|
Query Flooding
Query flooding is a method to search for a resource on a peer-to-peer network. It is simple and scales very poorly and thus is rarely used. Early versions of the Gnutella protocol operated by query flooding; newer versions use more efficient search algorithms. Operation A peer-to-peer network generally consists of a large number of nodes each connected to a small subset of the nodes and not all nodes in the network. If a node wants to find a resource on the network, which may be on a node it does not know about, it could simply broadcast its search query to its immediate neighbours. If the neighbours do not have the resource, it then asks its neighbours to forward the query to their neighbours in turn. This is repeated until the resource is found or all the nodes have been contacted, or perhaps a network-imposed hop limit is reached. Query flooding is simple to implement and is practical for small networks with few requests. It contacts all reachable nodes in the network and so c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer-to-peer Network
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the file sharing system Napster, originally released in 1999. The concept has inspired new structures and philosophies in many areas of human interaction. In such social contexts, peer-to-peer as a meme refers to the egalitarian soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work by adding resources to the system. In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that a company can increase sales given increased resources. For example, a package delivery system is scalable because more packages can be delivered by adding more delivery vehicles. However, if all packages had to first pass through a single warehouse for sorting, the system would not be as scalable, because one warehouse can handle only a limited number of packages. In computing, scalability is a characteristic of computers, networks, algorithms, networking protocols, programs and applications. An example is a search engine, which must support increasing numbers of users, and the number of topics it indexes. Webscale is a computer architectural approach that brings the capabilities of large-scale cloud computing companies into enterprise data centers. In mathematics, scalability mostly refers to closure u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnutella
Gnutella is a peer-to-peer network protocol. Founded in 2000, it was the first decentralized peer-to-peer network of its kind, leading to other, later networks adopting the model. In June 2005, Gnutella's population was 1.81 million computers increasing to over three million nodes by January 2006.On the Long-term Evolution of the Two-Tier Gnutella Overlay Rasti, Stutzbach, Rejaie, 2006. See Figure 2a. In late 2007, it was the most popular file-sharing network on the Internet with an estimated market share of more than 40%. History The first client (also called Gnutella) from which the network got its name was developed by Justin Frankel and Tom Pepper of Nullsoft in early 2000, soon after the company's acquisition by AOL. On March 14, the program was ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadcasting (networking)
In computer networking, telecommunication and information theory, broadcasting is a method of transferring a message to all recipients simultaneously. Broadcasting can be performed as a high-level operation in a program, for example, broadcasting in Message Passing Interface, or it may be a low-level networking operation, for example broadcasting on Ethernet. All-to-all communication is a computer communication method in which each sender transmits messages to all receivers within a group. In networking this can be accomplished using broadcast or multicast. This is in contrast with the point-to-point method in which each sender communicates with one receiver. Addressing methods There are four principal addressing methods in the Internet Protocol: Overview In computer networking, broadcasting refers to transmitting a packet that will be received by every device on the network. In practice, the scope of the broadcast is limited to a broadcast domain. Broadcasting is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hop (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, a hop is a portion of a signal's journey from source to receiver. Examples include: #The excursion of a radio wave from the Earth to the ionosphere and back to the Earth. The number of hops indicates the number of reflections from the ionosphere.Federal Standard 1037C #A similar excursion from an earth station to a communications satellite to another station, counted similarly except that if the return trip is not by satellite, then it is only a half hop. In computer network A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are ...s, a hop is the step from one network segment to the next. References Telecommunications engineering Radio frequency propagation {{Telecomm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
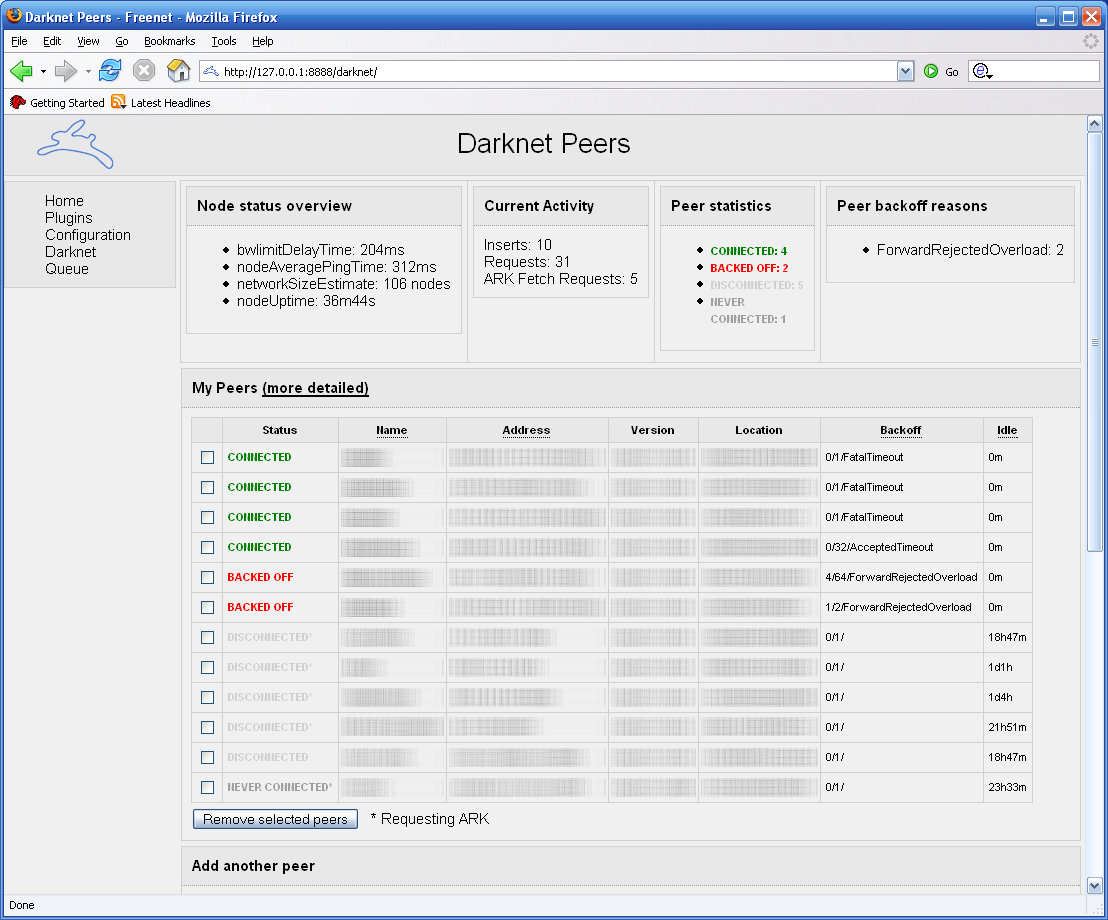
Freenet
Freenet is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship.What is Freenet? , ''Freenet: The Free network official website''.Taylor, Ian J. ''From P2P to Web Services and Grids: Peers in a Client/Server World''. London: Springer, 2005. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing |
Denial-of-service Attack
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connected to a network. Denial of service is typically accomplished by flooding the targeted machine or resource with superfluous requests in an attempt to overload systems and prevent some or all legitimate requests from being fulfilled. In a distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS attack), the incoming traffic flooding the victim originates from many different sources. More sophisticated strategies are required to mitigate this type of attack, as simply attempting to block a single source is insufficient because there are multiple sources. A DoS or DDoS attack is analogous to a group of people crowding the entry door of a shop, making it hard for legitimate customers to enter, thus disrupting trade. Criminal perpetrators of DoS attacks oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kad Network
The Kad network is a peer-to-peer (P2P) network which implements the Kademlia P2P overlay protocol. The majority of users on the Kad Network are also connected to servers on the eDonkey network, and Kad Network clients typically query known nodes on the eDonkey network in order to find an initial node on the Kad network. Usage The Kad network uses a UDP-based protocol to: * Find sources for eD2k hashes. * Search for eD2k hashes based on keywords in the file name. * Find comments and ratings for files (hashes). * Provide buddy services for firewalled ( Low ID) nodes. * Store locations, comments and (keywords out of) filenames. Note that the Kad network is not used to actually transfer files across the P2P network. Instead, when a file transfer is initiated, clients connect directly to each other (using the standard public IP network). This traffic is susceptible to blocking/shaping/tracking by an ISP or any other opportunistic middle-man. As with all decentralized networks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Hash Table
A distributed hash table (DHT) is a distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table: key–value pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key. The main advantage of a DHT is that nodes can be added or removed with minimum work around re-distributing keys. ''Keys'' are unique identifiers which map to particular ''values'', which in turn can be anything from addresses, to documents, to arbitrary data. Responsibility for maintaining the mapping from keys to values is distributed among the nodes, in such a way that a change in the set of participants causes a minimal amount of disruption. This allows a DHT to scale to extremely large numbers of nodes and to handle continual node arrivals, departures, and failures. DHTs form an infrastructure that can be used to build more complex services, such as anycast, cooperative web caching, distributed file systems, domain name services, instant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overlay Network
An overlay network is a computer network that is layered on top of another network. Structure Nodes in the overlay network can be thought of as being connected by virtual or logical links, each of which corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network. For example, distributed systems such as peer-to-peer networks and client–server applications are overlay networks because their nodes run on top of the Internet. The Internet was originally built as an overlay upon the telephone network, while today (through the advent of VoIP), the telephone network is increasingly turning into an overlay network built on top of the Internet. Uses Enterprise networks Enterprise private networks were first overlaid on telecommunication networks such as Frame Relay and Asynchronous Transfer Mode packet switching infrastructures but migration from these (now legacy) infrastructures to IP based MPLS networks and virtual private networks started (2001~ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnet URI Scheme
Magnet is a Uniform Resource Identifier, URI scheme that defines the format of magnet links, a de facto standard for identifying files (Uniform Resource Name, URN) by their content, via Cryptographic hash function, cryptographic hash value rather than by their location. Although magnet links can be used in a number of contexts, they are particularly useful in peer-to-peer file sharing networks because they allow resources to be referred to without the need for a continuously available host, and can be generated by anyone who already has the file, without the need for a central authority to issue them. This makes them popular for use as "guaranteed" search terms within the file sharing community where anyone can distribute a magnet link to ensure that the resource retrieved by that link is the one intended, regardless of how it is retrieved. History The standard for Magnet Uniform Resource Identifier, URIs was developed by Bitzi in 2002, partly as a "vendor- and project-neutral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |