|
Quasi-periodic Oscillations
In X-ray astronomy, quasi-periodic oscillation (QPO) is the manner in which the X-ray light from an astronomical object flickers about certain frequencies. In these situations, the X-rays are emitted near the inner edge of an accretion disk in which gas swirls onto a compact object such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole. The QPO phenomenon promises to help astronomers understand the innermost regions of accretion disks and the masses, radii, and spin periods of white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. QPOs could help test Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity which makes predictions that differ most from those of Newtonian gravity when the gravitational force is strongest or when rotation is fastest (when a phenomenon called the Lense–Thirring effect comes into play). However, the various explanations of QPOs remain controversial and the conclusions reached from their study remain provisional. A QPO is identified by performing a power spectrum of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used, with this or similar meanings, in many scientific and technical disciplines, including physics, acoustical engineering, telecommunications, and statistical forecasting. White noise refers to a statistical model for signals and signal sources, rather than to any specific signal. White noise draws its name from white light, although light that appears white generally does not have a flat power spectral density over the visible band. In discrete time, white noise is a discrete signal whose samples are regarded as a sequence of serially uncorrelated random variables with zero mean and finite variance; a single realization of white noise is a random shock. Depending on the context, one may also require that the samples be independent and have identical probability distribution (in other words independent and iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron-star Oscillation
Asteroseismology studies the internal structure of the Sun and other stars using oscillations. These can be studied by interpreting the temporal frequency spectrum acquired through observations. In the same way, the more extreme neutron stars might be studied and hopefully give us a better understanding of neutron-star interiors, and help in determining the equation of state for matter at nuclear densities. Scientists also hope to prove, or discard, the existence of so-called quark stars, or strange stars, through these studies. Fundamental information can be obtained of the General Relativity Theory by observing the gravitational radiation from oscillating neutron stars. Types of oscillations The modes of oscillations are divided into subgroups, each with different characteristic behavior. First they are divided into toroidal and spherical modes, with the latter further divided into radial and non-radial modes. Spherical modes are oscillations in the radial direction while toroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasiperiodicity
Quasiperiodicity is the property of a system that displays irregular periodicity. Periodic behavior is defined as recurring at regular intervals, such as "every 24 hours". Quasiperiodic behavior is a pattern of recurrence with a component of unpredictability that does not lend itself to precise measurement. It is different from the mathematical concept of an almost periodic function, which has increasing regularity over multiple periods. The mathematical definition of quasiperiodic function is a completely different concept; the two should not be confused. Climatology Climate oscillations that appear to follow a regular pattern but which do not have a fixed period are called ''quasiperiodic''. Within a dynamical system such as the ocean-atmosphere oscillations may occur regularly, when they are forced by a regular external forcing: for example, the familiar winter-summer cycle is forced by variations in sunlight from the (very close to perfectly) periodic motion of the earth around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Iron K Line
The K-line is a spectral peak in astronomical spectrometry used, along with the L-line, to observe and describe the light spectrum of stars. The K-line is associated with iron (Fe) and is described as being from emissions at ~6.4keV (thousands of electron volts). On 5 October 2006 NASA announced the results of research using the Japanese JAXA Suzaku satellite, after earlier work with the XMM-Newton satellite. "The observations include clocking the speed of a black hole's spin rate and measuring the angle at which matter pours into the void, as well as evidence for a wall of X-ray light pulled back and flattened by gravity." The study teams observed X-ray emissions from the "broad iron K line" near the event horizon of several super-massive black holes of galaxies called MCG-6-30-15 and MCG-5-23-16. The normally narrow K-line is broadened by the doppler shift (red shift or blue shift) of the X-ray light emitted by matter being affected by the gravity of the black hole. The resu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
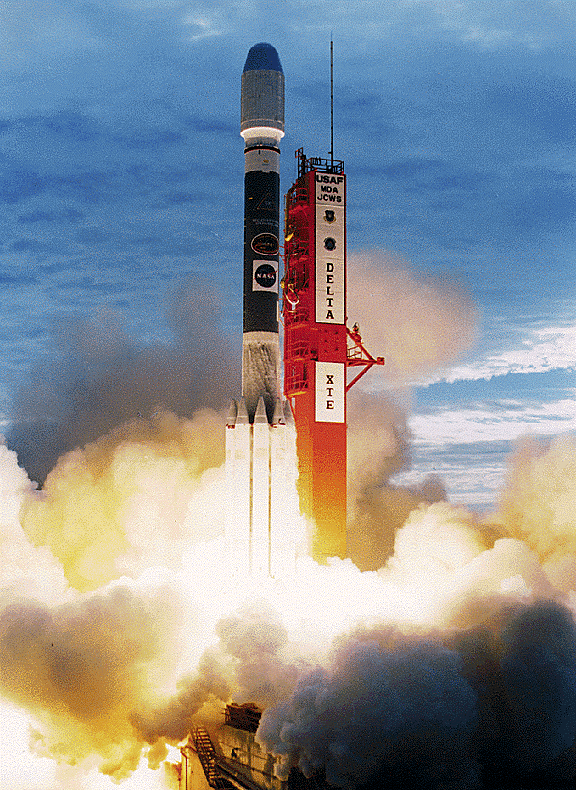
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer
The Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) was a NASA satellite that observed the time variation of astronomical X-ray sources, named after physicist Bruno Rossi. The RXTE had three instruments — an All Sky Monitor, the High-Energy X-ray Timing Experiment (HEXTE) and the Proportional Counter Array. The RXTE observed X-rays from black holes, neutron stars, X-ray pulsars and X-ray bursts. It was funded as part of the Explorer program, and was also called Explorer 69. RXTE had a mass of and was launched from Cape Canaveral on 30 December 1995, at 13:48:00 UTC, on a Delta II launch vehicle. Its International Designator is 1995-074A. Mission The X-Ray Timing Explorer (XTE) mission has the primary objective to study the temporal and broad-band spectral phenomena associated with stellar and galactic systems containing compact objects in the energy range 2--200 KeV, and in time scales from microseconds to years. The scientific instruments consists of two pointed instruments, the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddington Luminosity
The Eddington luminosity, also referred to as the Eddington limit, is the maximum luminosity a body (such as a star) can achieve when there is balance between the force of radiation acting outward and the gravitational force acting inward. The state of balance is called hydrostatic equilibrium. When a star exceeds the Eddington luminosity, it will initiate a very intense radiation-driven stellar wind from its outer layers. Since most massive stars have luminosities far below the Eddington luminosity, their winds are mostly driven by the less intense line absorption. The Eddington limit is invoked to explain the observed luminosity of accreting black holes such as quasars. Originally, Sir Arthur Eddington took only the electron scattering into account when calculating this limit, something that now is called the classical Eddington limit. Nowadays, the modified Eddington limit also counts on other radiation processes such as bound-free and free-free radiation (see Bremsstrahlung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Earth (similar to the way a lighthouse can be seen only when the light is pointed in the direction of an observer), and is responsible for the pulsed appearance of emission. Neutron stars are very dense and have short, regular rotational periods. This produces a very precise interval between pulses that ranges from milliseconds to seconds for an individual pulsar. Pulsars are one of the candidates for the source of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays. (See also centrifugal mechanism of acceleration.) The periods of pulsars make them very useful tools for astronomers. Observations of a pulsar in a binary neutron star system were used to indirectly confirm the existence of gravitational radiation. The first extrasolar planets were discovered aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoll Sources
An atoll () is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon partially or completely. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical oceans and seas where corals can grow. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean. Two different, well-cited models, the subsidence and antecedent karst models, have been used to explain the development of atolls.Droxler, A.W. and Jorry, S.J., 2021. ''The Origin of Modern Atolls: Challenging Darwin's Deeply Ingrained Theory.'' ''Annual Review of Marine Science'', 13, pp.537-573. According to Charles Darwin's ''subsidence model'', the formation of an atoll is explained by the subsidence of a volcanic island around which a coral fringing reef has formed. Over geologic time, the volcanic island becomes extinct and eroded as it subsides completely beneath the surface of the ocean. As the volcanic island subsides, the coral fringing reef becomes a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z Sources
Z (or z) is the 26th and last letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual names in English are ''zed'' () and ''zee'' (), with an occasional archaic variant ''izzard'' ()."Z", ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "zee", ''op. cit''. Name and pronunciation In most English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand and the United Kingdom, the letter's name is ''zed'' , reflecting its derivation from the Greek ''zeta'' (this dates to Latin, which borrowed Y and Z from Greek), but in American English its name is ''zee'' , analogous to the names for B, C, D, etc., and deriving from a late 17th-century English dialectal form. Another English dialectal form is ''izzard'' . This dates from the mid-18th century and probably derives fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorentz Distribution
The Cauchy distribution, named after Augustin Cauchy, is a continuous probability distribution. It is also known, especially among physicists, as the Lorentz distribution (after Hendrik Lorentz), Cauchy–Lorentz distribution, Lorentz(ian) function, or Breit–Wigner distribution. The Cauchy distribution f(x; x_0,\gamma) is the distribution of the -intercept of a ray issuing from (x_0,\gamma) with a uniformly distributed angle. It is also the distribution of the ratio of two independent normally distributed random variables with mean zero. The Cauchy distribution is often used in statistics as the canonical example of a "pathological" distribution since both its expected value and its variance are undefined (but see below). The Cauchy distribution does not have finite moments of order greater than or equal to one; only fractional absolute moments exist., Chapter 16. The Cauchy distribution has no moment generating function. In mathematics, it is closely related to the Poiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |