|
Qian Zhao
The Han-Zhao (; 304–329 AD), or Former Zhao (), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Liu (Luandi) clan of Xiongnu ethnicity during the Sixteen Kingdoms period of Chinese history. In Chinese historiography, it was given two conditional state titles, the Northern Han (; ) for the state proclaimed in 304 by Liu Yuan, and the Former Zhao (; ) for the state proclaimed in 319 by Liu Yao. The reference to them as separate states should be considered misleading, given that when Liu Yao changed the name of the state from “Han” to “Zhao” in 319, he treated the state as having been continuous from the time that Liu Yuan founded it in 304; instead, he de-established his imperial lineage from the Han dynasty and claimed ancestry directly from Modu Chanyu. The reason it is also referred to as "Former Zhao" in historiography is to distinguish it from the similarly-named dynasty founded by Shi Le in 319, which was also known officially as "Zhao" (labeled "Later Zhao" in Chine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, is head of state for life or until abdication. The political legitimacy and authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutional monarchy), to fully autocratic (absolute monarchy), and can expand across the domains of the executive, legislative, and judicial. The succession of monarchs in many cases has been hereditical, often building dynastic periods. However, elective and self-proclaimed monarchies have also happened. Aristocrats, though not inherent to monarchies, often serve as the pool of persons to draw the monarch from and fill the constituting institutions (e.g. diet and court), giving many monarchies oligarchic elements. Monarchs can carry various titles such as emperor, empress, king, queen, raja, khan, tsar, sultan, shah, or pharaoh. Monarchies can form federations, personal unions and realms with vassals through personal association with the monarch, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luandi
The Luandi (; alternatively written as Xulianti ) was the ruling clan of the ancient Xiongnu that flourished between 3rd century BCE to 4th century CE. The form Luandi comes from the ''Book of Han'', while the form Xulianti comes from the ''Book of Later Han''. Lanhai Wei and Hui Li reconstruct the Old Chinese pronunciation of 挛鞮 as *lyuan-tlïγ, evolving from an earlier 虚连题 (*Hala-yundluγ), as a result of a historical sound shift involving the initial dropping of *h- by demonstrating its occurrence in several historical sources. Furthermore, the conjugation of the roots *hala, meaning colorful; *yund meaning horse, *-luγ as the participle suffix would have resulted in the semantic meaning "tribe with skewbald horses" in an early Turkic dialect, allowing it to be further identified with the historical Ulayundluğ tribe. Moreover, the authors argue that the conquest of the same clan by the Xue in the 4th century CE eventually gave birth to the Xueyantuo. Anna D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinicization
Sinicization, sinofication, sinification, or sinonization (from the prefix , 'Chinese, relating to China') is the process by which non-Chinese societies come under the influence of Chinese culture, particularly the language, societal norms, culture, and ethnic identity of the Han people—the largest ethnic group of China. Areas of influence include diet, writing, industry, education, language/lexicon, law, architectural style, politics, philosophy, religion, science and technology, value systems, and lifestyle. In particular, ''sinicization'' may refer to processes or policies of acculturation, assimilation, or cultural imperialism of norms from China on neighboring East Asian societies, or on minority ethnic groups within China. Evidence of this process is reflected in the histories of Korea, Japan, and Vietnam in the adoption of the Chinese writing system, which has long been a unifying feature in the Sinosphere as the vehicle for exporting Chinese culture to other As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Breed
A horse breed is a selectively bred population of domesticated horses, often with pedigrees recorded in a breed registry. However, the term is sometimes used in a broader sense to define landrace animals of a common phenotype located within a limited geographic region, or even feral "breeds" that are naturally selected. Depending on definition, hundreds of "breeds" exist today, developed for many different uses. Horse breeds are loosely divided into three categories based on general temperament: spirited "hot bloods" with speed and endurance; "cold bloods," such as draft horses and some ponies, suitable for slow, heavy work; and "warmbloods," developed from crosses between hot bloods and cold bloods, often focusing on creating breeds for specific riding purposes, particularly in Europe. Horse breeds are groups of horses with distinctive characteristics that are transmitted consistently to their offspring, such as conformation, color, performance ability, or disposition. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Cao
Cao Cao () (; 155 – 15 March 220), courtesy name Mengde (), was a Chinese statesman, warlord and poet. He was the penultimate Grand chancellor (China), grand chancellor of the Eastern Han dynasty, and he amassed immense power in the End of the Han dynasty, dynasty's final years. As one of the central figures of the Three Kingdoms period, Cao Cao laid the foundations for what became the state of Cao Wei, and he was posthumously honoured as "Emperor Wu of Wei", despite the fact that he never officially proclaimed himself Emperor of China or Son of Heaven. Cao Cao remains a controversial historical figure—he is often portrayed as a cruel and merciless tyrant in literature, but he has also been praised as a brilliant ruler, military genius, and great poet possessing unrivalled charisma, who treated his subordinates like family. During the fall of the Eastern Han dynasty, Cao Cao was able to secure most of northern China—which was at the time the most populated and developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bing (province)
Bingzhou, or Bing Province, was a location in ancient China. According to legend, when Yu the Great (c. 2200 BC-2100 BC) tamed the flood, he divided the land of China into the Nine Provinces. Historical texts such as the ''Rites of Zhou'', and "Treatise on Geography" section (volume 28) of the ''Book of Han'', recorded that Bingzhou was one of the Nine Provinces. Bingzhou covered roughly the areas around present-day Baoding, Hebei, and Taiyuan and Datong in Shanxi. History Han dynasty and earlier Since the fifth century BC Bingzhou had been separated from the Ordos Desert repeatedly by a series of walls that would form the Great Wall of China. In 106 BCE, during the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE – 9 CE), Emperor Wu divided the Han Empire into thirteen administrative divisions, of which Bingzhou was one. Bingzhou covered most of present-day Shanxi and parts of Hebei and Inner Mongolia. During the Eastern Han dynasty (25–220) Bingzhou's capital was designated in Jinyang County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordos Desert
The Ordos Desert () is a desert/steppe region in Northwest China, administrated under the prefecture of Ordos City in the Inner Mongolian Autonomous Region (centered ca. ). It extends over an area of approximately , and comprises two sub-deserts: China's 7th-largest desert, the Kubuqi Desert, in the north; and China's 8th-largest desert, the Mu Us Desert, in the south. Wedged between the arable Hetao region to the north and the Loess Plateau to the south, the soil of the Ordos Desert is mostly a mixture of dry clay and sand, and as a result is poorly suited for agriculture. Location The Ordos Desert is almost completely encircled in the west, north and east by a great rectangular bend of the middle Yellow River known as the Ordos Loop. Mountain ranges separate the Ordos from the Gobi Desert north and east of the Yellow River. The northern border serves as the southern border of the Mu Us Desert. The mountain chains separating the Ordos from the central Gobi in the north of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu Empire
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After their previous rivals, the Yuezhi, migrated west into Central Asia during the 2nd century BC, the Xiongnu became a dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with adjacent Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, as one of the "Five Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
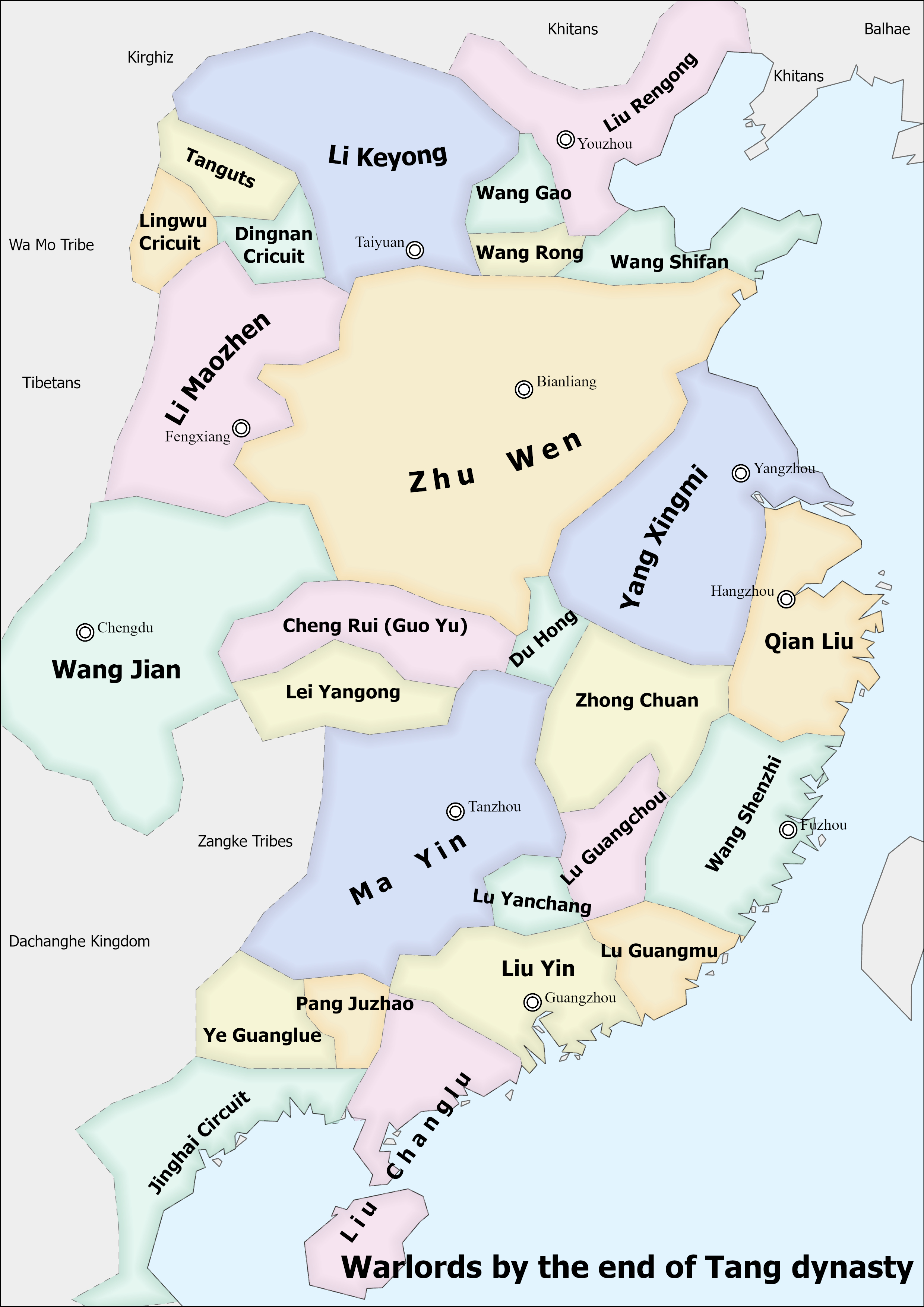
Five Dynasties And Ten Kingdoms Period
The Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period (), from 907 to 979, was an era of political upheaval and division in 10th-century Imperial China. Five dynastic states quickly succeeded one another in the Central Plain, and more than a dozen concurrent dynastic states were established elsewhere, mainly in South China. It was a prolonged period of multiple political divisions in Chinese imperial history. Traditionally, the era is seen as beginning with the fall of the Tang dynasty in 907 and reaching its climax with the founding of the Song dynasty in 960. In the following 19 years, Song gradually subdued the remaining states in South China, but the Liao dynasty still remained in China's north (eventually succeeded by the Jin dynasty), and the Western Xia was eventually established in China's northwest. Many states had been '' de facto'' independent long before 907 as the Tang dynasty's control over its officials waned, but the key event was their recognition as sovereign by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Han
The Northern Han () was a dynastic state of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Liu Min (), formerly known as Liu Chong (), and lasted from 951 to 979. Founding of the Northern Han The short-lived state of Later Han fell in 950 because of Guo Wei, a powerful military governor's ''de facto'' coup. Liu Min founded the Northern Han Kingdom, sometimes referred to as the Eastern Han, in 951 claiming that he was the legitimate heir to the imperial throne of Later Han. Liu Min immediately restored the traditional relationship with the Khitans, who had founded the Liao dynasty. Sources conflict as to the origin of the Later Han and Northern Han emperors; some indicate sinicized Shatuo ancestry while some traditional historical sources claims that the emperors claimed patrilineal Han Chinese ancestry. Territorial extent The Northern Han was a small kingdom located in Shanxi with its capital located at Taiyuan. Shanxi had been a traditional base of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Later Zhao
The Later Zhao (; 319–351) was a dynasty of the Sixteen Kingdoms in northern China. It was founded by the Shi family of the Jie ethnicity. The Jie were most likely a Yeniseian people and spoke next to Chinese one of the Yeniseian languages.Vovin, Alexander. "Did the Xiongnu speak a Yeniseian language?". Central Asiatic Journal 44/1 (2000), pp. 87–104. The Later Zhao was the second in territorial size to the Former Qin dynasty that once unified northern China under Fu Jiān. When Later Zhao was founded by former Han general Shi Le, the capital was at Xiangguo (襄國, in modern Xingtai, Hebei), but in 335 Shi Hu moved the capital to Yecheng (鄴城, in modern Handan, Hebei), where it would remain for the rest of the state's history (except for Shi Zhi's brief attempt to revive the state at Xiangguo). Rulers of the Later Zhao Rulers family tree See also *Jie (ethnic group) * Wei–Jie war *List of past Chinese ethnic groups * Wu Hu * Buddhism in China *''Memoirs of Emine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modu Chanyu
Modu, Maodun, Modun (, from Old Chinese (220 B.C.E.): *''mouᴴ-tuən'' or *''mək-tuən'', c. 234 – c. 174 BCE) was the son of Touman and the founder of the empire of the Xiongnu. He came to power by ordering his men to kill his father in 209 BCE. Modu ruled from 209 BCE to 174 BCE. He was a military leader under his father Touman and later Chanyu of the Xiongnu Empire, based on the Mongolian Plateau. He secured the throne and established a powerful Xiongnu Empire by successfully unifying the tribes of the Mongolian-Manchurian grassland in response to the loss of Xiongnu pasture lands to invading Qin forces commanded by Meng Tian in 215 BCE. While Modu rode and then furthered the wave of militarization and effectively centralized Xiongnu power, the Qin quickly fell into disarray with the death of the first emperor in 210 BCE, leaving Modu a free hand to expand his Xiongnu Empire into one of the largest of his time. The eastern border stretched as far as the Liao River, the wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |