|
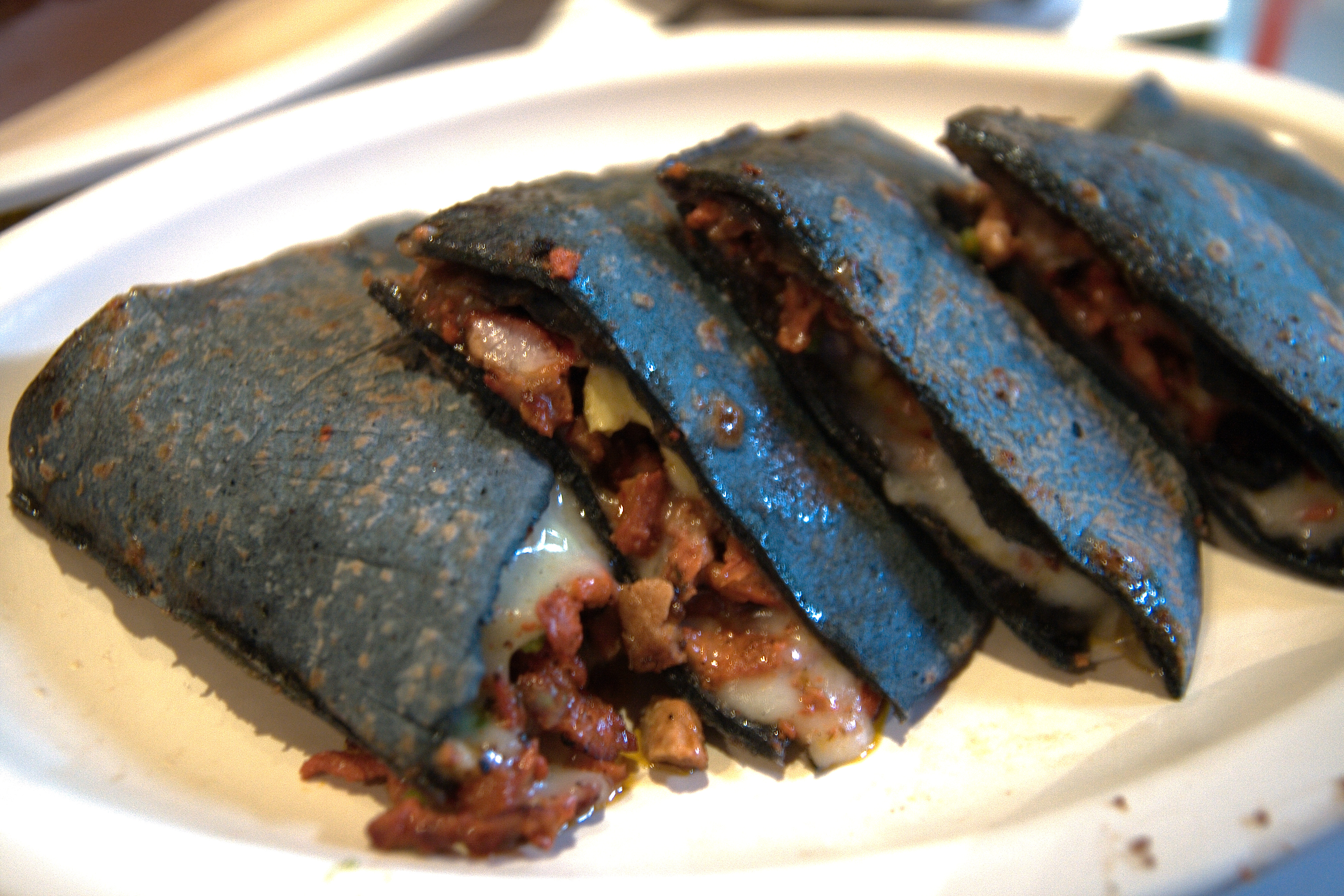
Quesadilla
A quesadilla (; ; Mexican diminutive of ''quesada'') is a Mexican dish consisting of a tortilla that is filled primarily with cheese, and sometimes meats, spices, and other fillings, and then cooked on a griddle or stove. Traditionally, a corn tortilla is used, but it can also be made with a flour tortilla. A ''full quesadilla'' is made with two tortillas that hold a layer of cheese between them. A ''half'' is a single tortilla that has been filled with cheese and folded into a half-moon shape. History The quesadilla has its origins in colonial Mexico. The quesadilla as a dish has changed and evolved over many years as people have experimented with different variations of it. Quesadillas are frequently sold at Mexican restaurants all over the world. Types Original Mexican quesadilla In the central and southern regions of Mexico, a quesadilla is a flat circle of cooked corn masa, called a ''tortilla'', warmed to soften it enough to be folded in half, and then filled. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quesadilla
A quesadilla (; ; Mexican diminutive of ''quesada'') is a Mexican dish consisting of a tortilla that is filled primarily with cheese, and sometimes meats, spices, and other fillings, and then cooked on a griddle or stove. Traditionally, a corn tortilla is used, but it can also be made with a flour tortilla. A ''full quesadilla'' is made with two tortillas that hold a layer of cheese between them. A ''half'' is a single tortilla that has been filled with cheese and folded into a half-moon shape. History The quesadilla has its origins in colonial Mexico. The quesadilla as a dish has changed and evolved over many years as people have experimented with different variations of it. Quesadillas are frequently sold at Mexican restaurants all over the world. Types Original Mexican quesadilla In the central and southern regions of Mexico, a quesadilla is a flat circle of cooked corn masa, called a ''tortilla'', warmed to soften it enough to be folded in half, and then filled. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
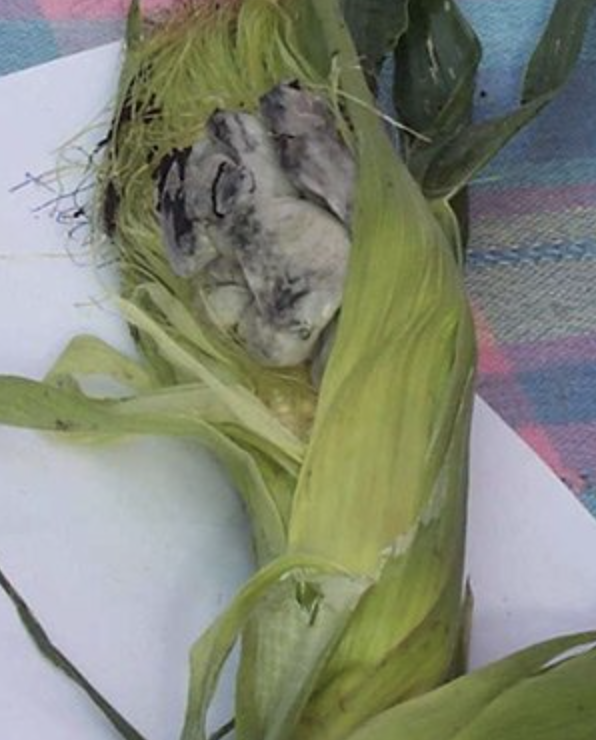
Huitlacoche
Corn smut is a plant disease caused by the pathogenic fungus ''Ustilago maydis'' that causes smut on maize and teosinte. The fungus forms galls on all above-ground parts of corn species. It is edible, and is known in Mexico as the delicacy ''huitlacoche''; which is eaten, usually as a filling, in quesadillas and other tortilla-based foods, and in soups. Etymology In Mexico, corn smut is known as ''huitlacoche'' (, sometimes spelled ''cuitlacoche''). This word entered Spanish in Mexico from Classical Nahuatl, though the Nahuatl words from which huitlacoche is derived are debated. In modern Nahuatl, the word for ''huitlacoche'' is ''cuitlacochin'' (), and some sources deem ''cuitlacochi'' to be the classical form.Guido Gómez de Silva, "Diccionario breve de mexicanismos", Fondo de Cultura Económica, Mexico 2001. Entries for "huitlacoche" and "cuicacoche o cuiltacoche". Some sources wrongly give the etymology as coming from the Nahuatl words ''cuitlatl'' ("excrement" or "rear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corn Tortilla
In North America, a corn tortilla or just tortilla (, ) is a type of thin, unleavened flatbread, made from hominy, that is the whole kernels of maize treated with alkali to improve their nutrition in a process called nixtamalization. A simple dough made of ground, dried hominy, salt and water is then formed into flat discs and cooked on a very hot surface, generally an iron griddle called a comal. A similar flatbread from South America, called an '' arepa'' (though ''arepas'' are made with ground maize, not hominy, and are typically much thicker than tortillas), predates the arrival of Europeans to America, and was called ''tortilla'' by the Spanish from its resemblance to the traditional Spanish round, unleavened cakes and omelettes (originally made without potatoes, which are native to South America). The Aztecs and other Nahuatl-speakers call tortillas tlaxcalli (''Nahuatl Dictionary.'' (1997). Wired Humanities Project. University of Oregon. Retrieved August 29, 2012, frol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico '' The World Factbook''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by area; with approximately 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guacamole
Guacamole (; (informally shortened to ''guac'' in the United States since the 1980s) is an avocado-based dip, spread, or salad first developed in Mexico. In addition to its use in modern Mexican cuisine, it has become part of international cuisine as a dip, condiment and salad ingredient. Etymology and pronunciation The name comes from Classical Nahuatl , which literally translates to 'avocado sauce', from ''āhuacatl'' 'avocado' + ''mōlli'' 'sauce'. In Mexican Spanish, it is pronounced . In American English, it tends to be pronounced , and this pronunciation is also common in British English, but is more common. History Avocado seeds were first found in the Tehuacan Valley of Mexico around 9,000–10,000 years ago (7000–8000 BCE) and had been domesticated by various Mesoamerican groups by 5000 BCE. They were likely cultivated in the Supe Valley in Peru as early as 3100 BCE. In the early 1900s, avocados frequently went by the name ''alligator pear''. In the 169 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerica, Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Pre-Columbian era, Then as now it was prized for its large and unusually Avocado oil, oily fruit. The tree likely originated in the highlands bridging south-central Mexico and Guatemala. Its fruit, sometimes also referred to as an alligator or avocado pear, is botanically a large Berry (botany), berry containing a single large seed. Avocado trees are partially Self-pollination, self-pollinating, and are often Plant propagation, propagated through grafting to maintain consistent fruit output. Avocados are presently cultivated in the Tropics, tropical and Mediterranean climates of many countries. Agriculture in Mexico, Mexico is the world's List of countries by avocado production, leading producer of avocados as of 2020, supplying nearly 30% of the glo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calabaza
Calabaza is the generic name in the Spanish language for any type of winter squash. Within an English-language context it specifically refers to what is also known as the West Indian pumpkin, a winter squash typically grown in the West Indies, tropical America, and the Philippines. Calabaza is the common name for ''Cucurbita moschata'' in Cuba, Florida, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines (where it is also spelled ''kalabasa''). ''C. moschata'' is also known as ''auyama'' in Colombia, the Dominican Republic and Venezuela; ''ayote'' in Central America; ''zapallo'' in certain countries of South America; and "pumpkin", "squash", or "calabash" in English-speaking islands. Etymology The French term ''calebasse'', and hence the English "calabash", is based on the older Spanish. Cultivars In North America, the Spanish word ''calabaza'' may refer to any of several species of squash of the genus ''Cucurbita''. The term is most commonly used for cultivars of the species '' C. moschata'', w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
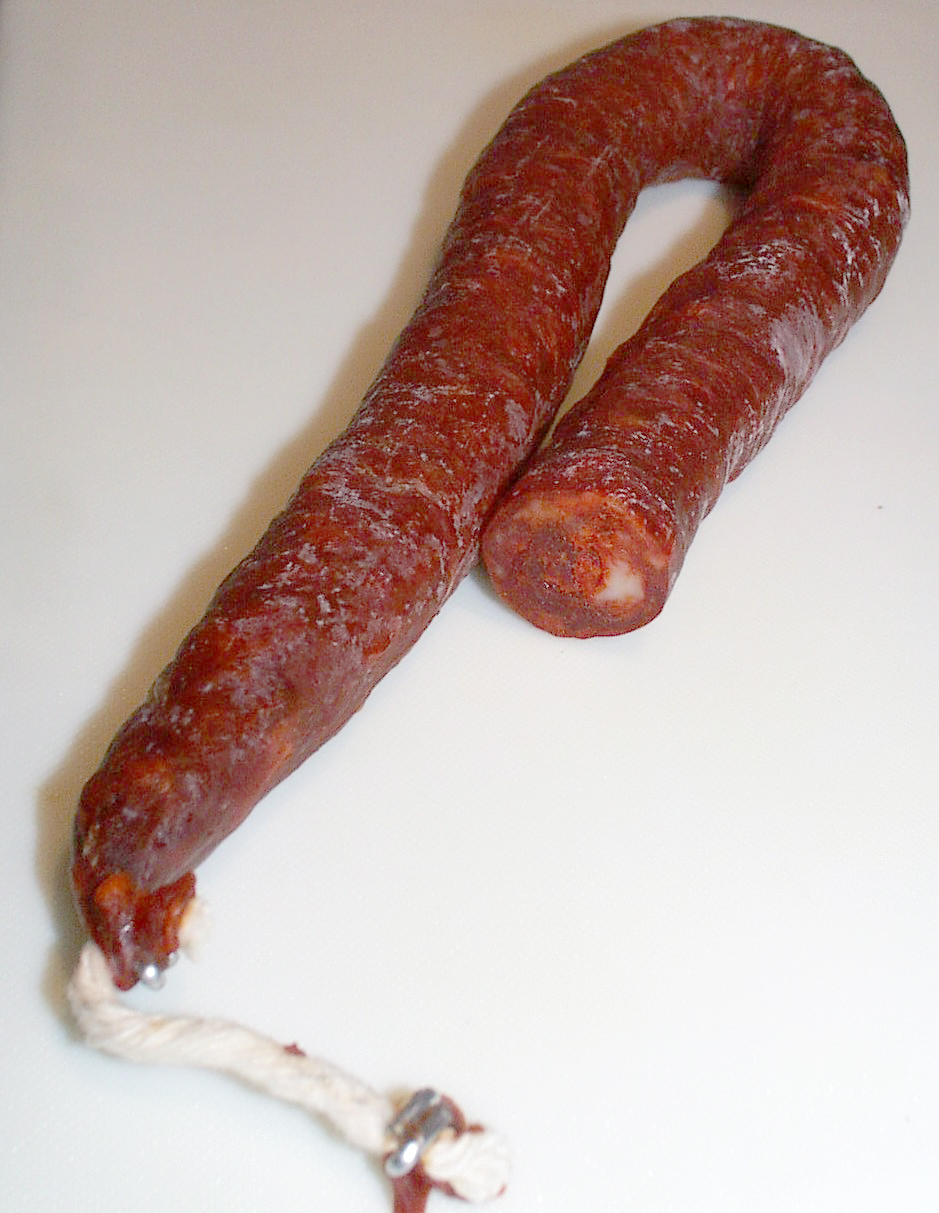
Chorizo
Chorizo (, from Spanish ; similar to but distinct from Portuguese ) is a type of pork cured meat originating from the Iberian Peninsula. In Europe, chorizo is a fermented, cured, smoked meat, which may be sliced and eaten without cooking, or added as an ingredient to add flavor to other dishes. Elsewhere, some sausages sold as chorizo may not be fermented and cured, and require cooking before eating. Spanish and Portuguese are distinctly different products, despite both getting their smokiness and deep red color from dried, smoked, red peppers (/). Iberian chorizo is eaten sliced in a sandwich, grilled, fried, or simmered in liquid, including apple cider or other strong alcoholic beverages such as . It is also used as a partial replacement for ground (minced) beef or pork. Names The word ''chorizo'' probably comes from the Late Latin 'salted', via the Portuguese ; it is a doublet of the Spanish word 'sausage', which was transmitted through Italian . In Engl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Sites
Google Sites is a structured wiki and web page creation tool included as part of the free, web-based Google Docs Editors suite offered by Google. The service also includes Google Docs, Google Sheets, Google Slides, Google Drawings, Google Forms, and Google Keep. Google Sites is only available as a web application. The app allows users to create and edit files online while collaborating with other users in real-time. History Google Sites started out as JotSpot, the name and sole product of a software company that offered enterprise social software. It was targeted mainly at small-sized and medium-sized businesses. The company was founded by Joe Kraus and Graham Spencer, co-founders of Excite. In February 2006, JotSpot was named part of Business 2.0, "Next Net 25", and in May 2006, it was honored as one of InfoWorld's "15 Start-ups to Watch". In October 2006, JotSpot was acquired by Google. Google announced a prolonged data transition of webpages created using Google Pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comal (cookware)
A comal is a smooth, flat griddle typically used in Mexico, Central America, and parts of South America, to cook tortillas and arepas, toast spices and nuts, sear meat, and generally prepare food. Similar cookware is called a budare in South America. Some comals are concave and made of ''barro'' (clay). These are still made and used by the indigenous peoples of Mexico and Central America. Comals are similar to the American griddle or the Indian tawa, and are often used and named interchangeably with these. Comals for home use are generally made from heavy cast iron, and sized to fit over either one burner on the stovetop (round) or two burners front to back (elongated oval). In many indigenous and pre-Hispanic cultures, the comal is handed down from grandmother to mother to daughter, the idea being that a comal tempered over many years of usage will heat faster and cook cleaner. History The history of such cooking methods dates back to the pre-Columbian era, when powdered-homin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_squash_from_the_Philippines.jpg)

