|
Qianmen
Qianmen () is the colloquial name for Zhengyangmen (; Manchu:; Möllendorff:tob šun-i duka, literally meaning "Gate of the Zenith Sun"), a gate in Beijing's historic city wall. The gate is situated to the south of Tiananmen Square and once guarded the southern entry into the Inner City. Although much of Beijing's city walls were demolished, Zhengyangmen remains an important geographical marker of the city. The city's central north–south axis passes through Zhengyangmen's main gate. It was formerly named Lizhengmen (), meaning "beautiful portal". History Zhengyangmen was first built in 1419 during the Ming dynasty and once consisted of the gatehouse proper and an archery tower, which were connected by side walls and together with side gates, formed a large barbican. The gate guarded the direct entry into the imperial city. The city's first railway station, known as the Qianmen Station, was built just outside the gate. During the Boxer Rebellion of 1900 in the late Qing dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qianmen 14 April 2010
Qianmen () is the colloquial name for Zhengyangmen (; Manchu:; Möllendorff:tob šun-i duka, literally meaning "Gate of the Zenith Sun"), a gate in Beijing's historic city wall. The gate is situated to the south of Tiananmen Square and once guarded the southern entry into the Inner City. Although much of Beijing's city walls were demolished, Zhengyangmen remains an important geographical marker of the city. The city's central north–south axis passes through Zhengyangmen's main gate. It was formerly named Lizhengmen (), meaning "beautiful portal". History Zhengyangmen was first built in 1419 during the Ming dynasty and once consisted of the gatehouse proper and an archery tower, which were connected by side walls and together with side gates, formed a large barbican. The gate guarded the direct entry into the imperial city. The city's first railway station, known as the Qianmen Station, was built just outside the gate. During the Boxer Rebellion of 1900 in the late Qing dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing City Fortifications
The Beijing city fortifications were Defensive wall, walls with series of towers and gates constructed in the city of Beijing, China in the early 1400s until they were partially demolished in 1965 for the construction of the 2nd Ring Road and Line 2, Beijing Subway, Line 2 of the Beijing Subway. The original walls were preserved in the southeastern part of the city, just south of the Beijing railway station. The entire perimeter of the Inner and Outer city walls stretched for approximately . Beijing was the capital of China for the majority of the Yuan Dynasty, Yuan, Ming Dynasty, Ming, and Qing Dynasty, Qing Dynasties, as well as a secondary capital to the Liao Dynasty, Liao and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin Dynasties. As such, the city required an extensive fortification system around the Forbidden City, the Imperial City, Beijing, Imperial City, the Inner city, and the Outer city. Fortifications included gate towers, gates, archways, watchtowers, barbicans, barbican towers, bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing Subway
The Beijing Subway is the rapid transit system of Beijing Municipality that consists of 25 lines including 20 rapid transit lines, two airport rail links, one maglev line and 2 light rail lines, and 463 stations. The rail network extends across 12 urban and suburban districts of Beijing and into one district of Langfang in neighboring Hebei province. With 3.8484 billion trips delivered in 2018, an average of 10.544 million trips per day, the Beijing Subway is the world's busiest metro system. Single-day ridership set a record of 13.7538 million on July 12, 2019. The Beijing Subway opened in 1971 and is the oldest metro system in mainland China and on the mainland of East Asia. Before the system began its rapid expansion in 2002, the subway had only two lines. The existing network still cannot adequately meet the city's mass transit needs. Beijing Subway's extensive expansion plans call for of lines serving a projected 18.5 million trips every day when Phase 2 Constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in Northern China, and is governed as a municipality under the direct administration of the State Council with 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighboring Tianjin to the southeast; together, the three divisions form the Jingjinji megalopolis and the national capital region of China. Beijing is a global city and one of the world's leading centres for culture, diplomacy, politics, finance, busine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiananmen Square
Tiananmen Square or Tian'anmen Square (; 天安门广场; Pinyin: ''Tiān'ānmén Guǎngchǎng''; Wade–Giles: ''Tʻien1-an1-mên2 Kuang3-chʻang3'') is a city square in the city center of Beijing, China, named after the eponymous Tiananmen ("Gate of Heavenly Peace") located to its north, which separates it from the Forbidden City. The square contains the Monument to the People's Heroes, the Great Hall of the People, the National Museum of China, and the Mausoleum of Mao Zedong. Mao Zedong proclaimed the founding of the People's Republic of China in the square on October 1, 1949; the anniversary of this event is still observed there. The size of Tiananmen Square is 765 x 282 meters (215,730 m2 or 53.31 acres). It has great cultural significance as it was the site of several important events in Chinese history. Outside China, the square is best known for the 1989 protests and massacre that ended with a military crackdown, which is also known as the Tiananmen Square Massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
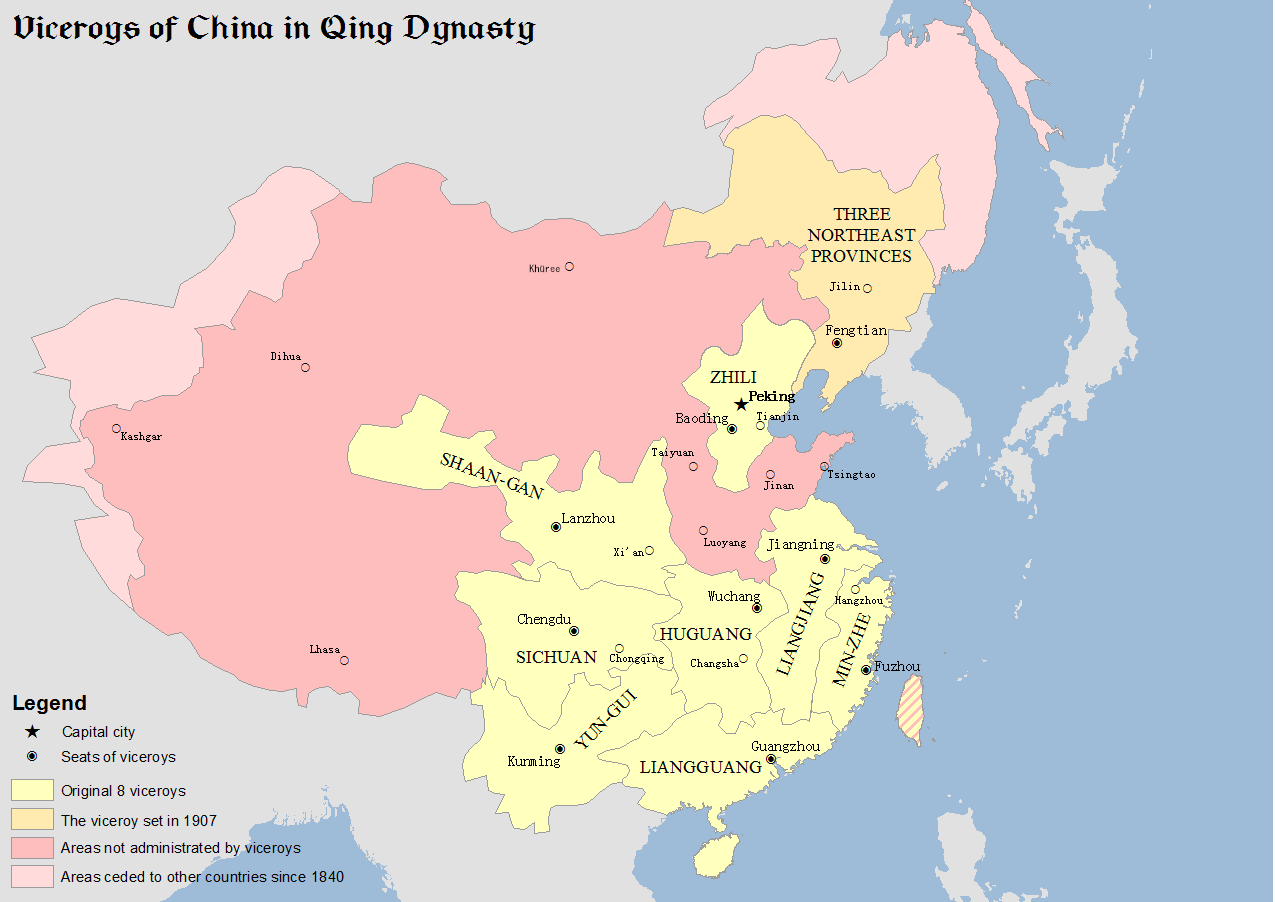
Viceroy Of Zhili
The Viceroy of Zhili, fully referred to in Chinese as the Governor-General of Zhili and Surrounding Areas Overseeing Military Affairs and Food Production, Manager of Waterways, Director of Civil Affairs, was one of eight regional Viceroys during the Qing dynasty. The Viceroy of Zhili was an important post because the province of Zhili, which literally means "directly ruled", was the area surrounding the imperial capital, Beijing. The administrative centre was in Tianjin even though the provincial capital was in Baoding. The Viceroy's duties as well as responsibilities have never been defined entirely. Generally speaking, the Viceroy oversaw the military and civil affairs of Zhili, Shandong and Henan provinces. The Viceroy of Zhili was also highly influential in imperial court politics. History The office was first created on 30 September 1649 during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, but was later abolished on 1 June 1658. On 23 November 1661, during the reign of the Kangxi Emperor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Shikai
Yuan Shikai (; 16 September 1859 – 6 June 1916) was a Chinese military and government official who rose to power during the late Qing dynasty and eventually ended the Qing dynasty rule of China in 1912, later becoming the Emperor of China. He first tried to save the dynasty with a number of modernization projects including bureaucratic, fiscal, judicial, educational, and other reforms, despite playing a key part in the failure of the Hundred Days' Reform. He established the first modern army and a more efficient provincial government in North China during the last years of the Qing dynasty before forcing the abdication of the Xuantong Emperor, the last monarch of the Qing dynasty in 1912. Through negotiation, he became the first President of the Republic of China in 1912. This army and bureaucratic control were the foundation of his autocratic rule. In 1915 he attempted to restore the hereditary monarchy in China, with himself as the Hongxian Emperor (). His death in 1916 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
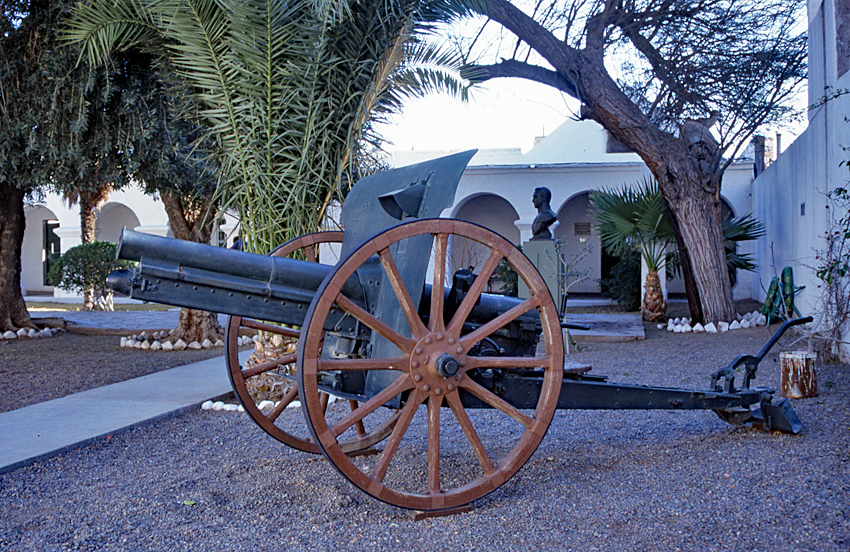
Krupp Gun
The Krupp gun is a family of artillery pieces that was used by several world armies from the nineteenth century onwards. History In 1811, Friedrich Krupp founded his cast-steel factory ''Gusstahlfabrik'', but it was his son, Alfred Krupp, who attained notable success. The principal characteristic of Krupp guns was that they were made of steel at the time when everyone else still used bronze, cast iron and sometimes wrought iron. Alfred Krupp was introduced to the Bessemer process to mass-produce steel by his London agent and friend, Alfred Longsdon, in 1859-60. After a lengthy period of trial and error, this steel was developed to such quality that the royal factory of Woolwich in England acquired steel from Krupp to manufacture guns that conformed to British naval standards. Also, Krupp was one of the first manufacturers to design practical breechloading guns for army use. In 1856, Fried. Krupp A.G., produced a 9 cm ( 6-Pfünder-Feldkanone C/61) rifled breechloader of cast ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangxu Emperor
The Guangxu Emperor (14 August 1871 – 14 November 1908), personal name Zaitian, was the tenth Emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the ninth Qing emperor to rule over China proper. His reign lasted from 1875 to 1908, but in practice he ruled, without Empress Dowager Cixi's influence, only from 1889 to 1898. He initiated the Hundred Days' Reform, but was abruptly stopped when the empress dowager launched a coup in 1898, after which he became powerless and was held under house arrest until his death by poisoning. His era name, "Guangxu", means "glorious succession". The emperor died in 1908 and it was widely suspected at the time that he had been poisoned. A forensic examination on his remains confirmed in 2008 that the cause of death was arsenic poisoning. The level of arsenic in his remains was 2,000 times higher than normal. Accession to the throne and upbringing Zaitian was the second son of Yixuan (Prince Chun), and his primary spouse Yehenara Wanzhen, a younger siste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbidden City
The Forbidden City () is a palace complex in Dongcheng District, Beijing, China, at the center of the Imperial City of Beijing. It is surrounded by numerous opulent imperial gardens and temples including the Zhongshan Park, the sacrificial Imperial Ancestral Temple, the Beihai Park, and the Jingshan Park. It is officially administered by the Palace Museum. The Forbidden City was constructed from 1406 to 1420, and was the former Chinese imperial palace and winter residence of the Emperor of China from the Ming dynasty (since the Yongle Emperor) to the end of the Qing dynasty, between 1420 and 1924. The Forbidden City served as the home of Chinese emperors and their households and was the ceremonial and political center of the Chinese government for over 500 years. Since 1925, the Forbidden City has been under the charge of the Palace Museum, whose extensive collection of artwork and artifacts were built upon the imperial collections of the Ming and Qing dynasties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of China
The Chinese Communist Party (CCP), officially the Communist Party of China (CPC), is the founding and sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Under the leadership of Mao Zedong, the CCP emerged victorious in the Chinese Civil War against the Kuomintang, and, in 1949, Mao proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China. Since then, the CCP has governed China with eight smaller parties within its United Front and has sole control over the People's Liberation Army (PLA). Each successive leader of the CCP has added their own theories to the party's constitution, which outlines the ideological beliefs of the party, collectively referred to as socialism with Chinese characteristics. As of 2022, the CCP has more than 96 million members, making it the second largest political party by party membership in the world after India's Bharatiya Janata Party. The Chinese public generally refers to the CCP as simply "the Party". In 1921, Chen Duxiu and Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
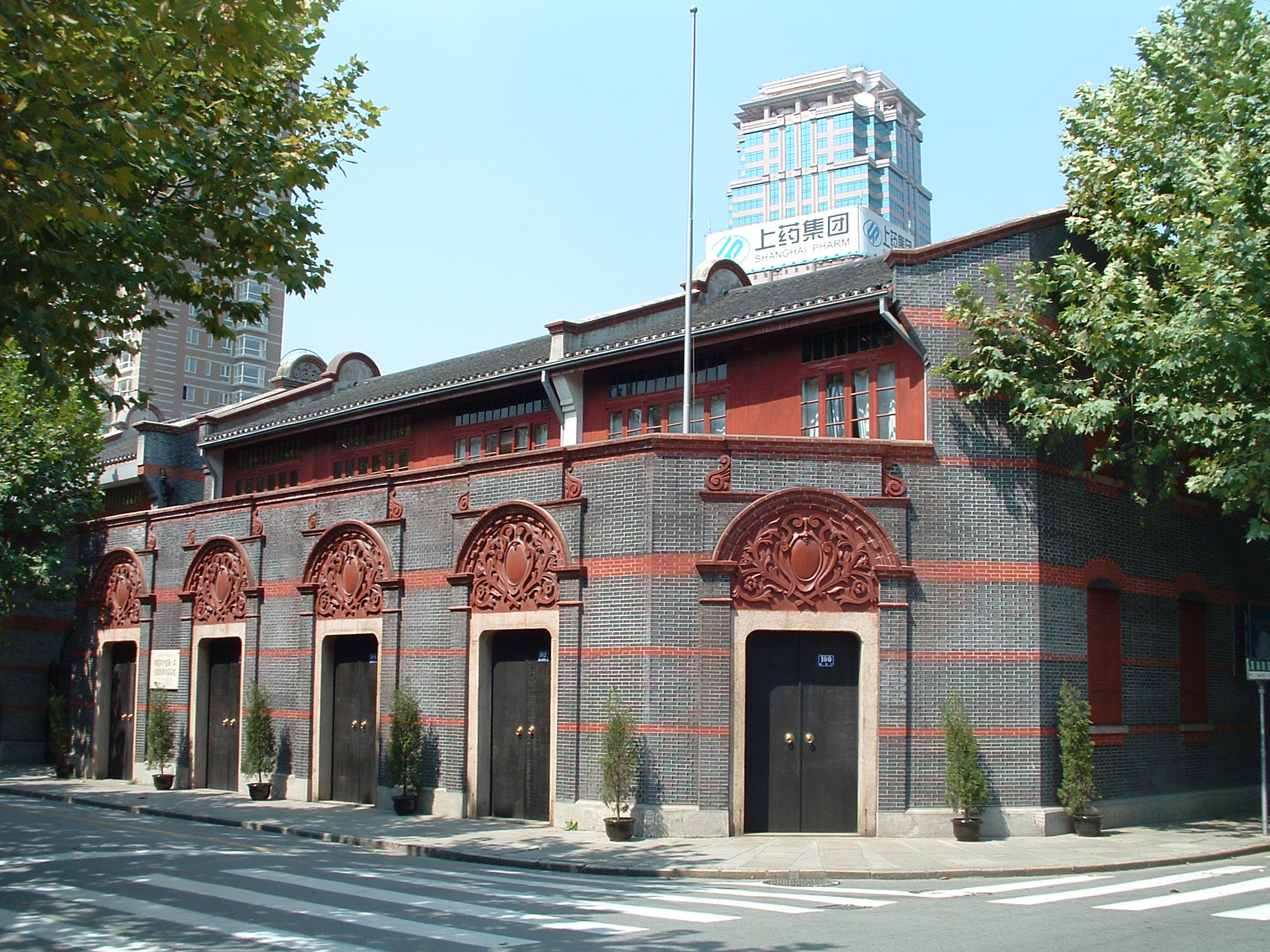
Yamen
A ''yamen'' (''ya-men''; ; Manchu: ''yamun'') was the administrative office or residence of a local bureaucrat or mandarin in imperial China. A ''yamen'' can also be any governmental office or body headed by a mandarin, at any level of government: the offices of one of the Six Ministries is a ''yamen'', but so is a prefectural magistracy. The term has been widely used in China for centuries, but appeared in English during the Qing dynasty. Overview Within a local ''yamen'', the bureaucrat administered the government business of the town or region. Typical responsibilities of the bureaucrat includes local finance, capital works, judging of civil and criminal cases, and issuing decrees and policies. Typically, the bureaucrat and his immediate family would live in a residence attached to the ''yamen''. This was especially so during the Qing dynasty, when imperial law forbade a person from taking government office in his native province. ''Yamen''s varied greatly in size de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14572085030).jpg)