|
Quaise
Quaise, Inc was founded in 2018 to develop a millimeter-wave drilling system for converting existing power stations to use superdeep geothermal energy. The system repurposes existing gyrotron technology to drill 20 kilometers beneath the surface, where temperatures exceed 400 °C. No fracking is required, avoiding the potential for earthquakes that have occurred in other geothermal systems. Drilling using this technique is hoped to be fast, with boreholes aimed to be completed in 100 days using existing 1MW gyrotrons. Overview Existing geothermal power stations can only be deployed in rare locations where adequate heat is located within 3 km of the surface. These resources are of a comparatively low temperature, and require seismically risky stimulation techniques. Further, drilling at these depths is expensive and slow. Instead, Quaise plans to drill quickly to deep depths using a gyrotron and waveguide, vaporizing the rock by heating it. Temperatures at 20 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrotron
High-power 140 GHz gyrotron for plasma heating in the Wendelstein 7-X fusion experiment, Germany. A gyrotron is a class of high-power linear-beam vacuum tubes that generates millimeter-wave electromagnetic waves by the cyclotron resonance of electrons in a strong magnetic field. Output frequencies range from about 20 to 527 GHz, covering wavelengths from microwave to the edge of the terahertz gap. Typical output powers range from tens of kilowatts to 1–2 megawatts. Gyrotrons can be designed for pulsed or continuous operation. The gyrotron was invented by Soviet scientists at NIRFI, based in Nizhny Novgorod, Russia. Principle The gyrotron is a type of free-electron maser that generates high-frequency electromagnetic radiation by stimulated cyclotron resonance of electrons moving through a strong magnetic field. It can produce high power at millimeter wavelengths because as a ''fast-wave'' device its dimensions can be much larger than the wavelength of the radiation. This is unli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pressure in Earth's interior cause some rock to melt and solid mantle to behave plastically. This results in parts of the mantle convecting upward since it is lighter than the surrounding rock. Temperatures at the core–mantle boundary can reach over 4000 °C (7200 °F). Geothermal heating, using water from hot springs, for example, has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since ancient Roman times. More recently geothermal power, the term used for generation of electricity from geothermal energy, has gained in importance. It is estimated that the earth's geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs, although only a very small fraction is currently being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy is the thermal energy in the Earth's crust which originates from the formation of the planet and from radioactive decay of materials in currently uncertain but possibly roughly equal proportions. The high temperature and pressure in Earth's interior cause some rock to melt and solid mantle to behave plastically. This results in parts of the mantle convecting upward since it is lighter than the surrounding rock. Temperatures at the core–mantle boundary can reach over 4000 °C (7200 °F). Geothermal heating, using water from hot springs, for example, has been used for bathing since Paleolithic times and for space heating since ancient Roman times. More recently geothermal power, the term used for generation of electricity from geothermal energy, has gained in importance. It is estimated that the earth's geothermal resources are theoretically more than adequate to supply humanity's energy needs, although only a very small fraction is currently being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millimeter-wave
Extremely high frequency (EHF) is the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) designation for the band of radio frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum from 30 to 300 gigahertz (GHz). It lies between the super high frequency band and the far infrared band, the lower part of which is the terahertz band. Radio waves in this band have wavelengths from ten to one millimetre, so it is also called the millimetre band and radiation in this band is called millimetre waves, sometimes abbreviated MMW or mmWave. Millimetre-length electromagnetic waves were first investigated by Indian physicist Jagadish Chandra Bose, who generated waves of frequency up to 60GHz during experiments in 18941896. Compared to lower bands, radio waves in this band have high atmospheric attenuation: they are absorbed by the gases in the atmosphere. Absorption increases with frequency until at the top end of the band the waves are attenuated to zero within a few meters. Absorption by humidity in the atmosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induced Seismicity In Basel
Induced seismicity in Basel led to suspension of its hot dry rock enhanced geothermal systems project. A seismic-hazard evaluation was then conducted, resulting in the cancellation of the project in December 2009. Basel, Switzerland sits atop a historically active fault and most of the city was destroyed in a magnitude 6.5 earthquake in 1356. But the Basel project, although it had established an operational approach for addressing induced earthquakes, had not performed a thorough seismic risk assessment before starting geothermal stimulation. Seismic events in Basel reached the trip point of Richter Magnitude 2.9 six days after the main stimulation was started on December 2, despite precautionary reduction of the injection rate earlier that same day upon reaching earlier "soft" thresholds. However, further tremors exceeding magnitude 3 were recorded on 6 January (measuring 3.1), 16 January 2007 (3.2), and 2 February 2007 (3.2). In all, between December 2006 and March 2007, the six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geothermal Power
Geothermal power is electrical power generated from geothermal energy. Technologies in use include dry steam power stations, flash steam power stations and binary cycle power stations. Geothermal electricity generation is currently used in 26 countries,Geothermal Energy AssociationGeothermal Energy: International Market Update May 2010, p. 4-6. while geothermal heating is in use in 70 countries. As of 2019, worldwide geothermal power capacity amounts to 15.4 gigawatts (GW), of which 23.9 percent or 3.68 GW are installed in the United States. International markets grew at an average annual rate of 5 percent over the three years to 2015, and global geothermal power capacity is expected to reach 14.5–17.6 GW by 2020. Based on current geologic knowledge and technology the Geothermal Energy Association (GEA) publicly discloses, the GEA estimates that only 6.9 percent of total global potential has been tapped so far, while the IPCC reported geothermal power potential to be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well Stimulation
Well stimulation is a well intervention performed on an oil or gas well to increase production by improving the flow of hydrocarbons from the reservoir into the well bore. It may be done using a well stimulator structure or using off shore ships / drilling vessels, also known as "Well stimulation vessels". Cleaning the formation The assortment of drilling fluid pumped down the well during drilling and completion can often cause damage to the surrounding formation by entering the reservoir rock and blocking the pore throats (the channels in the rock throughout which the reservoir fluids flow). Similarly, the act of perforating can have a similar effect by jetting debris into the perforation channels. Both these situations reduce the permeability in the near well bore area and so reduce the flow of fluids into the well bore. A simple and safe solution is to pump diluted acid mixtures from surface into the well to dissolve the offending material. Once dissolved, permeability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citation Needed
" itation needed''" is a tag added by Wikipedia editors to unsourced statements in articles requesting citations to be added. The phrase is reflective of the policies of verifiability and no original research on Wikipedia and has become a general Internet meme. On the English Wikipedia, the display effect looks like this: Usage on Wikipedia The tag was first used on Wikipedia in 2006. By Wikipedia policy, editors should add citations for content, to ensure accuracy and neutrality, and to avoid original research. The on needed tag is used to mark statements that lack such citations. , there were more than 350,000 pages on Wikipedia containing at least one instance of the tag. Users who click the tag will be directed to pages about Wikipedia's verifiability policy and its application using the tag. Usage outside Wikipedia In 2008, Matt Mechtley created stickers with " n needed, encouraging people to stick them on advertisements. In 2010, American television hosts Jon Stew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waveguide
A waveguide is a structure that guides waves, such as electromagnetic waves or sound, with minimal loss of energy by restricting the transmission of energy to one direction. Without the physical constraint of a waveguide, wave intensities decrease according to the inverse square law as they expand into three-dimensional space. There are different types of waveguides for different types of waves. The original and most common meaningInstitute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, “The IEEE standard dictionary of electrical and electronics terms”; 6th ed. New York, N.Y., Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, c1997. IEEE Std 100-1996. d. Standards Coordinating Committee 10, Terms and Definitions; Jane Radatz, (chair)/ref> is a hollow conductive metal pipe used to carry high frequency radio waves, particularly microwaves. Dielectric waveguides are used at higher radio frequencies, and transparent dielectric waveguides and optical fibers serve as waveguides f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
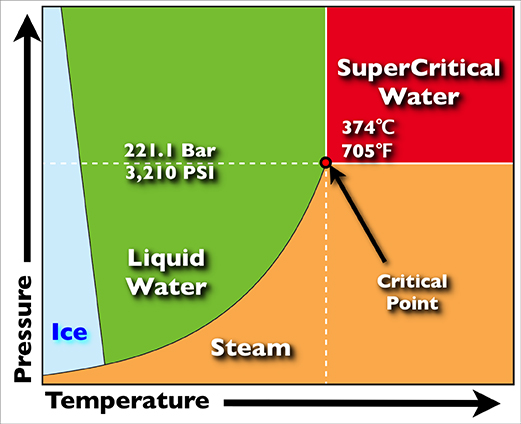
Supercritical Fluid
A supercritical fluid (SCF) is any substance at a temperature and pressure above its critical point, where distinct liquid and gas phases do not exist, but below the pressure required to compress it into a solid. It can effuse through porous solids like a gas, overcoming the mass transfer limitations that slow liquid transport through such materials. SCF are much superior to gases in their ability to dissolve materials like liquids or solids. Also, near the critical point, small changes in pressure or temperature result in large changes in density, allowing many properties of a supercritical fluid to be "fine-tuned". Supercritical fluids occur in the atmospheres of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn, the terrestrial planet Venus, and probably in those of the ice giants Uranus and Neptune. Supercritical water is found on Earth, such as the water issuing from black smokers, a type of underwater hydrothermal vent. They are used as a substitute for organic solvents in a range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercritical Steam Generator
A supercritical steam generator is a type of boiler that operates at supercritical pressure, frequently used in the production of electric power. In contrast to a subcritical boiler in which bubbles can form, a supercritical steam generator operates at pressures above the critical pressure. Therefore, liquid water immediately becomes indistinguishable from steam. Water passes below the critical point as it does work in a high pressure turbine and enters the generator's condenser, resulting in slightly less fuel use. The efficiency of power plants with supercritical steam generators is higher than with subcritical steam. Only with high pressure can higher temperature steam be converted more efficiently to mechanical energy in the turbine (as given by Carnot's theorem). Technically, the term "boiler" should not be used for a supercritical pressure steam generator as no "boiling" actually occurs in the device. History of supercritical steam generation Contemporary supercritica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |