|
Quipu
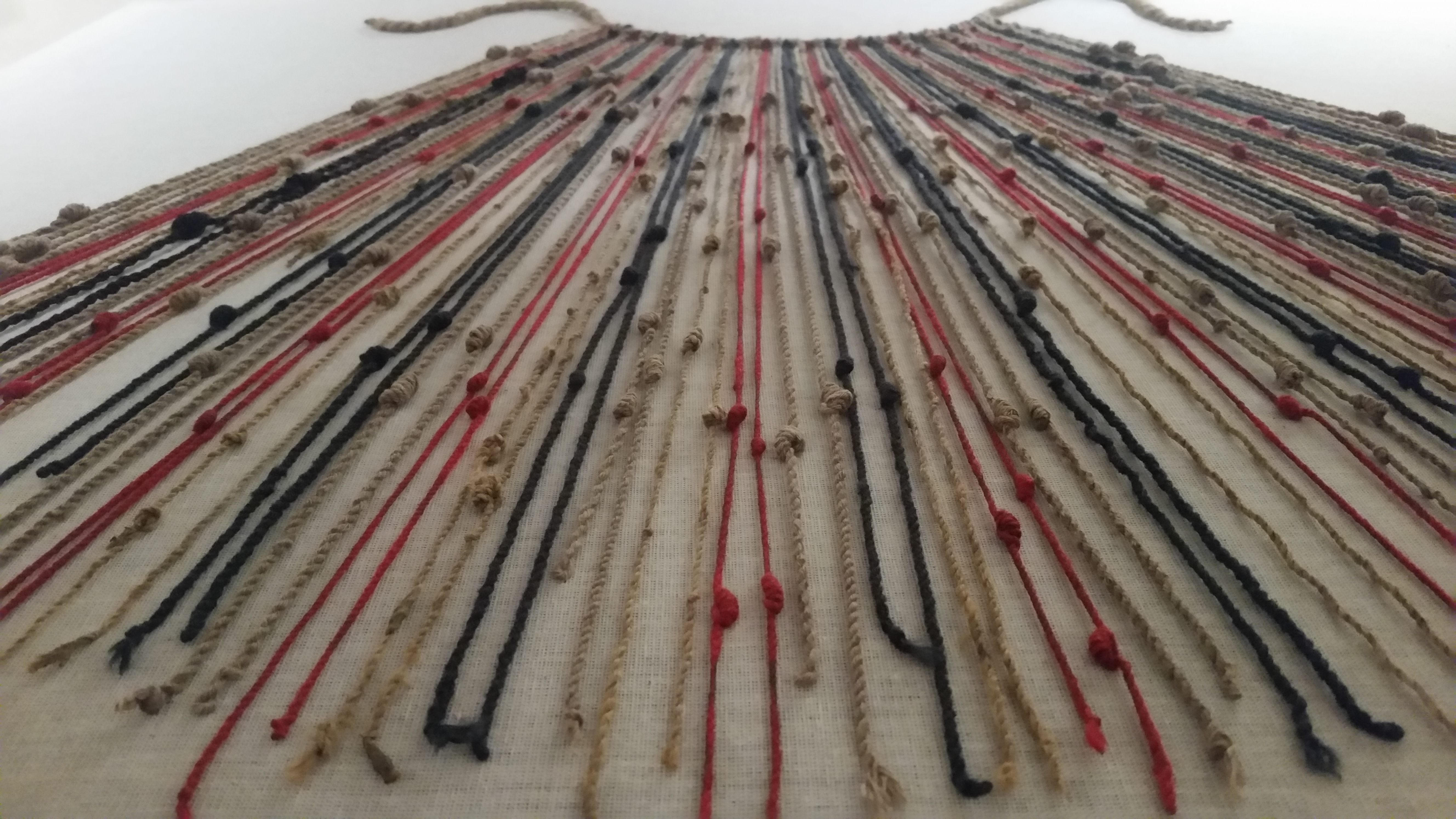
''Quipu'' (also spelled ''khipu'') are recording devices fashioned from strings historically used by a number of cultures in the region of Andean South America. A ''quipu'' usually consisted of cotton or camelid fiber strings. The Inca people used them for collecting data and keeping records, monitoring tax obligations, collecting census records, calendrical information, and for military organization. The cords stored numeric and other values encoded as knots, often in a base ten positional system. A ''quipu'' could have only a few or thousands of cords. The configuration of the ''quipus'' has been "compared to string mops." Archaeological evidence has also shown the use of finely carved wood as a supplemental, and perhaps sturdier, base to which the color-coded cords would be attached. A relatively small number have survived. Objects that can be identified unambiguously as ''quipus'' first appear in the archaeological record in the first millennium AD (though debated q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quipo In The Museo Machu Picchu, Casa Concha, Cusco
''Quipu'' (also spelled ''khipu'') are recording devices fashioned from strings historically used by a number of cultures in the region of Andean South America. A ''quipu'' usually consisted of cotton or camelid fiber strings. The Inca people used them for collecting data and keeping records, monitoring tax obligations, collecting census records, calendrical information, and for military organization. The cords stored numeric and other values encoded as knots, often in a base ten positional system. A ''quipu'' could have only a few or thousands of cords. The configuration of the ''quipus'' has been "compared to string mops." Archaeological evidence has also shown the use of finely carved wood as a supplemental, and perhaps sturdier, base to which the color-coded cords would be attached. A relatively small number have survived. Objects that can be identified unambiguously as ''quipus'' first appear in the archaeological record in the first millennium AD (though debated quip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca People
The Andean civilizations were complex societies of many cultures and peoples mainly developed in the river valleys of the coastal deserts of Peru. They stretched from the Andes of southern Colombia southward down the Andes to Chile and northwest Argentina. Archaeologists believe that Andean civilizations first developed on the narrow coastal plain of the Pacific Ocean. The Caral or Norte Chico civilization of Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3200 BCE. Despite severe environmental challenges, the Andean civilizations domesticated a wide variety of crops, some of which became of worldwide importance. The Andean civilizations were also noteworthy for monumental architecture, textile weaving, and many unique characteristics of the societies they created. Less than a century prior to the arrival of the Spanish conquerors, the Incas, from their homeland centered on the city of Cusco, united most of the Andean cultures into one single empire that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incan Empire
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, ( Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The Inca civilization arose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire in 1532 and by 1572, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru, what are now western Ecuador, western and south central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and a large portion of modern-day Chile, and into a state comparable to the historical empires of Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norte Chico Civilization
Caral-Supe (also known as Caral and Norte Chico) was a complex pre-Columbian-era society that included as many as thirty major population centers in what is now the Caral region of north-central coastal Peru. The civilization flourished between the fourth and second millennia BC, with the formation of the first city generally dated to around 3500 BC, at Huaricanga, in the Fortaleza area. It is from 3100 BC onward that large-scale human settlement and communal construction become clearly apparent, which lasted until a period of decline around 1800 BC. Since the early twenty-first century, it has been established as the oldest-known civilization in the Americas. This civilization flourished along three rivers, the Fortaleza, the Pativilca, and the Supe. These river valleys each have large clusters of sites. Farther south, there are several associated sites along the Huaura River. The alternative name, Caral-Supe, is derived from the city of Caral in the Supe Valley, a large a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechua Language
Quechua (, ; ), usually called ("people's language") in Quechuan languages, is an indigenous language family spoken by the Quechua peoples, primarily living in the Peruvian Andes. Derived from a common ancestral language, it is the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with an estimated 8–10 million speakers as of 2004.Adelaar 2004, pp. 167–168, 255. Approximately 25% (7.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechuan language. It is perhaps most widely known for being the main language family of the Inca Empire. The Spanish encouraged its use until the Peruvian struggle for independence of the 1780s. As a result, Quechua variants are still widely spoken today, being the co-official language of many regions and the second most spoken language family in Peru. History Quechua had already expanded across wide ranges of the central Andes long before the expansion of the Inca Empire. The Inca were one among many peoples in present-day Peru who alread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predecessor states between 1492 and 1976. One of the largest empires in history, it was, in conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, the first to usher the European Age of Discovery and achieve a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, territories in Western Europe], Africa, and various islands in Spanish East Indies, Asia and Oceania. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming the first empire known as " the empire on which the sun never sets", and reached its maximum extent in the 18th century. An important element in the formation of Spain's empire was the dynastic union between Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon in 1469, known as the Catholic Monarchs, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, coverin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
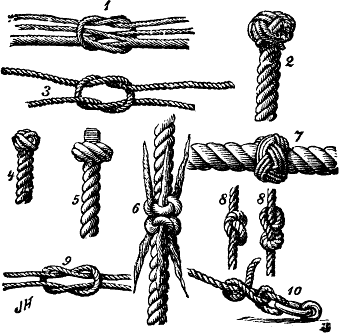
Knot
A knot is an intentional complication in Rope, cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including List of hitch knots, hitches, List of bend knots, bends, List of loop knots, loop knots, and Rope splicing, splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ''bend'' fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a ''loop knot'' is any knot creating a loop; and ''splice'' denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their Topology, topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory. History Knots and knotting have been used and studied throughout history. For example, Chinese knotting is a decorative handicraft art that began as a form of Chines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan People
The Tibetan people (; ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 6.7 million. In addition to the majority living in Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live in the Chinese provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yunnan, as well as in India, Nepal, and Bhutan. Tibetan languages belong to the Tibeto-Burman language group. The traditional or mythological explanation of the Tibetan people's origin is that they are the descendants of the human Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa and rock ogress Ma Drag Sinmo. It is thought that most of the Tibeto-Burman speakers in Southwest China, including Tibetans, are direct descendants from the ancient Qiang people. Most Tibetans practice Tibetan Buddhism, although some observe the indigenous Bon religion and there is a small Muslim minority. Tibetan Buddhism influences Tibetan art, drama and architecture, while the harsh geography of Tibet has produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type of tomb, or the tomb may be considered to be within the mausoleum. Overview The word ''mausoleum'' (from Greek μαυσωλείον) derives from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (near modern-day Bodrum in Turkey), the grave of King Mausolus, the Persian satrap of Caria, whose large tomb was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Historically, mausolea were, and still may be, large and impressive constructions for a deceased leader or other person of importance. However, smaller mausolea soon became popular with the gentry and nobility in many countries. In the Roman Empire, these were often in necropoles or along roadsides: the via Appia Antica retains the ruins of many private mausolea for kilometres ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A ''decimal numeral'' (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , where is an inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_p360.png)



.png)


.jpeg/1200px-Taj_Mahal_(Edited).jpeg)