|
Quasi-phase-matching
Quasi-phase-matching is a technique in nonlinear optics which allows a positive net flow of energy from the pump frequency to the signal and idler frequencies by creating a periodic structure in the nonlinear medium. Momentum is conserved, as is necessary for phase-matching, through an additional momentum contribution corresponding to the wavevector of the periodic structure. Consequently, in principle any three-wave mixing process that satisfies energy conservation can be phase-matched. For example, all the optical frequencies involved can be collinear, can have the same polarization, and travel through the medium in arbitrary directions. This allows one to use the largest nonlinear coefficient of the material in the nonlinear interaction. Quasi-phase-matching ensures that there is positive energy flow from the pump frequency to signal and idler frequencies even though all the frequencies involved are not phase locked with each other. Energy will always flow from pump to signal as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after the constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Coefficient
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after the const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear Optics
Nonlinear optics (NLO) is the branch of optics that describes the behaviour of light in ''nonlinear media'', that is, media in which the polarization density P responds non-linearly to the electric field E of the light. The non-linearity is typically observed only at very high light intensities (when the electric field of the light is >108 V/m and thus comparable to the atomic electric field of ~1011 V/m) such as those provided by lasers. Above the Schwinger limit, the vacuum itself is expected to become nonlinear. In nonlinear optics, the superposition principle no longer holds. History The first nonlinear optical effect to be predicted was two-photon absorption, by Maria Goeppert Mayer for her PhD in 1931, but it remained an unexplored theoretical curiosity until 1961 and the almost simultaneous observation of two-photon absorption at Bell Labs and the discovery of second-harmonic generation by Peter Franken ''et al.'' at University of Michigan, both shortly after the constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodic Poling
Periodic poling is a formation of layers with alternate orientation in a birefringent material. The domains are regularly spaced, with period in a multiple of the desired wavelength of operation. The structure is designed to achieve quasi-phase-matching (QPM) in the material. Periodically poled crystals are frequently used as nonlinear optical materials. They are more efficient at second-harmonic generation than crystals of the same material without periodic structure. The material for the crystals is usually a wide band gap inorganic crystal, or in some cases a suitable organic polymer. Some popular materials in current use are potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP), lithium niobate, and lithium tantalate. The periodic structure is created in the crystal using a range of techniques. Pulsed electric field, electron bombardment, thermal pulsing, or other methods can be used to reposition the atoms in the lattice Lattice may refer to: Arts and design * Latticework, an ornamental cris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavevector
In physics, a wave vector (or wavevector) is a vector used in describing a wave, with a typical unit being cycle per metre. It has a magnitude and direction. Its magnitude is the wavenumber of the wave (inversely proportional to the wavelength), and its direction is perpendicular to the wavefront. In isotropic media, this is also the direction of wave propagation. A closely related vector is the angular wave vector (or angular wavevector), with a typical unit being radian per metre. The wave vector and angular wave vector are related by a fixed constant of proportionality, 2π radians per cycle. It is common in several fields of physics to refer to the angular wave vector simply as the ''wave vector'', in contrast to, for example, crystallography. It is also common to use the symbol ''k'' for whichever is in use. In the context of special relativity, ''wave vector'' can refer to a four-vector, in which the (angular) wave vector and (angular) frequency are combined. Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence Length
In physics, coherence length is the propagation distance over which a coherent wave (e.g. an electromagnetic wave) maintains a specified degree of coherence. Wave interference is strong when the paths taken by all of the interfering waves differ by less than the coherence length. A wave with a longer coherence length is closer to a perfect sinusoidal wave. Coherence length is important in holography and telecommunications engineering. This article focuses on the coherence of classical electromagnetic fields. In quantum mechanics, there is a mathematically analogous concept of the quantum coherence length of a wave function. Formulas In radio-band systems, the coherence length is approximated by :L = \frac \approx \frac ~, where \, c \, is the speed of light in a vacuum, \, n \, is the refractive index of the medium, and \, \mathrm f \, is the bandwidth of the source or \, \lambda \, is the signal wavelength and \, \Delta \lambda \, is the width of the range of wavelengths i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sum-frequency Generation
Sum-frequency generation (SFG) is a second order nonlinear optical process based on the annihilation of two input photons at angular frequencies \omega_1 and \omega_2 while, simultaneously, one photon at frequency \omega_3 is generated. As with any second order \chi^ phenomenon in nonlinear optics, this can only occur under conditions where: the light is interacting with matter, which is asymmetric (for example, surfaces and interfaces); the light has a very high intensity (typically from a pulsed laser). Sum-frequency generation is a "parametric process", meaning that the photons satisfy energy conservation, leaving the matter unchanged: :\hbar\omega_3 = \hbar\omega_1 + \hbar\omega_2 Second-harmonic generation A special case of sum-frequency generation is second-harmonic generation, in which \omega_1=\omega_2. In fact, in experimental physics, this is the most common type of sum-frequency generation. This is because in second-harmonic generation, only one input light beam is req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaginary Unit
The imaginary unit or unit imaginary number () is a solution to the quadratic equation x^2+1=0. Although there is no real number with this property, can be used to extend the real numbers to what are called complex numbers, using addition and multiplication. A simple example of the use of in a complex number is 2+3i. Imaginary numbers are an important mathematical concept; they extend the real number system \mathbb to the complex number system \mathbb, in which at least one root for every nonconstant polynomial exists (see Algebraic closure and Fundamental theorem of algebra). Here, the term "imaginary" is used because there is no real number having a negative square. There are two complex square roots of −1: and -i, just as there are two complex square roots of every real number other than zero (which has one double square root). In contexts in which use of the letter is ambiguous or problematic, the letter or the Greek \iota is sometimes used instead. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
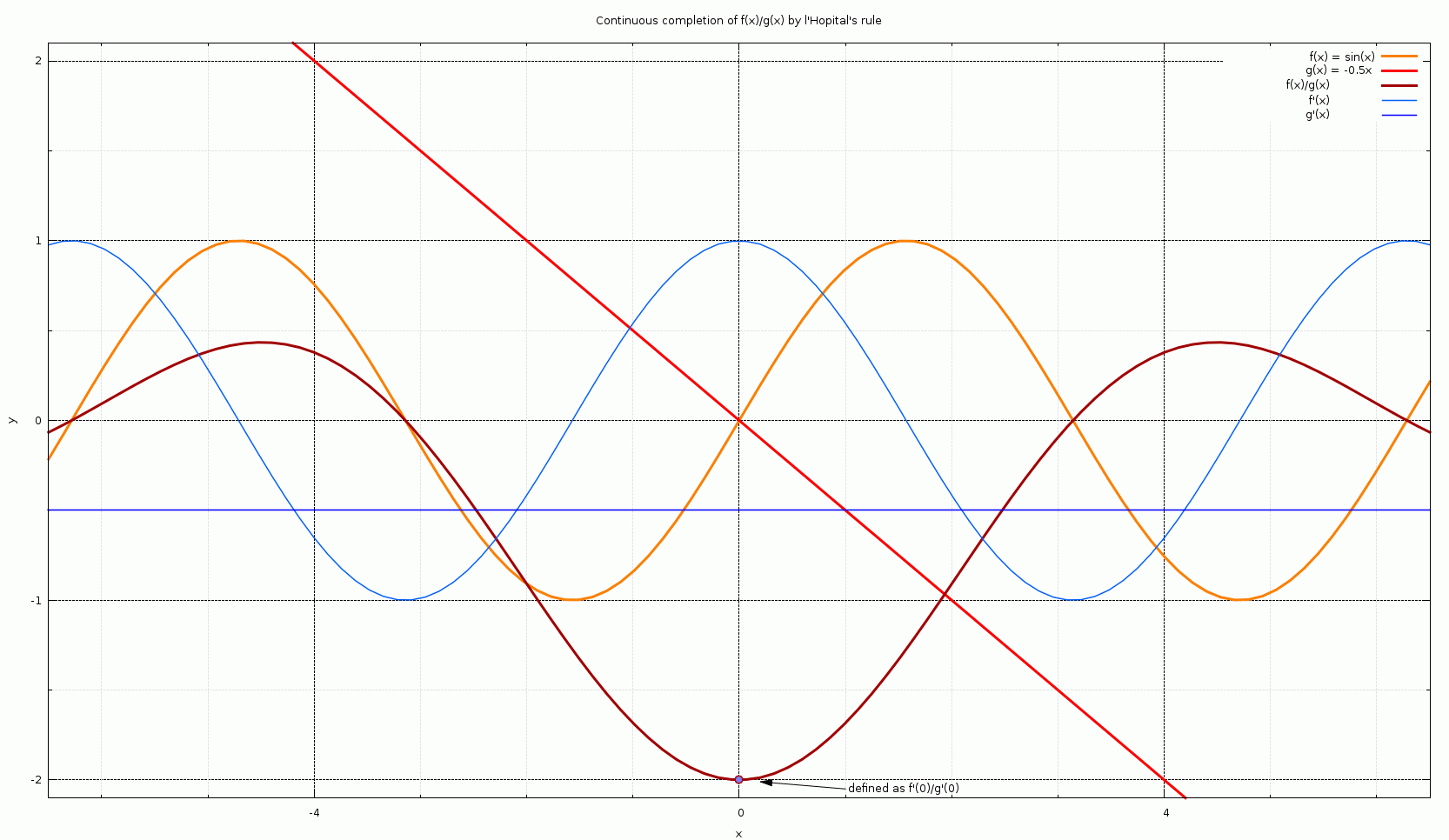
L'Hôpital's Rule
In calculus, l'Hôpital's rule or l'Hospital's rule (, , ), also known as Bernoulli's rule, is a theorem which provides a technique to evaluate limits of indeterminate forms. Application (or repeated application) of the rule often converts an indeterminate form to an expression that can be easily evaluated by substitution. The rule is named after the 17th-century French mathematician Guillaume de l'Hôpital. Although the rule is often attributed to l'Hôpital, the theorem was first introduced to him in 1694 by the Swiss mathematician Johann Bernoulli. L'Hôpital's rule states that for functions and which are differentiable on an open interval except possibly at a point contained in , if \lim_f(x)=\lim_g(x)=0 \text \pm\infty, and g'(x)\ne 0 for all in with , and \lim_\frac exists, then :\lim_\frac = \lim_\frac. The differentiation of the numerator and denominator often simplifies the quotient or converts it to a limit that can be evaluated directly. History Guillaume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
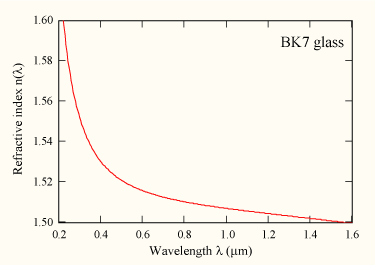
Sellmeier Equation
The Sellmeier equation is an empirical relationship between refractive index and wavelength for a particular transparent medium. The equation is used to determine the dispersion of light in the medium. It was first proposed in 1872 by Wolfgang Sellmeier and was a development of the work of Augustin Cauchy on Cauchy's equation for modelling dispersion. The equation In its original and the most general form, the Sellmeier equation is given as : n^2(\lambda) = 1 + \sum_i \frac , where ''n'' is the refractive index, ''λ'' is the wavelength, and ''B''i and ''C''i are experimentally determined ''Sellmeier coefficients''. These coefficients are usually quoted for λ in micrometres. Note that this λ is the vacuum wavelength, not that in the material itself, which is λ/n. A different form of the equation is sometimes used for certain types of materials, e.g. crystals. Each term of the sum representing an absorption resonance of strength ''B''i at a wavelength . For example, the coe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difference Frequency Generation
Difference, The Difference, Differences or Differently may refer to: Music * ''Difference'' (album), by Dreamtale, 2005 * ''Differently'' (album), by Cassie Davis, 2009 ** "Differently" (song), by Cassie Davis, 2009 * ''The Difference'' (album), Pendleton, 2008 * "The Difference" (The Wallflowers song), 1997 * "The Difference", a song by Westlife from the 2009 album ''Where We Are'' * "The Difference", a song by Nick Jonas from the 2016 album ''Last Year Was Complicated'' * "The Difference", a song by Meek Mill featuring Quavo, from the 2016 mixtape '' DC4'' * "The Difference", a song by Matchbox Twenty from the 2002 album ''More Than You Think You Are'' * "The Difference", a 2020 song by Flume featuring Toro y Moi * "The Difference", a 2022 song by Ni/Co which represented Alabama in the ''American Song Contest'' * "Differences" (song), by Ginuwine, 2001 Science and mathematics * Difference (mathematics), the result of a subtraction * Difference equation, a type of recurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |