|
Queensland Churches Together
The National Council of Churches in Australia (NCCA) is an ecumenical organisation bringing together a number of Australia's Christian churches in dialogue and practical cooperation. The NCCA works in collaboration with state ecumenical councils around Australia. It is an associate council of the World Council of Churches, a member of the Christian Conference of Asia and a partner of other national ecumenical bodies throughout the world. "Act for Peace" is the international aid agency of the NCCA, which aims to empower war-torn communities to protect refugees, reduce poverty, prevent conflicts and manage disasters. Background The modern ecumenical movement began to take shape at the end of the 19th century. Initiatives among students and between church mission agencies led the way. In Australia these included the Australian Student Christian Movement, formed in 1896, and the National Missionary Council, created in 1926. Organised ecumenism in Australia at the national church le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Ecumenism
Ecumenism (), also spelled oecumenism, is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjective ''ecumenical'' is thus applied to any initiative that encourages greater cooperation and union among Christian denominations and churches. The fact that all Christians belonging to mainstream Christian denominations profess faith in Jesus as Lord and Saviour over a believer's life, believe that the Bible is the infallible, inerrant and inspired word of God (John 1:1), and receive baptism according to the Trinitarian formula is seen as being a basis for ecumenism and its goal of Christian unity. Ecumenists cite John 17:20-23 as the biblical grounds of striving for church unity, in which Jesus prays that Christians "may all be one" in order "that the world may know" and believe the Gospel message. In 1920, the Ecumenical Patriarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Methodist Church In Australia
The Chinese Methodist Church in Australia is based in Melbourne. The theology of the Church is in line with Methodism worldwide. It is Wesleyan in theology and its liturgy contains both traditional and contemporary services. The Church was started by members from the Methodist Churches of Malaysia and Singapore who were either sent to Australia or emigrated there. It is found in all the major cities of Australia. It was originally known as the Methodist Church in Australia but disagreement rose over its name with the Uniting Church in Australia, with the latter refusing to allow its entry into the World Methodist Council. To solve this disagreement, the name was changed to the Chinese Methodist Church in Australia and after the Uniting Church in Australia dropped its veto, it was subsequently welcomed into the World Methodist Council. The first bishop was the Reverend, Dr. James Ha, who was elected to office on 28 November 2002, when the Annual Conference was officially formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syriac Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = syc , image = St_George_Syriac_orthodox_church_in_Damascus.jpg , imagewidth = 250 , alt = Cathedral of Saint George , caption = Cathedral of Saint George, Damascus, Syria , type = Church of Antioch, Antiochian , main_classification = Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian , orientation = Oriental Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodox , scripture = Peshitta , theology = Miaphysitism , polity = Episcopal polity, Episcopal , structure = Koinonia, Communion , leader_title = Patriarch , leader_name = Ignatius Aphrem II Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch and All the East, Patriarch , fellowships_type = Catholicos of India, Catholicate of India , fellowships = Malankara Syriac Orthodox Church , associations = World Council of Churches , area = Middle East, India, and Assyrian–Chaldean� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
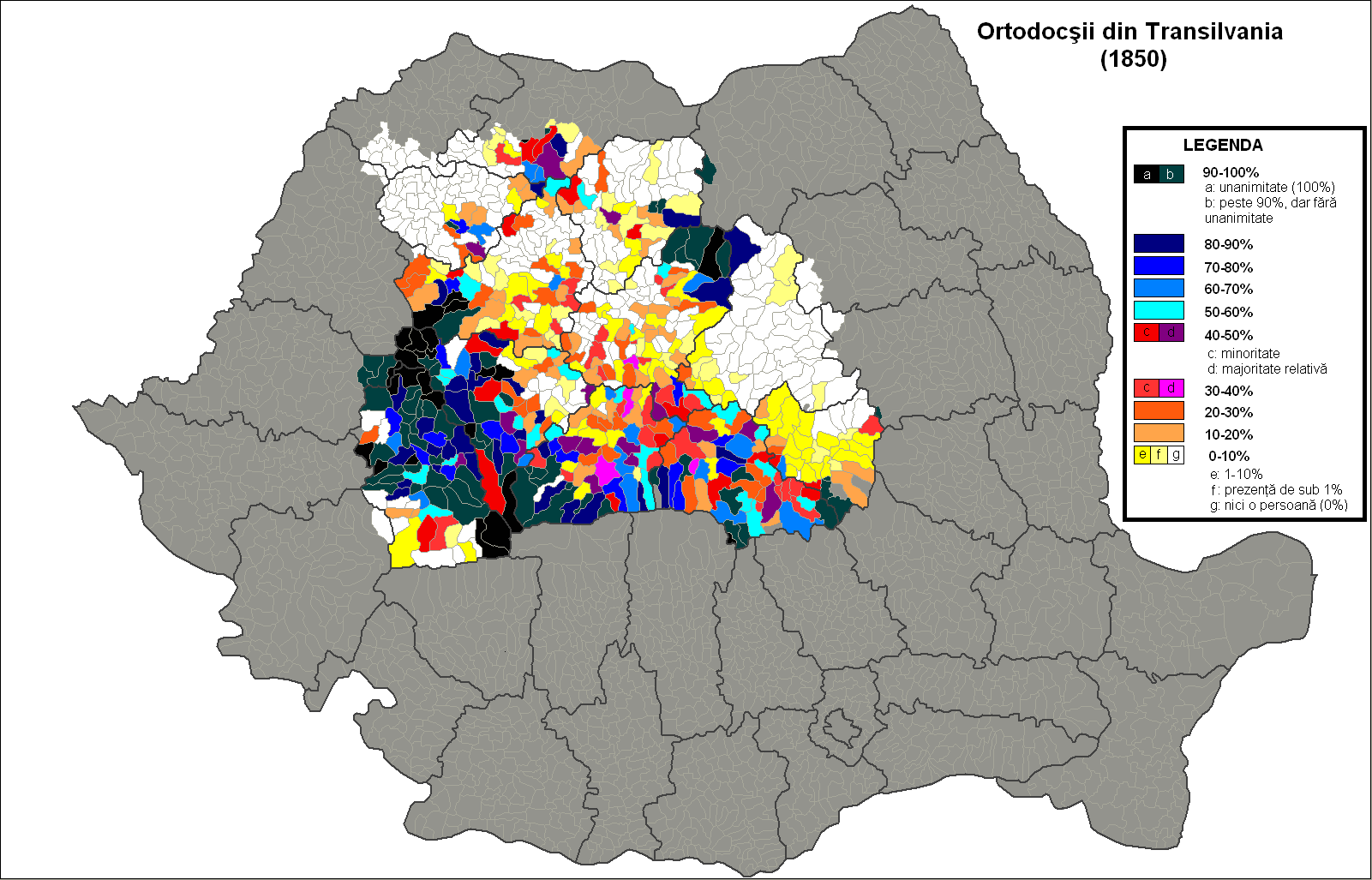
Romanian Orthodox Church
The Romanian Orthodox Church (ROC; ro, Biserica Ortodoxă Română, ), or Patriarchate of Romania, is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church in full communion with other Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches, and one of the nine patriarchates in the Eastern Orthodox Church organization, Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 1925, the church's Primate (bishop), Primate bears the title of Patriarch. Its jurisdiction covers the territories of Romania and Moldova, with additional dioceses for Romanians living in nearby Serbia and Hungary, as well as for diaspora communities in Central Europe, Central and Western Europe, North America and Oceania. It is the only autocephalous church within Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy to have a Romance languages, Romance language for liturgical use. The majority of Romania's population (16,367,267, or 85.9% of those for whom data were available, according to the 2011 census data), as well as some 720,000 Moldovans, belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Coleridge
Mark Benedict Coleridge (born 25 September 1948) is an Australian Catholic bishop. Since 11 May 2012 he has served as the sixth Roman Catholic Archbishop of Brisbane in Queensland. He previously served as the Archbishop of Canberra–Goulburn (2006–12) and as an auxiliary bishop of the Archdiocese of Melbourne (2002–06). Early life Mark Coleridge was born in Melbourne, Victoria. The third of five siblings born to Bernard and Marjorie (née Harvey) Coleridge, he was educated at Saint Joseph's School, Tranmere, South Australia, Rostrevor College, Adelaide, and St Kevin's College, Toorak. Contemplating a career in the Australian diplomatic service, he graduated from the University of Melbourne in 1968 with a Bachelor of Arts degree in English in French. As a Melbourne seminarian, he entered Corpus Christi College, then in Werribee and later in Glen Waverley and Clayton. On 18 May 1974, Coleridge was ordained a priest at St Patrick's Cathedral, Melbourne, by Bishop John A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's ability to experience the light within or see "that of God in every one". Some profess a priesthood of all believers inspired by the First Epistle of Peter. They include those with evangelical, holiness, liberal, and traditional Quaker understandings of Christianity. There are also Nontheist Quakers, whose spiritual practice does not rely on the existence of God. To differing extents, the Friends avoid creeds and hierarchical structures. In 2017, there were an estimated 377,557 adult Quakers, 49% of them in Africa. Some 89% of Quakers worldwide belong to ''evangelical'' and ''programmed'' branches that hold services with singing and a prepared Bible message coordinated by a pastor. Some 11% practice ''waiting worship'' or ''unprogramme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mar Thoma Church
The Malankara Mar Thoma Syrian Church, often shortened to Mar Thoma Church, and known also as the Reformed Syrian ChurchS. N. Sadasivan. A Social History of India'. APH Publishing; 2000. . p. 442. and the Mar Thoma Syrian Church of Malabar, is an autonomous Reformed Oriental church based in Kerala, India. While continuing many of the Syriac high church practices, the church is reformed in its theology and doctrines. It employs a reformed variant of the West Syriac Rite Divine Liturgy of Saint James, translated to Malayalam. The Mar Thoma Church sees itself as continuation of the Saint Thomas Christians, a community traditionally believed to have been founded in the first century by Thomas the Apostle, who is known as Mar Thoma (''Saint Thomas'') in Syriac,Mathew, K. S. (1993). ''The Faith and Practice of the Mar Thoma Church''. and describes itself as "Apostolic in origin, Universal in nature, Biblical in faith, Evangelical in principle, Ecumenical in outlook, Oriental i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutheran Church Of Australia
The Lutheran Church of Australia (LCA) is the major Lutheran denomination in Australia and New Zealand. It counts 540 congregations and 30,026 members according to official statistics. It was created from a merger of the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Australia and the United Evangelical Lutheran Church of Australia in 1966. History The first Lutherans to come to Australia in any significant number were the immigrants from Prussia, who arrived in 1838 with Pastor August Kavel. This period in Prussia was marked by a persecution of "Old Lutherans" who refused to join the Prussian Union under King Frederick Wilhelm. In 1841, a second wave of Prussian immigrants started, with the arrival of Pastor Gotthard Fritzsche. He settled with the migrants in his group in Lobethal and Bethanien (now Bethany) in South Australia. The Lutheran church of this period is referred to as the Kavel-Fritzsche Synod. A split occurred within the South Australian Lutheran community in 1846, and two s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Orthodox Church
The Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church (MOSC) also known as the Indian Orthodox Church (IOC) or simply as the Malankara Church, is an autocephalous Oriental Orthodox church headquartered in Devalokam, near Kottayam, India. The church serves India's Saint Thomas Christian (also known as ''Nasrani'') population. According to tradition, these communities originated in the missions of Thomas the Apostle in the 1st century (circa 52 AD).''The Encyclopedia of Christianity, Volume 5'' by Erwin Fahlbusch. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing – 2008. p. 285. . It employs the |
Archbishop Makarios Of Australia
Archbishop Makarios Griniezakis (Greek: Μακάριος Γρινιεζάκης; born 15 March 1973) is the current archbishop of the Greek Orthodox Church of Australia and the primate of the Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Australia, succeeding Archbishop Stylianos of Australia. Studies and career Prior to serving in the Greek Orthodox Church, Archbishop Makarios completed his elementary studies in his birthplace and at the Rizarios Ecclesiastical School of Athens. He is a graduate of the Higher Ecclesiastical School of Athens and of the Theological School of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens. He completed postgraduate studies at the Universities of Boston (Master of Sacred Theology), Harvard University (Master of Arts), and Monash University, (Master of Bioethics), whilst his doctoral dissertation was received and passed as “Excellent” by the Medical School of the University of Crete. The work was published under the title, “Cloning: Social, Ethical and Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Orthodox Church
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also called 'Eastern Orthodox,' 'Greek Catholic,' or generally 'the Greek Church. The narrower meaning designates "any of several independent churches within the worldwide communion of asternOrthodox Christianity that retain the use of the Greek language in formal ecclesiastical settings". Etymology Historically, the term "Greek Orthodox" has been used to describe all Eastern Orthodox churches, since the term "Greek" can refer to the heritage of the Byzantine Empire. During the first eight centuries of Christian history, most major intellectual, cultural, and social developments in the Christian Church took place in the Byzantine Empire or its sphere of influence, where the Greek language was widely spoken and used for most theological writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |