|
QPACE
QPACE (QCD Parallel Computing on the Cell Broadband Engine) is a massively parallel and scalable supercomputer designed for applications in lattice quantum chromodynamics. Overview The QPACE supercomputer is a research project carried out by several academic institutions in collaboration with the IBM Research and Development Laboratory in Böblingen, Germany, and other industrial partners including Eurotech, Knürr, and Xilinx. The academic design team of about 20 junior and senior scientists, mostly physicists, came from the University of Regensburg (project lead), the University of Wuppertal, DESY Zeuthen, Jülich Research Centre, and the University of Ferrara. The main goal was the design of an application-optimized scalable architecture that beats industrial products in terms of compute performance, price-performance ratio, and energy efficiency. The project officially started in 2008. Two installations were deployed in the summer of 2009. The final design was completed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Regensburg
The University of Regensburg (german: link=no, Universität Regensburg) is a public research university located in the medieval city of Regensburg, Bavaria, a city that is listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The university was founded on 18 July 1962 by the Landtag of Bavaria as the fourth full-fledged university in Bavaria. Following groundbreaking in 1965, the university officially opened to students during the 1967–1968 winter semester, initially housing faculties in Law and Business Sciences and Philosophy. During the summer semester of 1968 the faculty of Theology was created. Currently, the University of Regensburg houses eleven faculties. The university actively participates in the European Union's SOCRATES programme as well as several TEMPUS programmes. Its most famous academic, the previous Pope Benedict XVI, served as a professor there until 1977 and formally retained his chair in theology. History Attempts to establish a university in Regensburg had been advoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (microprocessor)
Cell is a multi-core microprocessor microarchitecture that combines a general-purpose PowerPC core of modest performance with streamlined coprocessing elements which greatly accelerate multimedia and vector processing applications, as well as many other forms of dedicated computation. It was developed by Sony, Toshiba, and IBM, an alliance known as "STI". The architectural design and first implementation were carried out at the STI Design Center in Austin, Texas over a four-year period beginning March 2001 on a budget reported by Sony as approaching US$400 million. Cell is shorthand for Cell Broadband Engine Architecture, commonly abbreviated ''CBEA'' in full or ''Cell BE'' in part. The first major commercial application of Cell was in Sony's PlayStation 3 game console, released in 2006. In May 2008, the Cell-based IBM Roadrunner supercomputer became the first TOP500 LINPACK sustained 1.0 petaflops system. Mercury Computer Systems also developed designs based on the Cell. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics (QCD) is the theory of the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons. Quarks are fundamental particles that make up composite hadrons such as the proton, neutron and pion. QCD is a type of quantum field theory called a non-abelian gauge theory, with symmetry group SU(3). The QCD analog of electric charge is a property called ''color''. Gluons are the force carriers of the theory, just as photons are for the electromagnetic force in quantum electrodynamics. The theory is an important part of the Standard Model of particle physics. A large body of experimental evidence for QCD has been gathered over the years. QCD exhibits three salient properties: * Color confinement. Due to the force between two color charges remaining constant as they are separated, the energy grows until a quark–antiquark pair is spontaneously produced, turning the initial hadron into a pair of hadrons instead of isolating a color charge. Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigabit Ethernet
In computer networking, Gigabit Ethernet (GbE or 1 GigE) is the term applied to transmitting Ethernet frames at a rate of a gigabit per second. The most popular variant, 1000BASE-T, is defined by the IEEE 802.3ab standard. It came into use in 1999, and has replaced Fast Ethernet in wired local networks due to its considerable speed improvement over Fast Ethernet, as well as its use of cables and equipment that are widely available, economical, and similar to previous standards. History Ethernet was the result of research conducted at Xerox PARC in the early 1970s, and later evolved into a widely implemented physical and link layer protocol. Fast Ethernet increased the speed from 10 to 100 megabits per second (Mbit/s). Gigabit Ethernet was the next iteration, increasing the speed to 1000 Mbit/s. * The initial standard for Gigabit Ethernet was produced by the IEEE in June 1998 as IEEE 802.3z, and required optical fiber. 802.3z is commonly referred to as 1000BASE-X, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transceiver
In radio communication, a transceiver is an electronic device which is a combination of a radio ''trans''mitter and a re''ceiver'', hence the name. It can both transmit and receive radio waves using an antenna, for communication purposes. These two related functions are often combined in a single device to reduce manufacturing costs. The term is also used for other devices which can both transmit and receive through a communications channel, such as ''optical transceivers'' which transmit and receive light in optical fiber systems, and ''bus transceivers'' which transmit and receive digital data in computer data buses. Radio transceivers are widely used in wireless devices. One large use is in two-way radios, which are audio transceivers used for bidirectional person-to-person voice communication. Examples are cell phones, which transmit and receive the two sides of a phone conversation using radio waves to a cell tower, cordless phones in which both the phone handset and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ECC Memory
Error correction code memory (ECC memory) is a type of computer data storage that uses an error correction code (ECC) to detect and correct n-bit data corruption which occurs in memory. ECC memory is used in most computers where data corruption cannot be tolerated, like industrial control applications, critical databases, and infrastructural memory caches. Typically, ECC memory maintains a memory system immune to single-bit errors: the data that is read from each word is always the same as the data that had been written to it, even if one of the bits actually stored has been flipped to the wrong state. Most non-ECC memory cannot detect errors, although some non-ECC memory with parity support allows detection but not correction. Description Error correction codes protect against undetected data corruption and are used in computers where such corruption is unacceptable, examples being scientific and financial computing applications, or in database and file servers. ECC can als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
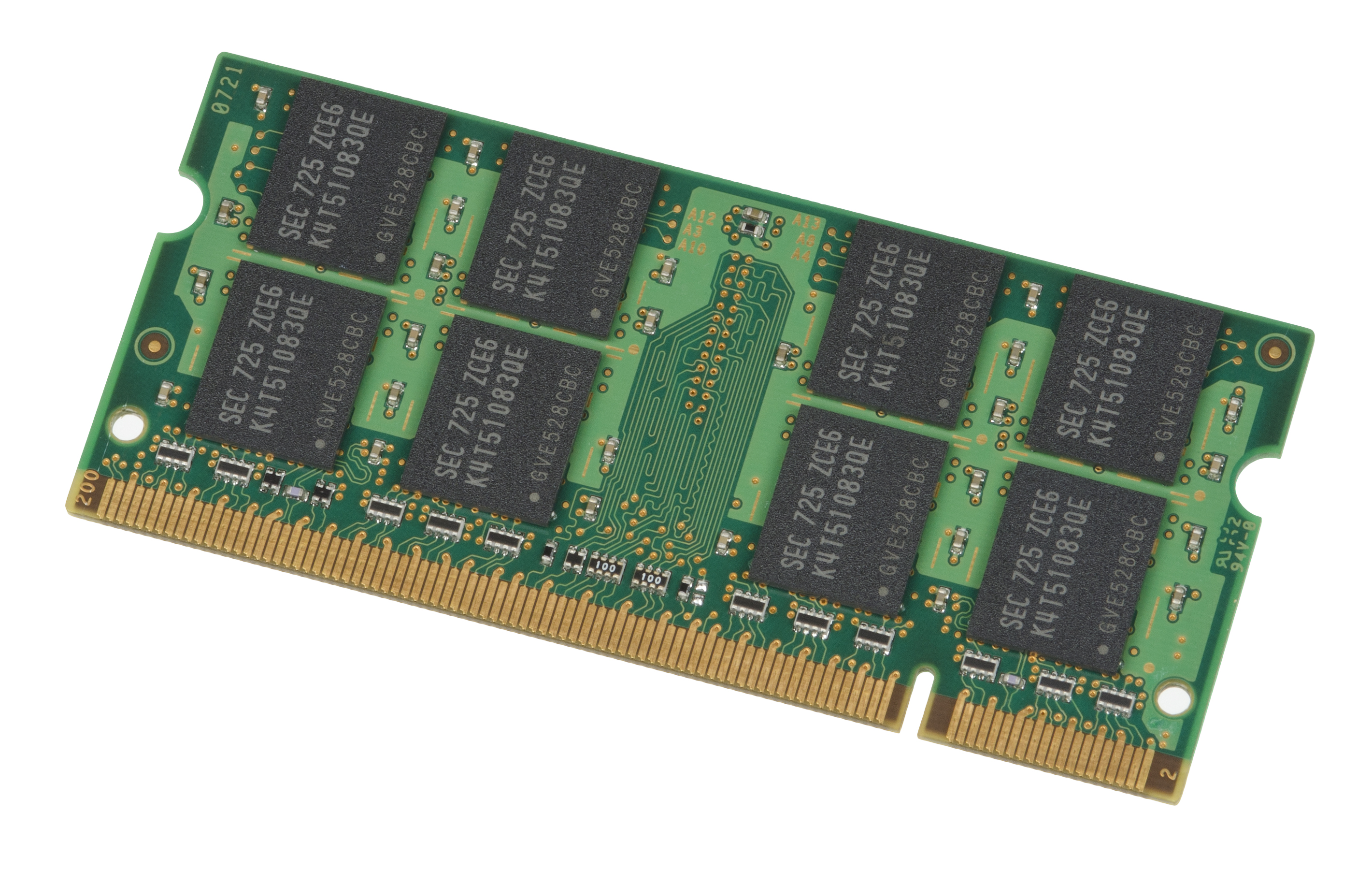
DDR2 SDRAM
Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM) is a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) interface. It superseded the original DDR SDRAM specification, and was itself superseded by DDR3 SDRAM (launched in 2007). DDR2 DIMMs are neither forward compatible with DDR3 nor backward compatible with DDR. In addition to double pumping the data bus as in DDR SDRAM (transferring data on the rising and falling edges of the bus clock signal), DDR2 allows higher bus speed and requires lower power by running the internal clock at half the speed of the data bus. The two factors combine to produce a total of four data transfers per internal clock cycle. Since the DDR2 internal clock runs at half the DDR external clock rate, DDR2 memory operating at the same external data bus clock rate as DDR results in DDR2 being able to provide the same bandwidth but with better latency. Alternatively, DDR2 memory operating at twice the external data ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backplane
A backplane (or "backplane system") is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used as a backbone to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications. A backplane is generally differentiated from a motherboard by the lack of on-board processing and storage elements. A backplane uses plug-in cards for storage and processing. Usage Early microcomputer systems like the Altair 8800 used a backplane for the processor and expansion cards. Backplanes are normally used in preference to cables because of their greater reliability. In a cabled system, the cables need to be flexed every time that a card is added or removed from the system; this flexing even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigurabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infiniband
InfiniBand (IB) is a computer networking communications standard used in high-performance computing that features very high throughput and very low latency. It is used for data interconnect both among and within computers. InfiniBand is also used as either a direct or switched interconnect between servers and storage systems, as well as an interconnect between storage systems. It is designed to be scalable and uses a switched fabric network topology. By 2014, it was the most commonly used interconnect in the TOP500 list of supercomputers, until about 2016. Mellanox (acquired by Nvidia) manufactures InfiniBand host bus adapters and network switches, which are used by large computer system and database vendors in their product lines. As a computer cluster interconnect, IB competes with Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and Intel Omni-Path. The technology is promoted by the InfiniBand Trade Association. History InfiniBand originated in 1999 from the merger of two competing designs: F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade Server
A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server fits inside a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system, which may itself be rack-mounted. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole. In a ''standard'' server-rack configuration, one rack unit or 1U— wide and tall—defines the minimum possible size of any equipment. The principal benefit and justification of blade computing relates to lifting this restrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM BladeCenter
The IBM BladeCenter was IBM's blade server architecture, until it was replaced by Flex System in 2012. The x86 division was later sold to Lenovo in 2014. History Introduced in 2002, based on engineering work started in 1999, the IBM eServer BladeCenter was relatively late to the blade server market. It differed from prior offerings in that it offered a range of x86 Intel server processors and input/output (I/O) options. The naming was changed to IBM BladeCenter in 2005. In February 2006, IBM introduced the BladeCenter H with switch capabilities for 10 Gigabit Ethernet and InfiniBand 4X. A web site called Blade.org was available for the blade computing community through about 2009. In 2012, the replacement Flex System was introduced. Enclosures IBM BladeCenter (E) The original IBM BladeCenter was later marketed as BladeCenter E. Power supplies have been upgraded through the life of the chassis from the original 1200 to 1400, 1800, 2000 and 2320 watt. The BladeCenter ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)