|
Quadrant Dentistry
Quadrant dentistry is a treatment approach sometimes used in individuals who need much dental treatment. Quadrant dentistry means that all the dental treatment required in a quadrant is carried out in a single appointment. This is perceived as convenient for some dentists and some patients, as fewer appointments are required overall. The dentition is divided into quadrants: * Upper right quadrant: upper right first incisor to upper right wisdom tooth * Upper left quadrant: upper left first incisor to upper left wisdom tooth * Lower right quadrant: lower right first incisor to lower right wisdom tooth * Lower left quadrant: lower left first incisor to lower left wisdom tooth Inferior alveolar nerve blocks anesthetize all the teeth in a lower quadrant, so it can be convenient as only one injection is required for quadrant dentistry carried out in the lower teeth. Rubber dam is often used in this technique. If a tooth extraction is carried out in the same appointment as placing an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonly Used Terms Of Relationship And Comparison In Dentistry
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body. Terms Combining of terms Most of the principal terms can be combined using their corresponding combining forms (such as ''mesio-'' for ''mesial'' and ''disto-'' for ''distal''). They provide names for directions (vectors) and axes; for example, the coronoapical axis is the long axis of a tooth. Such combining yields terms such as those in the following list. The abbreviations should be used only in restricted contexts, where they are explicitly defined and help avoid extensive repetition (for example, a journal article that uses the term "mesiodistal" dozens of times might use the abbreviation "MD"). The abbreviations are ambiguous: (1) they are not spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block
Inferior alveolar nerve block (abbreviated to IANB, and also termed inferior alveolar nerve anesthesia or inferior dental block) is a nerve block technique which induces anesthesia (numbness) in the areas of the mouth and face innervated by one of the inferior alveolar nerves which are paired on the left and right side. These areas are the skin and mucous membranes of the lower lip, the skin of the chin, the lower teeth and the labial gingiva of the anterior teeth, all unilaterally to the midline of the side on which the block is administered. However, depending on technique, the long buccal nerve may not be anesthetized by an IANB and therefore an area of buccal gingiva adjacent to the lower posterior teeth will retain normal sensation unless that nerve is anesthetized separately, via a (long) buccal nerve block. The inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve, the third division of the trigeminal nerve. This procedure attempts to anaesthetise the inferior alveol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
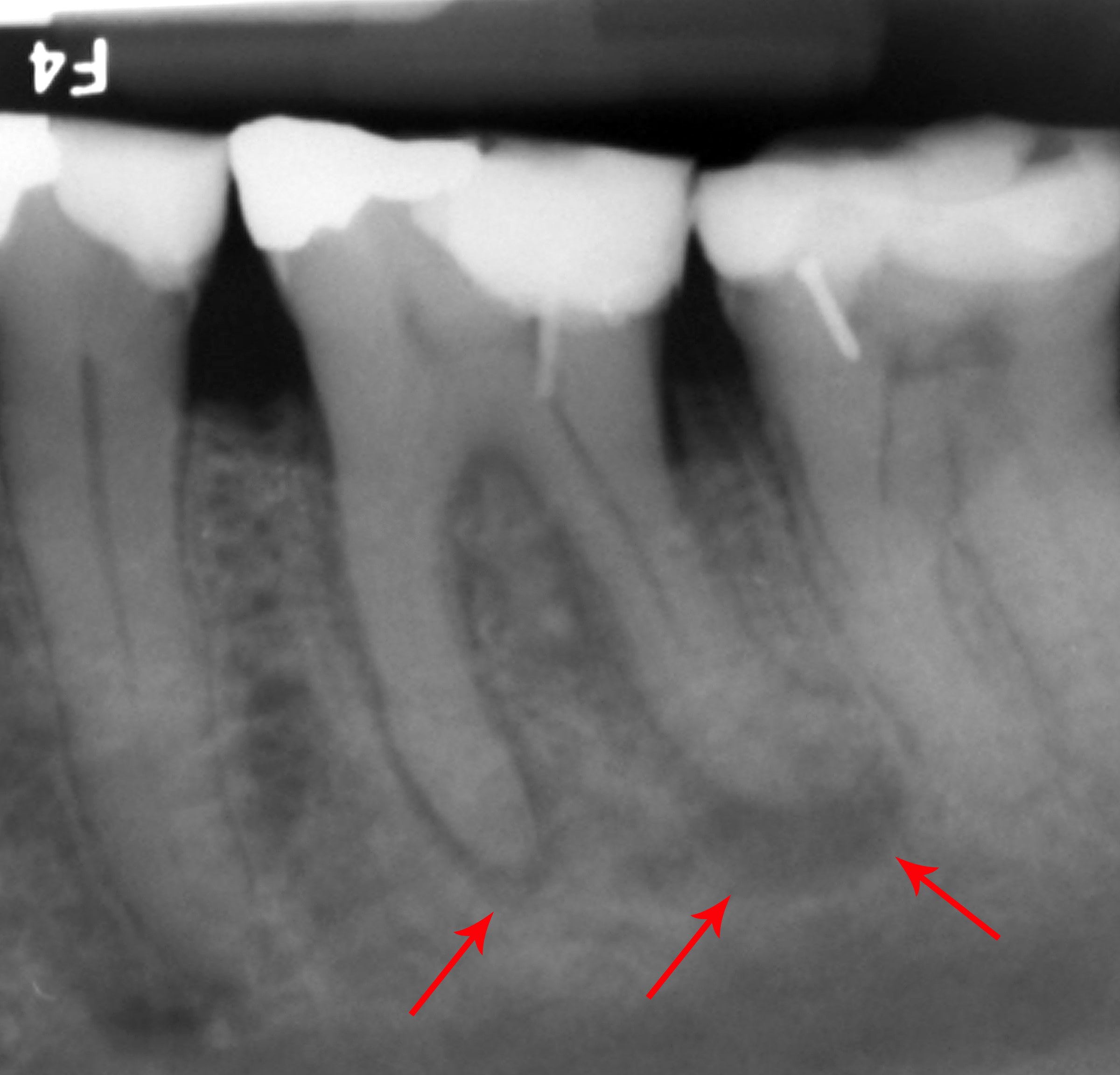
Dental Dam
A dental dam or rubber dam is a thin, square sheet, usually latex or nitrile, used in dentistry to isolate the operative site (one or more teeth) from the rest of the mouth. Sometimes termed "Kofferdam" (from German), it was designed in the United States in 1864 by . It is used mainly in endodontic, fixed prosthodontic (crowns, bridges) and general restorative treatments. Its purpose is both to prevent saliva interfering with the dental work (e.g. contamination of oral micro-organisms during root canal therapy, or to keep filling materials such as composite dry during placement and curing), and to prevent instruments and materials from being inhaled, swallowed or damaging the mouth. In dentistry, use of a rubber dam is sometimes referred to as ''isolation'' or ''moisture control''. Dental dams are also used for safer oral sex. Dentistry Background The technique used to apply the dental dam is selected according to the tooth requiring treatment. Several techniques can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Extraction
A dental extraction (also referred to as tooth extraction, exodontia, exodontics, or informally, tooth pulling) is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth (wisdom teeth that are stuck and unable to grow normally into the mouth) cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed (cleaning, antibiotics and operculectomy). In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted (often bicuspids) to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened. Procedure Extractions could be categorized into non-surgical (simple) and surgical, depending on the type of tooth to be removed and other fac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amalgam (dentistry)
Dental amalgam is a liquid Mercury (element), mercury and metal alloy mixture used in dentistry to dental filling, fill cavities caused by tooth decay. Low-copper amalgam commonly consists of mercury (element), mercury (50%), silver (~22–32%), tin (~14%), zinc (~8%) and other trace metals. Dental amalgams were first documented in a Tang Dynasty medical text written by Su Gong (苏恭) in 659, and appeared in Germany in 1528. In the 1800s, amalgam became the dental restorative material of choice due to its low cost, ease of application, strength, and durability. In July 2018 the EU prohibited amalgam for dental treatment of children under 15 years and of pregnant or breastfeeding women. History of use There are, according to Geir Bjørklund, indications that dental amalgam was used in the first part of the Tang Dynasty in China (AD 618–907), and in Germany by Strockerus in about 1528. Evidence of a dental amalgam first appears in the Tang Dynasty medical text ''Xinxiu ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amalgam Tattoo
Amalgam tattoo is a grey, blue or black area of discoloration on the mucous membranes of the mouth, typically on the gums of the lower jaw. It is a healthcare caused lesion, due to entry of dental amalgam into the soft tissues. It is common, painless, and benign, but it can be mistaken for melanoma. Signs and symptoms Amalgam tattoo usually occurs on the mandibular gingiva, often in an area in which an apicoectomy ("root-end filling") with amalgam was carried out. After the gingiva, the alveolar mucosa and the buccal mucosa are the next most common sites, although any mucosal site in the mouth is possible. It is painless, and appears as a blue-black or grey discolored macule on the surface of the mucosa. The borders of the tattoo are variable, and may be well defined, irregular or diffuse. Causes Amalgam tattoo is caused by implantation of amalgam into the tissues. It may occur in several ways: * During placement of an amalgam filling, e.g. if abrasions on the mucosa are pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |