|
Qauqaut
The Qauqaut () were a Taiwanese aboriginal people who lived primarily in the town of Su-ao in Yilan County. They spoke the Basay language, which is a Kavalanic language. According to Japanese anthropologist Inō Kanori, the Qauqaut people had been assimilated by the Kavalan people by early 20th century. The Qauqaut people are not recognised by the government of Taiwan. According to oral tradition from various Atayal villages, the Qauqaut originally settled in the middle portion of the Takiri River (Chinese pinyin: ''Liwuhsi''). In the mid-1700s, following pressure from Atayals, they moved to the east coast down the Takiri. Later, some moved north to Langsu in Nan'ao County. Early modern Chinese documents on the Kavalan territories reported that the Qauqaut were linguistically and culturally distinct from the other Formosan ethnic groups and that they did not intermarry with the other communities. Taiwanese linguist Paul Jen-kuei Li hypothesised that, in about 200 BCE, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basay Language
Basay was a Formosan language spoken around modern-day Taipei in northern Taiwan by the Basay, Qauqaut, and Trobiawan peoples. Trobiawan, Linaw, and Qauqaut were other dialects (''see East Formosan languages''). Basay data is mostly available from Erin Asai's 1936 field notes, which were collected from an elderly Basay speaker in Shinshe, Taipei, as well as another one in Yilan who spoken the Trobiawan dialect (Li 1999). However, the Shinshe informant's speech was heavily influenced by Taiwanese, and the Trobiawan informant, named Ipai, had heavy Kavalan influence in her speech. Li (1992) mentions four Basaic languages: Basay, Luilang, Nankan, Puting. Nankan and Puting are close to Kavalan, whereas Luilang is divergent.Tsuchida, Shigeru. 1985. Kulon: Yet another Austronesian language in Taiwan?. Bulletin of the Institute of Ethnology, Academia Sinica 60. 1-59. Syntax There are four optional case markers in Basay (Li 1999:646). *a – nominative, ligature (Shinshe dialect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographics Of Taiwan
The population of Taiwan is approximately 23.19 million as of September 2022. Immigration of Han Chinese to the Penghu islands started as early as the 13th century, while settlement of the main island occurred from the 16th century during the Ming–Qing transition. Further immigration occurred when workers were imported from Fujian in the 17th century. According to governmental statistics, in the early 21st century, 95% to 97% of Taiwan's population are Han Chinese, while about 2.3% are Taiwanese of Austronesian ethnicity.Taiwan ''''. |
East Formosan Languages
The East Formosan languages consist of various Formosan languages scattered across Taiwan, including Kavalan, Amis, and the extinct Siraya language. This grouping is supported by both Robert Blust and Paul Jen-kuei Li. Li considers the Siraya-speaking area in the southwestern plains of Taiwan to be the most likely homeland of the East Formosan speakers, where they then spread to the eastern coast of Taiwan and gradually migrated to the area of modern-day Taipei Taipei (), officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Located in Northern Taiwan, Taipei City is an enclave of the municipality of New Taipei City that sits about southwest of the n .... Languages *Kavalanic ** Kavalan ** Basay ** Qauqaut *Amis-Sakizaya **Sakizaya ** Amis * Sirayaic ** Siraya **Taivoan–Makatao *** Taivoan *** Makatao Luilang is often lumped together with the Ketagalan dialect of Basay, but is poorly attested and remains unclassified. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiwanese Indigenous Peoples
Taiwanese indigenous peoples (formerly Taiwanese aborigines), also known as Formosan people, Austronesian Taiwanese, Yuanzhumin or Gaoshan people, are the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, with the nationally recognized subgroups numbering about 569,000 or 2.38% of the island's population. This total is increased to more than 800,000 if the indigenous peoples of the plains in Taiwan are included, pending future official recognition. When including those of mixed ancestry, such a number is possibly more than a million. Academic research suggests that their ancestors have been living on Taiwan for approximately 6,500 years. A wide body of evidence suggests Taiwan's indigenous peoples maintained regular trade networks with regional cultures before the Han Chinese colonists began settling on the island from the 17th century. Taiwanese indigenous peoples are Austronesians, with linguistic and cultural ties to other Austronesian peoples in the region. Taiwan is also the origin and lingu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Jen-kuei Li
Paul Li, or Li Jen-kuei (; born 20 September 1936), is a research fellow at the Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica in Taipei, Taiwan. Li is a leading specialist on Formosan languages and has published dictionaries on the Pazeh and Kavalan language Kavalan (also known as Kvalan, Kebalan or Kbalan) was formerly spoken in the Northeast coast area of Taiwan by the Kavalan people (噶瑪蘭). It is an East Formosan language of the Austronesian family. Kavalan is no longer spoken in its orig ...s. References *Chang, Henry Yungli, Lillian Mei-chin Huang, and Dah-an Ho (eds.). ''Streams converging into an ocean: festschrift in honor of Professor Paul Jen-kuei Li on his 70th birthday ��川匯海: 李壬癸先生七秩壽慶論文集'. Taipei: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica, 2006.Curriculum Vitae External links 1936 births Linguists of Austronesian languages Linguists of Formosan languages Linguists from Taiwan People from Yilan County, Taiwan Living peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seediq Language
Seediq, also known as Sediq, Taroko, is an Atayalic language spoken in the mountains of Northern Taiwan by the Seediq and Taroko people. Subdivisions Seediq consists of three main dialects (Tsukida 2005). Members of each dialect group refer to themselves by the name of their dialect, while the Amis people call them "Taroko." #Truku (Truku) – 20,000 members including non-speakers. The Truku dialect, transcribed 德路固 in Chinese. #Toda (Tuuda) – 2,500 members including non-speakers. #Tgdaya (Tkdaya, Paran) – 2,500 members including non-speakers. Phonology In Seediq there are 19 consonant phonemes and 4 vowel phonemes. Among these, there are two velar fricatives, one voiceless and the other voiced, and a uvular stop. In both labial and alveolar plosive series, voice opposition is contrastive; velar and uvular series, however, only display voiceless sounds. The alveolar affricate has a marginal phonological status and is found in some interjections (such as ''teʼcu! ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
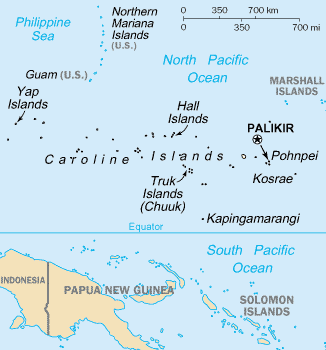
Caroline Islands
The Caroline Islands (or the Carolines) are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically, they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM) in the central and eastern parts of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end. Historically, this area was also called ''Nuevas Filipinas'' or New Philippines, because they were part of the Spanish East Indies and were governed from Manila in the Philippines. The Carolines are scattered across a distance of approximately 3,540 kilometers (2,200 miles), from the westernmost island, Tobi (island), Tobi, in Palau, to the easternmost island, Kosrae, a Administrative divisions of the Federated States of Micronesia, state of the FSM. Description The group consists of about 500 small coral islands, east of the Philippines, in the Pacific Ocean. The distance from Yap (one of the larger Caroline islands) to Manila is . Most of the islands are made up of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the International Date Line. Geographically, the country is part of the larger island group of Micronesia. The country's population of 58,413 people (at the 2018 World Bank Census) is spread out over five islands and 29 coral atolls, comprising 1,156 individual islands and islets. The capital and largest city is Majuro. It has the largest portion of its territory composed of water of any sovereign state, at 97.87%. The islands share maritime boundaries with Wake Island to the north, Kiribati to the southeast, Nauru to the south, and Federated States of Micronesia to the west. About 52.3% of Marshall Islanders (27,797 at the 2011 Census) live on Majuro. In 2016, 73.3% of the population were defined as being "urban". The UN also indicates a population d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |