|
QZSS
The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), also known as , is a four-satellite regional time transfer system and a satellite-based augmentation system developed by the Japanese government to enhance the United States-operated Global Positioning System (GPS) in the Asia-Oceania regions, with a focus on Japan. The goal of QZSS is to provide highly precise and stable positioning services in the Asia-Oceania region, compatible with GPS. Four-satellite QZSS services were available on a trial basis as of 12 January 2018, and officially started on 1 November 2018. A satellite navigation system independent of GPS is planned for 2023 with 7 satellites. History In 2002, the Japanese government authorized the development of QZSS, as a three-satellite regional time transfer system and a satellite-based augmentation system for the United States operated Global Positioning System (GPS) to be receivable within Japan. A contract was awarded to Advanced Space Business Corporation (ASBC), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QZSS Logo
The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), also known as , is a four-satellite regional time transfer system and a satellite-based augmentation system developed by the Japanese government to enhance the United States-operated Global Positioning System (GPS) in the Asia-Oceania regions, with a focus on Japan. The goal of QZSS is to provide highly precise and stable positioning services in the Asia-Oceania region, compatible with GPS. Four-satellite QZSS services were available on a trial basis as of 12 January 2018, and officially started on 1 November 2018. A satellite navigation system independent of GPS is planned for 2023 with 7 satellites. History In 2002, the Japanese government authorized the development of QZSS, as a three-satellite regional time transfer system and a satellite-based augmentation system for the United States operated Global Positioning System (GPS) to be receivable within Japan. A contract was awarded to Advanced Space Business Corporation (ASBC), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). One set of critical vulnerabilities in satellite communications are the signals that govern positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). Failure to properly secure these transmissions could not only disrupt satellite networks but wreak havoc on a host of dependent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
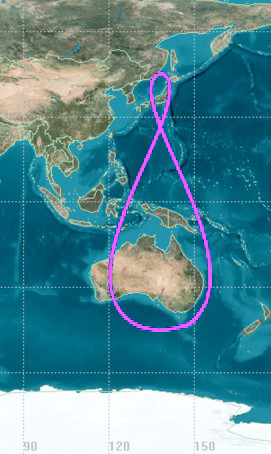
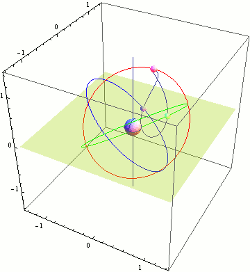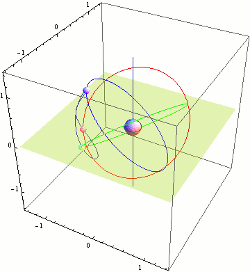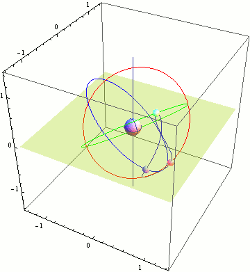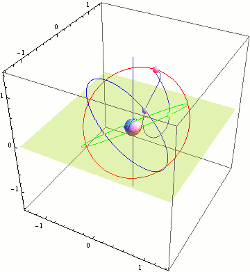
Tundra Orbit
A Tundra orbit (russian: орбита «Тундра») is a highly elliptical geosynchronous orbit with a high inclination (approximately 63.4°), an orbital period of one sidereal day, and a typical eccentricity between 0.2 and 0.3. A satellite placed in this orbit spends most of its time over a chosen area of the Earth, a phenomenon known as apogee dwell, which makes them particularly well suited for communications satellites serving high-latitude regions. The ground track of a satellite in a Tundra orbit is a closed figure 8 with a smaller loop over either the northern or southern hemisphere. This differentiates them from Molniya orbits designed to service high-latitude regions, which have the same inclination but half the period and do not loiter over a single region. Uses Tundra and Molniya orbits are used to provide high-latitude users with higher elevation angles than a geostationary orbit. This is desirable as broadcasting to these latitudes from a geostationary orbit ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radionavigation system owned by the United States government and operated by the United States Space Force. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provides geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephonic or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. The GPS project was started by the U.S. Department of Defense in 1973. The first prototype spacecraft was lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QZS-1R
QZS-1R is a Japanese navigation satellite consisting part of the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS). QZS-1R will replace the QZS-1 (Michibiki-1) satellite launched in September 2010. QZS-1 has a design life of ten years. As QZS-1 is an experimental satellite, it did not broadcast the MADOCA (Multi-GNSS Advanced Demonstration tool for Orbit and Clock Analysis) signal, which can be used for centimeter-order navigation. With the launch of QZS-1R, all satellites of QZSS will be capable of transmitting in the MADOCA signal, reaching operational capacity. Satellite QZS-1R is the fourth operational Quasi-Zenith Satellite to be launched. The design of the satellite is based on QZS-2 and 4, with minor differences such as an increase in the number of temperature sensors on board. Launch QZS-1R was launched on 26 October 2021 by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries is a Japanese multinational engineering, electrical equipment and electronics corporation headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosynchronous Orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital period means that, for an observer on Earth's surface, an object in geosynchronous orbit returns to exactly the same position in the sky after a period of one sidereal day. Over the course of a day, the object's position in the sky may remain still or trace out a path, typically in a figure-8 form, whose precise characteristics depend on the orbit's inclination and eccentricity. A circular geosynchronous orbit has a constant altitude of . A special case of geosynchronous orbit is the geostationary orbit, which is a circular geosynchronous orbit in Earth's equatorial plane with both inclination and eccentricity equal to 0. A satellite in a geostationary orbit remains in the same position in the sky to observers on the surface. Communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analemma
In astronomy, an analemma (; ) is a diagram showing the position of the Sun in the sky as seen from a fixed location on Earth at the same mean solar time, as that position varies over the course of a year. The diagram will resemble a figure eight. Globes of Earth often display an analemma as a two-dimensional figure of equation of time vs. declination of the Sun. The north–south component of the analemma results from the change in the Sun's declination due to the tilt of Earth's axis of rotation. The east–west component results from the nonuniform rate of change of the Sun's right ascension, governed by combined effects of Earth's axial tilt and orbital eccentricity. One can photograph an analemma by keeping a camera at a fixed location and orientation and taking multiple exposures throughout the year, always at the same time of day (disregarding daylight saving time, if applicable). Diagrams of analemmas frequently carry marks that show the position of the Sun at variou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ISA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNSS Augmentation
Augmentation of a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is a method of improving the navigation system's attributes, such as precision, reliability, and availability, through the integration of external information into the calculation process. There are many such systems in place, and they are generally named or described based on how the GNSS sensor receives the external information. Some systems transmit additional information about sources of error (such as clock drift, ephemeris, or ionospheric delay), others provide direct measurements of how much the signal was off in the past, while a third group provides additional vehicle information to be integrated in the calculation process. Satellite-based augmentation system Satellite-based augmentation systems (SBAS) support wide-area or regional augmentation through the use of additional satellite-broadcast messages. Using measurements from the ground stations, correction messages are created and sent to one or more satell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Orbit
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude above Earth's equator ( in radius from Earth's center) and following the direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to Earth's rotational period, one sidereal day, and so to ground observers it appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. The concept of a geostationary orbit was popularised by the science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke in the 1940s as a way to revolutionise telecommunications, and the first satellite to be placed in this kind of orbit was launched in 1963. Communications satellites are often placed in a geostationary orbit so that Earth-based satellite antennas do not have to rotate to track them but can be pointed permanently at the position in the sky where the sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean Anomaly
In celestial mechanics, the mean anomaly is the fraction of an elliptical orbit's period that has elapsed since the orbiting body passed periapsis, expressed as an angle which can be used in calculating the position of that body in the classical two-body problem. It is the angular distance from the pericenter which a fictitious body would have if it moved in a circular orbit, with constant speed, in the same orbital period as the actual body in its elliptical orbit. Definition Define as the time required for a particular body to complete one orbit. In time , the radius vector sweeps out 2 radians, or 360°. The average rate of sweep, , is then :n = \frac = \frac~, which is called the '' mean angular motion'' of the body, with dimensions of radians per unit time or degrees per unit time. Define as the time at which the body is at the pericenter. From the above definitions, a new quantity, , the ''mean anomaly'' can be defined :M = n\,(t - \tau) ~, which gives an angular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument Of Perigee
The argument of periapsis (also called argument of perifocus or argument of pericenter), symbolized as ''ω'', is one of the orbital elements of an orbiting body. Parametrically, ''ω'' is the angle from the body's ascending node to its periapsis, measured in the direction of motion. For specific types of orbits, terms such as argument of perihelion (for heliocentric orbits), argument of perigee (for geocentric orbits), argument of periastron (for orbits around stars), and so on, may be used (see apsis for more information). An argument of periapsis of 0° means that the orbiting body will be at its closest approach to the central body at the same moment that it crosses the plane of reference from South to North. An argument of periapsis of 90° means that the orbiting body will reach periapsis at its northmost distance from the plane of reference. Adding the argument of periapsis to the longitude of the ascending node gives the longitude of the periapsis. However, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |