|
Quaternary Phase
In materials chemistry, a quaternary phase is a chemical compound containing four elements. Some compounds can be molecular or ionic, examples being chlorodifluoromethane () sodium bicarbonate (). More typically quaternary phase refers to extended solids. A famous example are the yttrium barium copper oxide superconductors. See also *Binary compound *Ternary compound In inorganic chemistry and materials chemistry, a ternary compound or ternary phase is a chemical compound containing three different elements. While some ternary compounds are molecular, ''e.g.'' chloroform (), more typically ternary phases r ... References {{Reflist Chemical compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. The number of protons in the nucleus is the defining property of an element, and is referred to as its atomic number (represented by the symbol ''Z'') – all atoms with the same atomic number are atoms of the same element. Almost all of the baryonic matter of the universe is composed of chemical elements (among rare exceptions are neutron stars). When different elements undergo chemical reactions, atoms are rearranged into new compounds held together by chemical bonds. Only a minority of elements, such as silver and gold, are found uncombined as relatively pure native element minerals. Nearly all other naturally occurring elements occur in the Earth as compounds or mixtures. Air is primarily a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorodifluoromethane
Chlorodifluoromethane or difluoromonochloromethane is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC). This colorless gas is better known as HCFC-22, or R-22, or . It was commonly used as a propellant and refrigerant. These applications were phased out under the Montreal Protocol in developed countries in 2020 due to the compound's ozone depletion potential (ODP) and high global warming potential (GWP), and in developing countries this process will be completed by 2030. R-22 is a versatile intermediate in industrial organofluorine chemistry, e.g. as a precursor to tetrafluoroethylene. Production and current applications Worldwide production of R-22 in 2008 was about 800Gg per year, up from about 450Gg per year in 1998, with most production in developing countries. R-22 use is being phased out in developing countries, where it is largely used for air conditioning applications. Air conditioning sales are growing 20% annually in India and China. R-22 is prepared from chloroform: :HCCl3 + 2 HF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt (chemistry), salt composed of a sodium cation (Sodium, Na+) and a bicarbonate anion (Bicarbonate, HCO3−). Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline, but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). The natural mineral form is nahcolite. It is a component of the mineral natron and is found dissolved in many mineral springs. Nomenclature Because it has long been known and widely used, the salt has many different names such as baking soda, bread soda, cooking soda, and bicarbonate of soda and can often be found near baking powder in stores. The term ''baking soda'' is more common in the United States, while ''bicarbonate of soda'' is more common in Australia, United Kingdom and Ireland. and in many northern/central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yttrium Barium Copper Oxide
Yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a family of crystalline chemical compounds that display high-temperature superconductivity; it includes the first material ever discovered to become superconducting above the boiling point of liquid nitrogen (77 K) at about 93 K. Many YBCO compounds have the general formula Y Ba2 Cu3 O7−''x'' (also known as Y123), although materials with other Y:Ba:Cu ratios exist, such as Y Ba2 Cu4 Oy (Y124) or Y2 Ba4 Cu7 Oy (Y247). At present, there is no singularly recognised theory for high-temperature superconductivity. It is part of the more general group of rare-earth barium copper oxides (ReBCO) in which, instead of yttrium, other rare earths are present. History In April 1986, Georg Bednorz and Karl Müller, working at IBM in Zurich, discovered that certain semiconducting oxides became superconducting at relatively high temperature, in particular, a lanthanum barium copper oxide becomes superconducting at 35 K. This oxide was an oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Compound
In materials chemistry, a binary phase or binary compound is a chemical compound containing two different elements. Some binary phase compounds are molecular, e.g. carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). More typically binary phase refers to extended solids. Famous examples zinc sulfide, which contains zinc and sulfur, and tungsten carbide Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed int ..., which contains tungsten and carbon. Phases with higher degrees of complexity feature more elements, e.g. three elements in ternary phases, four elements in quaternary phases. References Chemical compounds {{chem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ternary Compound
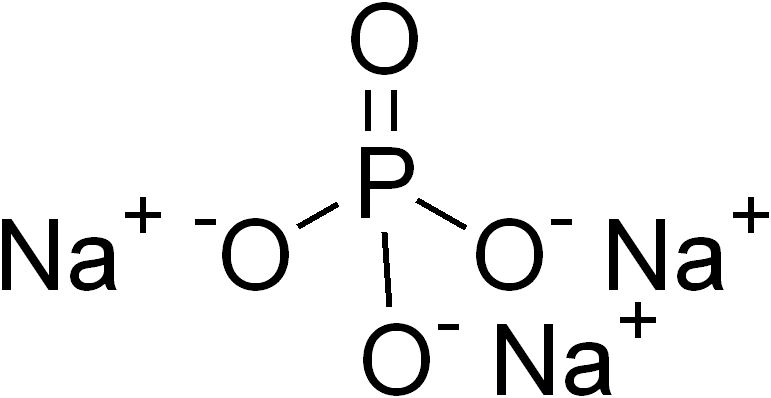
In inorganic chemistry and materials chemistry, a ternary compound or ternary phase is a chemical compound containing three different elements. While some ternary compounds are molecular, ''e.g.'' chloroform (), more typically ternary phases refer to extended solids. Famous example are the perovskites. Binary phases, with only two elements, have lower degrees of complexity than ternary phases. With four elements, quaternary phases are more complex. The number of isomers of a ternary compound provide a distinction between inorganic and organic chemistry: "In inorganic chemistry one or, at most, only a few compounds composed of any two or three elements were known, whereas in organic chemistry the situation was very different." Ternary crystalline compounds An example is sodium phosphate, . The sodium ion has a charge of 1+ and the phosphate ion has a charge of 3–. Therefore, three sodium ions are needed to balance the charge of one phosphate ion. Another example of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_black_and_white.png)