|
Quercus Douglasii
''Quercus douglasii'', known as blue oak, is a species of oak endemic to (and found only in) California, common in the Coast Ranges and the foothills of the Sierra Nevada. It is California's most drought-tolerant deciduous oak, and is a dominant species in the blue oak woodland ecosystem. It is occasionally known as mountain oak and iron oak. Description ''Quercus douglasii'' is a medium-sized tree with sparse foliage, generally tall, with a trunk in diameter at breast height. Trunks are typically solitary, but some trees have multiple trunks. The tallest recorded specimen was found in Alameda County, at . The trees grow slowly, about per year. Individual trees over 500 years old have been recorded. The bark is light gray with many medium-sized dark cracks. The blue-green leaves are tough and leathery, deciduous, long, and entire or shallowly lobed. The acorns are long, with a moderately sweet kernel, and mature in 6–7 months from pollination. ''Q. douglasii'' is mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, cattle, sheep, or swine. The vegetation of tended pasture, forage, consists mainly of grasses, with an interspersion of legumes and other forbs (non-grass herbaceous plants). Pasture is typically grazed throughout the summer, in contrast to meadow which is ungrazed or used for grazing only after being mown to make hay for animal fodder. Pasture in a wider sense additionally includes rangelands, other unenclosed pastoral systems, and land types used by wild animals for grazing or browsing. Pasture lands in the narrow sense are distinguished from rangelands by being managed through more intensive agricultural practices of seeding, irrigation, and the use of fertilizers, while rangelands grow primarily native vegetation, managed with extensive practices like co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
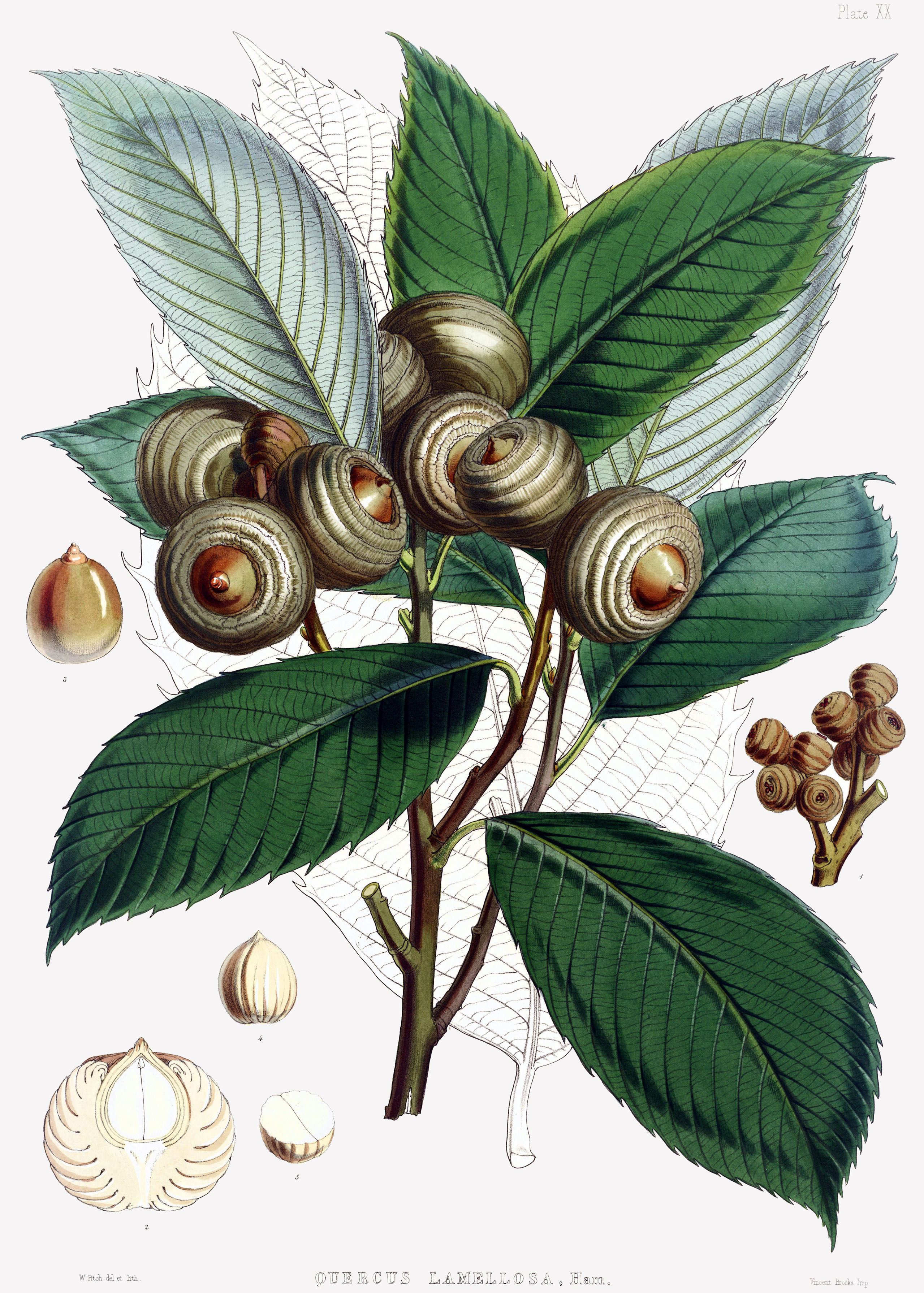
Glossary Of Leaf Morphology
The following is a list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article. The terms listed here all are supported by technical and professional usage, but they cannot be represented as mandatory or undebatable; readers must use their judgement. Authors often use terms arbitrarily, or coin them to taste, possibly in ignorance of established terms, and it is not always clear whether because of ignorance, or personal preference, or because usages change with time or context, or because of variation between specimens, even specimens from the same plant. For example, whether to call leaves on the same tree "acuminate", "lanceolate", or "linear" could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon White Oak
''Quercus garryana'' is an oak tree species of the Pacific Northwest, with a range stretching from southern California to southwestern British Columbia. It is commonly known as the Oregon white oak or Oregon oak or, in Canada, the Garry oak. It grows from sea level to an altitude of in the northern part of its range, and from in the south of the range in California. The eponymous Nicholas Garry was deputy governor of the Hudson's Bay Company. Description It is typically of medium height, growing slowly to around and occasionally as high as 100 ft, or in shrub form to tall. The trunks grow to thick, exceptionally . The bark is gray and fissured. It has the characteristic oval profile of other oaks when solitary, but is also known to grow in groves close enough together that crowns may form a canopy. The leaves are deciduous, long and 1–3 inches broad, with 3–7 deep lobes on each side, darker green on top and finely haired below. The flowers are catkins, the frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley Oak
''Quercus lobata'', commonly called the valley oak or roble, grows into the largest of California oaks. It is endemic to California, growing in interior valleys and foothills from Siskiyou County to San Diego County. Mature specimens may attain an age of up to 600 years. This deciduous oak requires year-round access to groundwater. Its thick, ridged bark is characteristic and resembles alligator hide. The valley oak's deeply lobed leaves assist in identification. Description The valley oak may surpass in height, with a sturdy trunk possibly exceeding in diameter. The "Henley Oak", in Covelo, California, is the tallest known valley oak, at . The branches have an irregular, spreading and arching appearance that produce a profound leafless silhouette in the clear winter sky. During autumn, the leaves turn a yellow to light orange color but become brown later in the season. In advancing age, the branches assume a drooping characteristic. The tree's pewter-colored rippled bark a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Live Oak
''Quercus agrifolia'', the California live oak, or coast live oak, is a highly variable, often evergreen oak tree, a type of live oak, native to the California Floristic Province. It may be shrubby, depending on age and growing location, but is generally a medium-sized tree. It grows west of the Sierra Nevada mountain range from Mendocino County, California, south to northern Baja California in Mexico. It is classified in the red oak section of oaks (''Quercus'' sect. ''Lobatae''). This species is commonly sympatric with canyon live oak (''Q. chrysolepis''), and the two may be hard to distinguish because their spinose leaves are superficially similar. Description Coast live oak typically has a much-branched trunk and reaches a mature height of . Some specimens may attain an age exceeding 1,000 years. Examples of this include the Grand Oak of Cherry Valley, California, the Encino Oak Tree, which died in the 1990s (part of the stump has been preserved) and the Pechanga Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interior Live Oak
''Quercus wislizeni'', known by the common name interior live oak, is an evergreen oak, highly variable and often shrubby, found in many areas of California in the United States continuing south into northern Baja California in Mexico. It generally occurs in foothills, being most abundant in the lower elevations of the Sierra Nevada, but also widespread in the Pacific Coast Ranges—where since 1980 it has been known as a separate species ''Quercus parvula''—and the San Gabriel Mountains. It was named for its collector, Friedrich Adolph Wislizenus (1810–1889). Description It is a large shrub or tree growing to tall, although where it is common in the low-elevation Sierra Nevada foothills it seldom exceeds . The dark-green leaves—appearing grayish from a distance—are usually small, long, thick, and often spiny-toothed at higher elevations, particularly on young trees. The male flowers are on catkins, the female flowers in leaf axils. The acorns are long, and mature the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray Pine
''Pinus sabiniana'' (sometimes spelled ''P. sabineana''), with vernacular names including towani pine, foothill pine, gray pine, bull pine, and digger pine, is a pine endemic to California in the United States. Some sources discourage using the name "digger pine," considering it pejorative ("digger" was a slur commonly used to refer to Indigenous Americans in the Great Basin and California). Description The ''Pinus sabiniana'' tree typically grows to , but can reach feet in height. The needles of the pine are in fascicles (bundles) of three, distinctively pale gray-green, sparse and drooping, and grow to in length. The seed cones are large and heavy, in length and almost as wide as they are long. When fresh, they weigh from , rarely over . The male cones grow at the base of shoots on the lower branches. File:Pinus sabiniana pollen cones Pinnacles, California.jpg, Pollen cones File:Pinus sabineana 00061.JPG, Bark File:J20161101-0079—Gray pine cone, pine nuts, and resin—R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canopy (biology)
In biology, the canopy is the aboveground portion of a plant cropping or crop, formed by the collection of individual plant crowns. In forest ecology, canopy also refers to the upper layer or habitat zone, formed by mature tree crowns and including other biological organisms ( epiphytes, lianas, arboreal animals, etc.). The communities that inhabit the canopy layer are thought to be involved in maintaining forest diversity, resilience, and functioning. Sometimes the term canopy is used to refer to the extent of the outer layer of leaves of an individual tree or group of trees. Shade trees normally have a dense canopy that blocks light from lower growing plants. Observation Early observations of canopies were made from the ground using binoculars or by examining fallen material. Researchers would sometimes erroneously rely on extrapolation by using more reachable samples taken from the understory. In some cases, they would use unconventional methods such as chairs susp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Oak
The genus ''Quercus'' contains about 500 species, some of which are listed here. The genus, as is the case with many large genera, is divided into subgenera and sections. Traditionally, the genus ''Quercus'' was divided into the two subgenera ''Cyclobalanopsis'', the ring-cupped oaks, and ''Quercus'', which included all the other sections. However, a comprehensive revision in 2017 identified different relationships. Now the genus is commonly divided into a subgenus ''Quercus'' and a sugenus ''Cerris'', with ''Cyclobalanopsis'' included in the latter. The sections of subgenus ''Quercus'' are mostly native to the New World, with the notable exception of the white oaks of sect. ''Quercus'' and the endemic Quercus pontica. In contrast, the sections of the subgenus ''Cerris'' are exclusively native to the Old World. Legend Species with evergreen foliage ("live oaks") are tagged '#'. Species in the genus have been recategorized between deciduous and evergreen on numerous occasions, alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Douglas (botanist)
David Douglas (25 June 1799 – 12 July 1834) was a Scottish botanist, best known as the namesake of the Douglas fir. He worked as a gardener, and explored the Scottish Highlands, North America, and Hawaii, where he died. Early life Douglas was born in Scone, Perthshire, the second son of John Douglas, a stonemason, and Jean Drummond. He attended Kinnoull School and upon leaving found work as an apprentice to William Beattie, head gardener at Scone Palace, the seat of the Earl of Mansfield. He spent seven years in this position, completing his apprenticeship, and then spent a winter at a college in Perth to learn more of the scientific and mathematical aspects of plant culture. After a further spell of working at Valleyfield House in Fife (during which time he had access to a library of botanical and zoological books) he moved to the Botanical Gardens of Glasgow University and attended botany lectures. William Jackson Hooker, who was Garden Director and Professor of Bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catkin
A catkin or ament is a slim, cylindrical flower cluster (a spike), with inconspicuous or no petals, usually wind-pollinated (anemophilous) but sometimes insect-pollinated (as in ''Salix''). They contain many, usually unisexual flowers, arranged closely along a central stem that is often drooping. They are found in many plant families, including Betulaceae, Fagaceae, Moraceae, and Salicaceae. Occurrence Catkin-bearing plants include many trees or shrubs such as birch, willow, aspen, hickory, sweet chestnut, and sweetfern (''Comptonia''). In many of these plants, only the male flowers form catkins, and the female flowers are single ( hazel, oak), a cone (alder), or other types (mulberry). In other plants (such as poplar), both male and female flowers are borne in catkins. In Britain, they can be seen in January or February, when many trees are bare for winter. They can even occur in December. Evolution For some time, catkins were believed to be a key synapomorphy among the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoecious
Monoecy (; adj. monoecious ) is a sexual system in seed plants where separate male and female cones or flowers are present on the same plant. It is a monomorphic sexual system alongside gynomonoecy, andromonoecy and trimonoecy. Monoecy is connected to anemophily. It can prevent self-pollination in an individual flower but cannot prevent self-pollination between male and female flowers on the same plant. Monoecy in angiosperms has been of interest for evolutionary biologists since Charles Darwin. Terminology Monoecious comes from the Greek words for one house. History The term monoecy was first introduced in 1735 by Carl Linnaeus. Darwin noted that the flowers of monoecious species sometimes showed traces of the opposite sex function. Monoecious hemp was first reported in 1929. Occurrence Monoecy is most common in temperate climates and is often associated with inefficient pollinators or wind-pollinated plants. It may be beneficial to reducing pollen-stigma interferenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |