1991) and Chairman of the Committee on the Operational Management of the Soviet Economy (August–December 1991). Long before 1991, most non-Soviet sources referred to the post as "Premier" or "Prime Minister." Twelve individuals held the post. Of these, two died in office of natural causes (Vladimir Lenin and Joseph Stalin), three resigned – Alexei Kosygin, Nikolai Tikhonov and Ivan Silayev – and three were concurrently party leader and head of government (Lenin, Stalin and Nikita Khrushchev). By this account, Ivan Silayev spent the shortest time in office at 119 days. At more than 16 years, Kosygin spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev stunned the communist world with his denunciation of his predecessor Joseph Stalin's crimes, and embarked on a policy of de-Stalinization with his key ally Anastas Mikoyan. He sponsored the early Soviet space program, and enactment of moderate reforms in domestic policy. After some false starts, and a narrowly avoided nuclear war over Cuba, he conducted successful negotiations with the United States to reduce Cold War tensions. In 1964, the Kremlin leadership stripped him of power, replacing him with Leonid Brezhnev as First Secretary and Alexei Kosygin as Premier. Khrushchev was born in 1894 in a village in western Russia. He was employed as a metal worker during his youth, and he was a political commissar during the Russian Civil Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SALT II
The Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) were two rounds of bilateral conferences and corresponding international treaties involving the United States and the Soviet Union. The Cold War superpowers dealt with arms control in two rounds of talks and agreements: SALT I and SALT II. Negotiations commenced in Helsinki, in November 1969. SALT I led to the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty and an interim agreement between the two countries. Although SALT II resulted in an agreement in 1979 in Vienna, the US Senate chose not to ratify the treaty in response to the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, which took place later that year. The Supreme Soviet did not ratify it either. The agreement expired on December 31, 1985, and was not renewed, although both sides continued to respect it. The talks led to the STARTs, or ''St''rategic ''A''rms ''R''eduction ''T''reaties, which consisted of START I, a 1991 completed agreement between the United States and the Soviet Union, and START II, a 1993 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8K69
The R-36 (russian: Р-36) is a family of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and space launch vehicles (Tsyklon) designed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The original R-36 was deployed under the GRAU index 8K67 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-9 Scarp. It was able to carry three warheads and was the first Soviet MRV (multiple re-entry vehicle) missile. The later version, the R-36M was produced under the GRAU designations 15A14 and 15A18 and was given the NATO reporting name SS-18 Satan. This missile was viewed by certain United States analysts as giving the Soviet Union Pre-emptive nuclear strike, first strike advantage over the U.S., particularly because of its rapid silo-reload ability, very heavy throw weight and extremely large number of atmospheric re-entry, re-entry vehicles. Some versions of the R-36M were deployed with 10 warheads and up to 40 penetration aids and the missile's high throw-weight made it theoretically capable of carrying more warh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missiles
Below is a list of missiles, sorted alphabetically into large categories and subcategories by name and purpose. Other missile lists Types of missiles: * Conventional guided missiles ** Air-to-air missile ** Air-to-surface missile ** Anti-radiation missile ** Anti-ballistic missile ** Anti-satellite weapon ** Anti-ship missile (list) ** Anti-submarine missile ** Anti-tank guided missile (list) ** Land-attack missile ** Shoulder-launched missiles ** Surface-to-air missile (list) ** Surface-to-surface missile ** Wire-guided missile * Cruise missiles ** Air-launched cruise missile ** Ground-launched cruise missile ** Submarine-launched cruise missile * Ballistic missiles ** Tactical ballistic missile ** Short-range ballistic missile ** Theatre ballistic missile ** Medium-range ballistic missile ** Intermediate-range ballistic missile ** Intercontinental ballistic missile (List of ICBMs/Comparison of ICBMs) ** Submarine-launched ballistic missile ** Air-launched ballistic missile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of Rockets
There are several different types of rockets. The following articles contain lists of rockets by type: * List of missiles * List of orbital launch systems * List of sounding rockets * List of military rockets * List of rocket stages See also * Comparison of orbital launch systems * Comparison of orbital launchers families * Comparison of space station cargo vehicles * Comparison of orbital rocket engines * Comparison of solid-fuelled orbital launch systems * List of space launch system designs * List of artillery#Rockets * List of rocket aircraft * Lists of weapons * Model rocket * NATO reporting name NATO reporting names are code names for military equipment from Russia, China, and historically, the Eastern Bloc (Soviet Union and other nations of the Warsaw Pact). They provide unambiguous and easily understood English words in a uniform manne ... (has lists of various Soviet missiles) {{DEFAULTSORT:Rockets *Rockets lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold War Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles Of The Soviet Union
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale. This corresponds to on the Celsius scale, on the Fahrenheit scale, and on the Rankine scale. Since temperature relates to the thermal energy held by an object or a sample of matter, which is the kinetic energy of the random motion of the particle constituents of matter, an object will have less thermal energy when it is colder and more when it is hotter. If it were possible to cool a system to absolute zero, all motion of the particles in a sample of matter would cease and they would be at complete rest in the classical sense. The object could be described as having zero thermal energy. Microscopically in the description of quantum mechanics, however, matter still has zero-point energy even at absolute zero, because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)