|
Quadrisecant
In geometry, a quadrisecant or quadrisecant line of a space curve is a line that passes through four points of the curve. This is the largest possible number of intersections that a generic space curve can have with a line, and for such curves the quadrisecants form a discrete set of lines. Quadrisecants have been studied for curves of several types: *Knots and links in knot theory, when nontrivial, always have quadrisecants, and the existence and number of quadrisecants has been studied in connection with knot invariants including the minimum total curvature and the ropelength of a knot. *The number of quadrisecants of a non-singular algebraic curve in complex projective space can be computed by a formula derived by Arthur Cayley. *Quadrisecants of arrangements of skew lines touch subsets of four lines from the arrangement. They are associated with ruled surfaces and the Schläfli double six configuration. Definition and motivation A quadrisecant is a line that intersects a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erika Pannwitz
Erika Pannwitz (May 26, 1904 in Hohenlychen, Germany – November 25, 1975 in Berlin) was a German mathematician who worked in the area of geometric topology. During World War II, Pannwitz worked as a cryptanalyst in the Department of Signal Intelligence Agency of the German Foreign Office (german: Auswärtiges Amt) colloquially known as Pers Z S. After the war, she became editor-in-chief of Zentralblatt MATH. Education and thesis Erika Pannwitz attended the Pannwitz Outdoor School in Hohenlychen until 10th grade, and graduated from Augusta State School in Berlin in 1922. She studied mathematics in Berlin, and also for a semester in Freiburg (1925) and Göttingen (1928). After passing her teaching exam in 1927 (in mathematics, physics, and chemistry), Pannwitz was promoted in 1931 to Dr Phil at Friedrich Wilhelms University with doctoral advisors Heinz Hopf and Erhard Schmidt. Her thesis titled: ''Eine elementargeometrische Eigenschaft von Verschlingungen und Knoten'' (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ropelength
In physical knot theory, each realization of a link or knot has an associated ropelength. Intuitively this is the minimal length of an ideally flexible rope that is needed to tie a given link, or knot. Knots and links that minimize ropelength are called ideal knots and ideal links respectively. Definition The ropelength of a knotted curve C is defined as the ratio L(C) = \operatorname(C)/\tau(C), where \operatorname(C) is the length of C and \tau(C) is the knot thickness of C. Ropelength can be turned into a knot invariant by defining the ropelength of a knot K to be the minimum ropelength over all curves that realize K. Ropelength minimizers One of the earliest knot theory questions was posed in the following terms: In terms of ropelength, this asks if there is a knot with ropelength 12. The answer is no: an argument using quadrisecants shows that the ropelength of any nontrivial knot has to be at least 15.66. However, the search for the answer has spurred research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
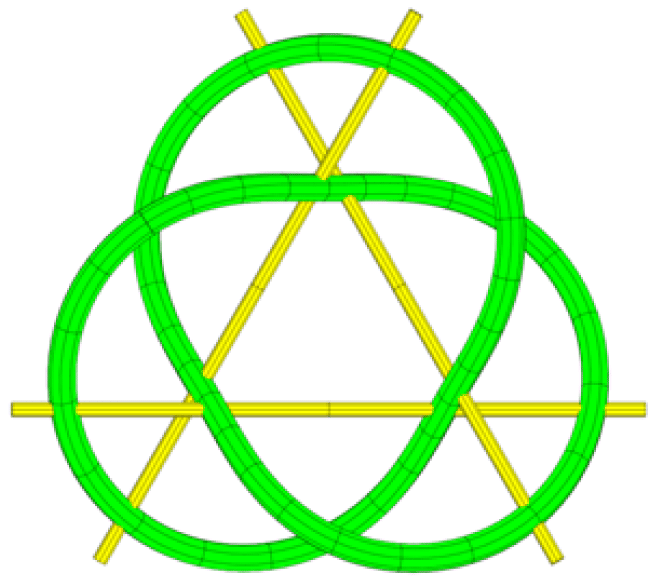
Trefoil Quadrisecants
A trefoil () is a graphic form composed of the outline of three overlapping rings, used in architecture and Christian symbolism, among other areas. The term is also applied to other symbols with a threefold shape. A similar shape with four rings is called a quatrefoil. Architecture Ornamentation 'Trefoil' is a term in Gothic architecture given to the ornamental foliation or cusping introduced in the heads of window-lights, tracery, and panellings, in which the centre takes the form of a three-lobed leaf (formed from three partially overlapping circles). One of the earliest examples is in the plate tracery at Winchester Cathedral (1222–1235). The fourfold version of an architectural trefoil is a quatrefoil. A simple trefoil shape in itself can be symbolic of the Trinity, while a trefoil combined with an equilateral triangle was also a moderately common symbol of the Christian Trinity during the late Middle Ages in some parts of Europe, similar to a barbed quatrefoil. Two form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schläfli Double Six
In geometry, the Schläfli double six is a configuration of 30 points and 12 lines, introduced by . The lines of the configuration can be partitioned into two subsets of six lines: each line is disjoint from ( skew with) the lines in its own subset of six lines, and intersects all but one of the lines in the other subset of six lines. Each of the 12 lines of the configuration contains five intersection points, and each of these 30 intersection points belongs to exactly two lines, one from each subset, so in the notation of configurations the Schläfli double six is written 125302. Construction As Schläfli showed, the double six may be constructed from any five lines ''a''1, ''a''2, ''a''3, ''a''4, ''a''5, that are all intersected by a common line ''b''6, but are otherwise in general position (in particular, each two lines ''a''''i'' and ''a''''j'' should be skew, and no four of the lines ''a''''i'' should lie on a common ruled surface). For each of the five lines ''a''''i'', th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linking Number
In mathematics, the linking number is a numerical invariant that describes the linking of two closed curves in three-dimensional space. Intuitively, the linking number represents the number of times that each curve winds around the other. In Euclidean space, the linking number is always an integer, but may be positive or negative depending on the orientation of the two curves (this is not true for curves in most 3-manifolds, where linking numbers can also be fractions or just not exist at all). The linking number was introduced by Gauss in the form of the linking integral. It is an important object of study in knot theory, algebraic topology, and differential geometry, and has numerous applications in mathematics and science, including quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, and the study of DNA supercoiling. Definition Any two closed curves in space, if allowed to pass through themselves but not each other, can be moved into exactly one of the following standard positions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Position
In algebraic geometry and computational geometry, general position is a notion of genericity for a set of points, or other geometric objects. It means the ''general case'' situation, as opposed to some more special or coincidental cases that are possible, which is referred to as special position. Its precise meaning differs in different settings. For example, generically, two lines in the plane intersect in a single point (they are not parallel or coincident). One also says "two generic lines intersect in a point", which is formalized by the notion of a generic point. Similarly, three generic points in the plane are not collinear; if three points are collinear (even stronger, if two coincide), this is a degenerate case. This notion is important in mathematics and its applications, because degenerate cases may require an exceptional treatment; for example, when stating general theorems or giving precise statements thereof, and when writing computer programs (see '' generic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's ''Elements'': "The urvedline is ��the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which ��will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image of an interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this article, these curves are sometimes called ''topological curves'' to distinguish them from more constrained curves suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygon
In geometry, a polygon () is a plane figure that is described by a finite number of straight line segments connected to form a closed '' polygonal chain'' (or ''polygonal circuit''). The bounded plane region, the bounding circuit, or the two together, may be called a polygon. The segments of a polygonal circuit are called its ''edges'' or ''sides''. The points where two edges meet are the polygon's '' vertices'' (singular: vertex) or ''corners''. The interior of a solid polygon is sometimes called its ''body''. An ''n''-gon is a polygon with ''n'' sides; for example, a triangle is a 3-gon. A simple polygon is one which does not intersect itself. Mathematicians are often concerned only with the bounding polygonal chains of simple polygons and they often define a polygon accordingly. A polygonal boundary may be allowed to cross over itself, creating star polygons and other self-intersecting polygons. A polygon is a 2-dimensional example of the more general polytope in any nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tame Knot
Tame may refer to: *Taming, the act of training wild animals * River Tame, Greater Manchester * River Tame, West Midlands and the Tame Valley * Tame, Arauca, a Colombian town and municipality * "Tame" (song), a song by the Pixies from their 1989 album ''Doolittle'' * TAME (IATA code: EQ), flag carrier of Ecuador * tert-Amyl methyl ether, an oxygenated chemical compound often added to gasoline. *Tame.it Tame is an analytic research tool for Twitter that was developed in 2012 by Arno Dirlam (CTO), Frederik Fischer (CEO) and Torsten Müller (CCO). Tame is a spin-off from Humboldt University of Berlin. The team of journalists and developers who de ..., a context search engine for Twitter *Tame, a variety of the Idi language of Papua New Guinea * Tame (surname), people with the surname * Tame Impala, the psychedelic music project of Australian multi-instrumentalist Kevin Parker. {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unknot
In the mathematical theory of knots, the unknot, not knot, or trivial knot, is the least knotted of all knots. Intuitively, the unknot is a closed loop of rope without a knot tied into it, unknotted. To a knot theorist, an unknot is any embedded topological circle in the 3-sphere that is ambient isotopic (that is, deformable) to a geometrically round circle, the standard unknot. The unknot is the only knot that is the boundary of an embedded disk, which gives the characterization that only unknots have Seifert genus 0. Similarly, the unknot is the identity element with respect to the knot sum operation. Unknotting problem Deciding if a particular knot is the unknot was a major driving force behind knot invariants, since it was thought this approach would possibly give an efficient algorithm to recognize the unknot from some presentation such as a knot diagram. Unknot recognition is known to be in both NP and co-NP. It is known that knot Floer homology and Kh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Space
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space. Originally, that is, in Euclid's ''Elements'', it was the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are Euclidean spaces of any positive integer dimension, including the three-dimensional space and the ''Euclidean plane'' (dimension two). The qualifier "Euclidean" is used to distinguish Euclidean spaces from other spaces that were later considered in physics and modern mathematics. Ancient Greek geometers introduced Euclidean space for modeling the physical space. Their work was collected by the ancient Greek mathematician Euclid in his ''Elements'', with the great innovation of '' proving'' all properties of the space as theorems, by starting from a few fundamental properties, called ''postulates'', which either were considered as evident (for example, there is exactly one straight line passing through two points), or seemed impossible to prove (paral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrangement Of Lines
In music, an arrangement is a musical adaptation of an existing composition. Differences from the original composition may include reharmonization, melodic paraphrasing, orchestration, or formal development. Arranging differs from orchestration in that the latter process is limited to the assignment of notes to instruments for performance by an orchestra, concert band, or other musical ensemble. Arranging "involves adding compositional techniques, such as new thematic material for introductions, transitions, or modulations, and endings. Arranging is the art of giving an existing melody musical variety".(Corozine 2002, p. 3) In jazz, a memorized (unwritten) arrangement of a new or pre-existing composition is known as a ''head arrangement''. Classical music Arrangement and transcriptions of classical and serious music go back to the early history of this genre. Eighteenth century J.S. Bach frequently made arrangements of his own and other composers' pieces. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |